Abstract
Here, we characterized behavioral abnormalities induced by prolonged social isolation in adult rodents. Social isolation induced both anxiety- and anhedonia-like symptoms and decreased cAMP response element–binding protein (CREB) activity in the nucleus accumbens shell (NAcSh). All of these abnormalities were reversed by chronic, but not acute, antidepressant treatment. However, although the anxiety phenotype and its reversal by antidepressant treatment were CREB-dependent, the anhedonia-like symptoms were not mediated by CREB in NAcSh. We found that decreased CREB activity in NAcSh correlated with increased expression of certain K+ channels and reduced electrical excitability of NAcSh neurons, which was sufficient to induce anxiety-like behaviors and was reversed by chronic antidepressant treatment. Together, our results describe a model that distinguishes anxiety- and depression-like behavioral phenotypes, establish a selective role of decreased CREB activity in NAcSh in anxiety-like behavior, and provide a mechanism by which antidepressant treatment alleviates anxiety symptoms after social isolation.
Depression and anxiety are common forms of mental illness in the general population. Although they are classified as distinct syndromes by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (American Psychiatric Association), symptoms of depression and anxiety often occur together and to widely varying extents in different subtypes of the illnesses. Despite the importance of these clinical phenomena, very little is known about the distinctions between depression- and anxiety-like symptoms in animal models1. Models of ‘active’ stress, such as foot shock, restraint stress, social defeat and learned helplessness, produce depression-and anxiety-like phenotypes; the molecular mechanisms of these models have been extensively studied, but specific molecular mediators of depression versus anxiety symptoms have not yet been described2–4. Even less well studied, however, is a ‘passive’ model of stress and social isolation in adulthood, which, as with active stress, mimics aspects of human depression and anxiety5,6. This lack of attention is unfortunate, as social isolation would appear to be particularly relevant to certain subtypes of human depression and anxiety disorders7,8.
Although social isolation has been studied, most models to date have focused on adulthood behaviors after isolation rearing early in life, either as pups or adolescents, which is a very different model than adulthood social isolation5. Reports on adulthood isolation provide evidence for a strong anxiety-like phenotype9,10, an increase in alcohol intake11, modulation of responses to rewarding stimuli9,10,12, changes in circadian rhythms13 and a dampening in running-induced neurogenesis14. Although reports on changes in neurochemistry are often conflicting, there appears to be decreased serotonergic and noradrenergic function and metabolism in several brain regions5; however, these changes have not been linked to associated behavioral abnormalities.
Previous work has shown that the activity of the transcription factor CREB in the NAcSh is a key regulator of an animal’s responses to emotional stimuli2,10,15–17. We recently provided evidence that prolonged social isolation of adult mice and rats induces a state of profound anxiety, which is mediated by decreased activity of CREB in the NAcSh. These anxiety symptoms induced by social isolation are blocked by viral-mediated overexpression of CREB in the NAcSh and local expression of a dominant-negative form of CREB (mCREB) mimics these symptoms in normal animals10. Conversely, activation of CREB activity in the NAcSh in response to active stress or to drugs of abuse dampens an individual’s responses to both rewarding and aversive stimuli2,15–19. This has led to the suggestion that CREB induction in this region may mediate a state of emotional numbing and contribute to depression-like symptoms such as anhedonia (decreased ability to experience pleasure) after a period of active stress20.
Here, we more fully characterized the behavioral phenotype induced by adulthood social isolation. We found that, despite a decrease in CREB activity in the NAcSh, this form of passive stress also induced symptoms of anhedonia and that chronic administration of a standard antidepressant medication reversed both the anxiety- and depression-like symptoms, and normalized CREB activity in the NAcSh, seen after social isolation. The anxiety-like symptoms, but not the anhedonia-like symptoms, were directly related to reduced CREB activity in this brain region. We then used DNA expression arrays to gain insight into the molecular mechanisms by which social isolation, antidepressants and CREB regulate NAcSh function. Our data support a scheme whereby downregulation of CREB activity, induced by social isolation, upregulates several K+ channels and depresses the excitability of NAcSh neurons, which then leads to anxiety-like symptoms. Together, these results provide information concerning the molecular mechanisms underlying the behavioral consequences of adulthood social isolation and offer insight into the generation of anxiety symptoms seen in affective syndromes.
RESULTS
Behavioral abnormalities induced by social isolation
The first step in this study was to characterize the behavioral phenotypes induced by prolonged social isolation in adulthood. Using classic, validated tests, we found several behavioral abnormalities in isolated compared with control (double-housed) rats (Fig. 1; see also Supplementary Results and Supplementary Fig. 1 online). These abnormalities included increases in anxiety-like behaviors (as measured by elevated plus maze, open field, locomotor activity and latency to initiate sexual behavior), abnormal locomotor habituation and forced swim behavior, and decreases in natural reward-related behaviors (such as responses to sex and sucrose).
Figure 1.
Social isolation induces behavioral deficits. (a) An increase in ejaculation latency was observed in socially isolated animals (socially isolated/control, SI/CON) compared with their double-housed controls (CON/CON). Under chronic imipramine (IMI) administration, this sexual behavior deficit in socially isolated animals was reversed (SI/IMI), whereas the same treatment induced a deficit in ejaculation latency for the double-housed animals (CON/IMI) (significant overall effect of drug: F1,48 =– 4.81, P < 0.05; significant interaction of drug on housing: F1,48 = 24.93, P < 0.001, n = 8–17 animals per group, * indicates significantly different (P < 0.05) from CON/CON). (b) Chronic imipramine reversed the anxiety-like phenotype of isolated animals in the elevated plus maze, but did not affect control animals (significant effect of drug on isolated animals, F1,43 = 13.09. P < 0.01, n = 10–14 animals per group). (c,d) The socially isolated animals (SI/CON) showed decreases in sucrose intake (F1,22 = 7.512, P < 0.01, n = 12, corrected for multiple comparisons; c) and sucrose preference (F1,22 = 7.335, P < 0.05, n = 12, corrected for multiple comparisons; d) compared with double-housed control (CON) animals. (e) The chronic administration of imipramine abolished the difference in sucrose intake between socially isolated animals (SI/IMI) and their double-housed controls (CON/IMI) (F4,48 = 0.404, nonsignificant (n.s.), n = 6–8; e) and also abolished their differences in sucrose preference (F4,48 = 1.366, n.s., n = 6–8; f).
We followed up on the largest magnitude findings, specifically, anxiety-like and natural reward–related deficits, to determine whether they could be reversed by antidepressant treatment. We replicated our earlier finding10 that social isolation induced increased latency for ejaculation in sexual behavior and found that chronic (28–32 d) treatment with the standard antidepressant medication imipramine (10 mg per kg of body weight per d) in the drinking water (as to not disturb the isolation procedure; see Methods) abolished this impairment in sexual behavior for isolated rats (Fig. 1a).
However, although chronic imipramine improved the sexual performance of socially isolated rats, the same drug treatment markedly impaired the performance of the control (double-housed) rats (Fig. 1a). Notably, studies have found a similar parallel in humans, with sexual side effects being seen in nondepressed individuals that are treated with antidepressants, whereas depressed individuals’ sexual behavior can actually improve after chronic treatment21–23. In contrast to chronic administration reversing the ejaculation deficits, short-term administration of imipramine (in the drinking water for 5 d) did not influence sexual behavior in either socially isolated or double-housed rats (data not shown).
We next determined whether the anxiety-like phenotype induced by prolonged social isolation in adulthood could also be reversed by antidepressant treatment. We found that isolation-induced anxiety behaviors, as measured in the elevated plus maze, were reversed by chronic imipramine administration, whereas imipramine did not affect the behavior of control rats in this assay (Fig. 1b).
Increased latency to ejaculation has been associated in animal models with depression-like phenotypes24,25, raising the possibility that this abnormality could represent a symptom of anhedonia that is induced by chronic social isolation. We thus sought to determine whether social isolation induces other anhedonia-like symptoms, such as deficits in sucrose preference, which can be seen after several types of active stress15,26. Social isolation decreased sucrose intake and sucrose preference (Fig. 1c,d), and this deficit in sucrose drinking was completely restored by chronic administration of imipramine (Fig. 1e,f). Acute imipramine treatment had no effect on either control or isolated rats (data not shown).
Role of CREB in NAcSh on anhedonia and anxiety behavior
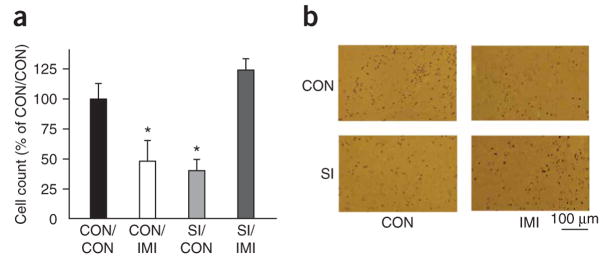
Given our prior evidence that prolonged social isolation of CRE (cAMP response element)-LacZ transgenic mice during adulthood decreased CREB activity in the NAcSh compared with group-housed mice10, we were interested in asking whether imipramine treatment affected this phenomenon. Chronic administration of imipramine completely restored levels of CREB activity in the NAcSh of isolated CRE-LacZ mice compared with those seen in group-housed controls (Fig. 2). We were interested to observe, however, that chronic imipramine treatment of group-housed mice significantly decreased CREB activity in this brain region (P < 0.001; Fig. 2).
Figure 2.
Social isolation and imipramine modulate CREB activity in the NAcSh. (a) CRE-mediated transcriptional activity in the NAcSh of CRE-LacZ mice was decreased in group-housed animals after chronic imipramine administration (CON/IMI) (intraperitoneal injection, 10 mg per kg) and in animals after chronic social isolation (SI/CON) compared with group-housed control animals (CON/CON). Notably, chronic administration of imipramine in socially isolated animals (SI/IMI) corrected their deficit of CRE-activity compared with SI/CON animals (significant interaction of drug and housing: F1,23 = 23.94, P < 0.001, * indicates significantly different (P < 0.05) from CON/CON). (b) Representative photomicrographs of β-galactosidase immunoreactivity (that is, CRE activity).
Activation of the mesolimbic dopamine system has been shown to be important in the response to sex-related environmental cues and in naive and experienced sexual behavior in both male and female rodent models27–29. Previous studies have shown that levels of CREB activity in the NAcSh regulate several emotional responses in normal animals2,10,15–20,30. However, the effects of CREB in the social isolation model have not yet been fully explored. We therefore studied the influence of CREB activity in this brain region on a range of behavioral abnormalities, including sexual behavior, seen after social isolation. We previously showed that herpes simplex virus (HSV)-mediated over-expression of CREB in the NAcSh of isolated animals reversed the increase in anxiety-like behavior exhibited by these animals, but did not influence their latency to ejaculation10. However, this method only overexpresses CREB for a few days, whereas chronic imipramine, which reversed the ejaculation latency deficit, restored CREB levels over a much longer time frame. To address this problem, we used AAV (adeno-associated virus) vectors to overexpress CREB in the NAcSh of adult male rats for 4 weeks. Notably, we confirmed that AAV-CREB infection in the NAcSh caused a sustained increase in CREB activity and that this increase was seen during prolonged social isolation, despite the absence of external stimuli (see Supplementary Methods online).
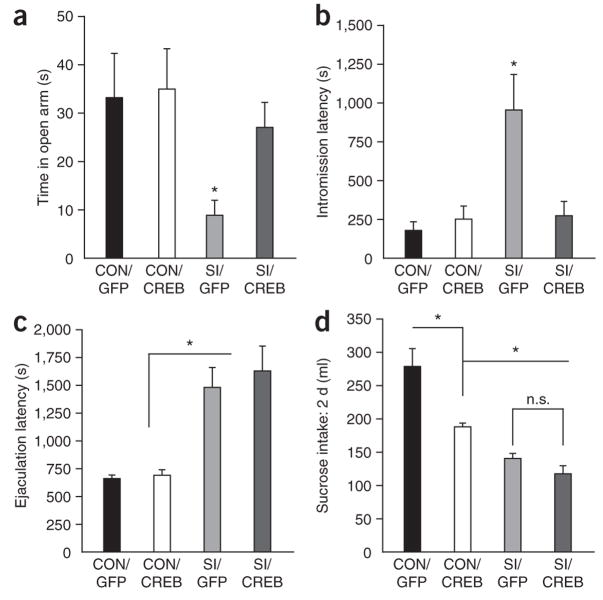
Similar to HSV-CREB overexpression, more prolonged AAV-CREB overexpression suppressed the anxiety phenotype found in isolated rats, as measured in the elevated plus maze (Fig. 3a) and by the latency to initiate sexual behavior (Fig. 3b), but did not affect the behavior of control rats. We also observed freezing behavior on presentation of the female in control, viral-injected, isolated rats (social isolation/control), an abnormality that was not observed in the other groups of rats (data not shown). Despite these effects, however, AAV-CREB, as with HSV-CREB, did not affect the ejaculation latency in isolated rats (Fig. 3c), and it did not treat the deficit seen in sucrose preference under these conditions (Fig. 3d). In fact, AAV-CREB overexpression in the NAcSh of non-isolated control rats decreased sucrose intake (Fig. 3d), as found previously with HSV-CREB injections2.
Figure 3.
Increasing CREB activity in NAcSh of socially isolated animals reverses the anxiety-like behavior, but not the reward-related deficits, induced by social isolation. (a,b) AAV-mediated overexpression of CREB in the NAcSh decreased anxiety-like behavior in isolated animals on the elevated plus maze (significant main effect of housing F1,52 = 4.54, P < 0.05, significant difference between SI/GFP and SI/CREB, n = 9–17 animals per group; a), and social isolation significantly increased initiation of sexual behavior and CREB overexpression in the nucleus accumbens reversed this deficit (significant main effect of virus, F1,35 = 4.6, P < 0.05; significant main effect of housing, F1,36 = 8.02, P < 0.01; significant interaction of virus and housing, F1,36 = 6.90, P < 0.05, n = 8–11 animals per group; b). (c,d) However, CREB overexpression did not affect the deficit in the ejaculation latency (significant effect of housing, F1,33 = 37.30, P < 0.001; no significant interaction, n.s., n = 8–11; c) or sucrose intake (1% sucrose solution) (P > 0.13, n = 13; d). Conversely, CREB overexpression in grouped-housed animals (CON) significantly decreased sucrose intake (CON/GFP versus CON/CREB;* indicates P < 0.05, n = 4).
Regulation of gene expression in NAcSh by social isolation
To gain insight into the molecular basis by which prolonged social isolation in adulthood alters NAcSh function, we first conducted a DNA expression array analysis of socially isolated rats compared with double housed ones. This initial analysis led to several findings, including isolation-induced changes in CREB-related transcription factors (for example, ATF2), several protein kinases (for example, Ca2+/calmodulin kinases and Janus kinase) and several types of K+ channels (an abbreviated list of regulated genes is provided in Table 1; full gene lists are shown in Supplementary Table 1 online). We were interested to note that social isolation upregulated many more genes than it downregulated in the NAcSh. This is similar to active forms of stress, for example, chronic social defeat stress, in which many-fold more genes are upregulated rather than are downregulated, depending on the time period after the last stress3,26.
Table 1.
Examples of genes regulated in rat NAc by social isolation, CREB or imipramine
| SI/CON versus CON/CON | SI/CREB versus SI/GFP | SI/IMI versus SI/CON | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UP (279) | UP (35) | UP (25) | ||||||
| Gene | P value | Fold Δ | Gene | P value | Fold Δ | Gene | P value | Fold Δ |
| Atf2 | 0.021 | 1.235 | Grm8 | 0.040 | 1.555 | Ppp1r15b | 0.043 | 1.896 |
| Adra2c | 0.009 | 1.325 | Cacng5 | 0.040 | 1.331 | Gsr | 0.025 | 1.439 |
| Camk1 | 0.033 | 1.310 | Neuroregulin2 | 0.031 | 1.348 | |||
| Camk4 | 0.001 | 1.368 | DOWN (471) | Spata7 | 0.041 | 1.319 | ||
| Clcn3 | 0.004 | 1.239 | Prkch | 0.014 | 1.300 | |||
| Csnk1e | 0.041 | 1.394 | Nts | 0.014 | 1.830 | DOWN (125) | ||
| Hdac4 | 0.014 | 1.349 | Ache | 0.023 | 1.396 | Map3k10 | 0.037 | 1.670 |
| Jak2 | 0.005 | 1.238 | Vamp2 | 0.017 | 1.556 | Map3k3 | 0.025 | 1.397 |
| Kcna1 | 0.044 | 1.261 | Kcnc3 | 0.037 | 2.290 | Grinl1a | 0.015 | 1.376 |
| Kcnj4 | 0.017 | 1.283 | Cacna1a | 0.012 | 1.370 | Gria2 | 0.047 | 1.324 |
| Kcnma1 | 0.027 | 1.245 | Gabrg3 | 0.042 | 1.496 | Dgka | 0.024 | 1.417 |
| Kcnd2 | 0.021 | 1.247 | Histone H2a | 0.045 | 1.755 | Gpr48 | 0.016 | 1.316 |
| Kcnd3 | 0.028 | 1.246 | Hdac10 | 0.0002 | 1.339 | Bhlhb9 | 0.015 | 1.359 |
| Kcns2 | 0.032 | 1.231 | Smarca4 | 0.021 | 1.419 | Bmpr1a | 0.025 | 1.684 |
| Kcnq3 | 0.042 | 1.362 | Hsf1 | 0.024 | 1.431 | |||
| Prkch | 0.050 | 1.284 | Grina | 0.039 | 1.305 | |||
| Smarca2 | 0.048 | 1.296 | Grin2b | 0.008 | 1.305 | |||
| Comtd | 0.038 | 1.480 | ||||||
| DOWN (3) | Cart | 0.024 | 1.495 | |||||
| Cdc2l5 | 0.004 | 1.900 | Vgf | 0.034 | 1.650 | |||
| Ppp3r2 | 0.038 | 1.502 | Gpr88 | 0.031 | 1.538 | |||
| Nnat | 0.004 | 1.294 | Il13ra1 | 0.042 | 1.382 | |||
| CON/CREB versus CON/GFP | CON/CREB versus CON/GFP | CON/IMI versus CON/CON | ||||||
|
| ||||||||
| UP (69) | DOWN (continued) | UP (144) | ||||||
| Gene | P value | Fold Δ | Gene | P value | Fold Δ | Gene | P value | Fold Δ |
| Kcns3 | 0.043 | 1.911 | Csnk1g1 | 0.029 | 1.465 | Htr3b | 0.026 | 1.329 |
| Irs1 | 0.023 | 1.636 | Kcnc3 | 0.016 | 1.377 | Htr4 | 0.022 | 2.801 |
| Cacng5 | 0.007 | 1.420 | Kcna4 | 0.024 | 1.588 | Prkch | 0.018 | 1.526 |
| Cacna2d3 | 0.016 | 1.755 | Ache | 0.038 | 1.355 | |||
| DOWN (931) | Kcnip2 | 0.028 | 1.628 | Ppp1r1a | 0.029 | 1.375 | ||
| Htr4 | 0.038 | 2.030 | Grm5 | 0.006 | 1.393 | Drd1a | 0.049 | 1.467 |
| Th | 0.016 | 1.436 | Grm4 | 0.008 | 1.440 | PDE 1B | 0.009 | 1.411 |
| Adora2a | 0.048 | 1.852 | Cdk6 | 0.011 | 1.852 | Adora2a | 0.034 | 1.387 |
| Prkch | 0.044 | 1.740 | Rgs2 | 0.007 | 1.544 | Kcnh4 | 0.039 | 1.350 |
| Drd1a | 0.032 | 1.852 | Rgs3 | 0.027 | 1.775 | Ppp1r2 | 0.013 | 1.390 |
| Ppp1r1b | 0.042 | 1.960 | Rgs8 | 0.037 | 1.634 | GPR149 | 0.020 | 1.684 |
| Pde10a | 0.041 | 1.705 | Rgs9 | 0.044 | 1.879 | Nts | 0.021 | 1.763 |
| Pde1c | 0.011 | 1.673 | Rgs10 | 0.028 | 1.476 | |||
| Camk4 | 0.045 | 1.559 | Gpr6 | 0.032 | 1.764 | DOWN (253) | ||
| Pde4b | 0.045 | 1.550 | Gpr88 | 0.039 | 1.889 | Adra2a | 0.045 | 1.773 |
| Adcy5 | 0.023 | 1.879 | Gpr149 | 0.041 | 1.961 | Gria3 | 0.032 | 1.671 |
| Cart | 0.044 | 1.825 | Gad1 | 0.041 | 1.702 | Kcnmb4 | 0.014 | 1.539 |
| Junb | 0.029 | 1.801 | Dgkb | 0.049 | 1.557 | Homer1 | 0.040 | 1.494 |
| Kcnj4 | 0.024 | 1.588 | Gpr51 | 0.046 | 1.536 | |||
| Calb1 | 0.037 | 1.512 | ||||||
CON, control; IMI, imipramine; SI, social isolation.
We next investigated how chronic imipramine treatment or CREB overexpression in the NAcSh modifies these patterns of gene expression in social isolation or control (double-housed) rats. First, there was a marked difference in the number of genes that were affected by imipramine or CREB in isolated versus control animals. Under both AAV-CREB and chronic imipramine conditions, double-housed rats showed significant changes (P < 0.05, corrected for multiple comparisons) in the expression of nearly twofold more genes than in socially isolated animals. These observations suggest that there may be epi-genetic changes that dampen aspects of gene regulation in the isolation condition. This possibility is supported by the observation that histone-modifying related genes (for example, Hdac4 (histone deacetylase 4) and Smarca2) are upregulated with social isolation. HDACs are known to inhibit gene transcription by removing acetyl groups from histones, thereby tightening histone-DNA interactions and making chromatin less accessible to transcription factors31. In addition, HDAC4 has previously been shown to block the rewarding effects of cocaine when overexpressed in the nucleus accumbens (NAc)32. These results raise the possibility that some of the behavioral symptoms induced by social isolation may be mediated by regulation of HDAC4 expression.
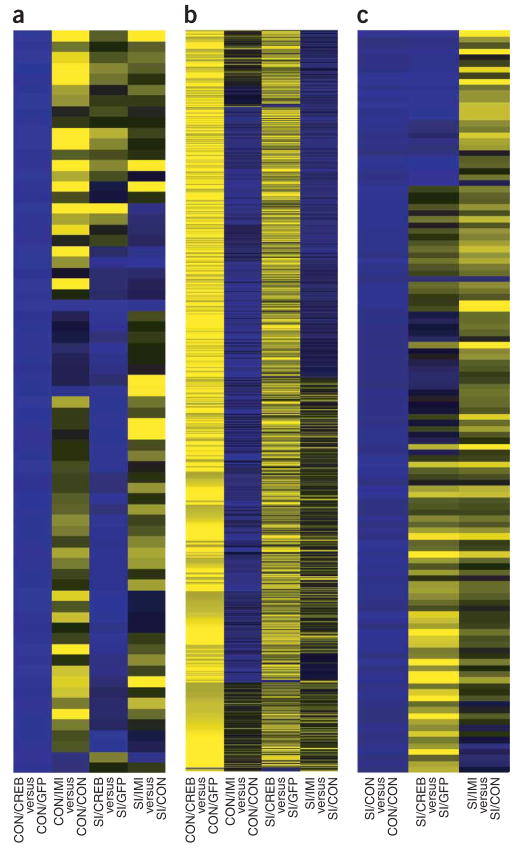
In addition, heat maps highlighted the very different effects induced by chronic imipramine or CREB in the NAcSh of socially isolated versus double-housed rats (Fig. 4a–c). Overexpression of CREB in the NAcSh of double-housed animals induced a pattern of gene expression that was, in general, opposite to that induced by chronic imipramine in double-housed animals (Fig. 4a,b). This is consistent with the ability of chronic imipramine to lower CREB activity in the NAcSh of normal animals (see Fig. 2) and with prior reports of CREB overexpression in non-isolated animals increasing certain depressive-like behaviors2,16,17. In contrast, CREB’s effects were very different in socially isolated animals. The genes that are upregulated in socially isolated rats compared with those under control conditions are generally opposite in isolated rats treated with imipramine versus control isolated animals. However, isolated rats with CREB overexpression, when compared with isolated rats with GFP (green fluorescent protein, control virus), showed only a partial reversal of the pattern that we observed in the socially isolated rats versus double-housed rats. Together, these patterns of overall gene expression mirror the effects of CREB and imipramine on behavioral phenotypes in isolated and control animals.
Figure 4.
Patterns of gene regulation in the NAcSh of socially isolated versus double-housed animals. (a,b) The pattern of genes that were upregulated (blue, a) or downregulated (yellow, b) by CREB observed in double-housed animals with CREB overexpression in the NAcSh was generally opposite to that seen in double-housed animals with imipramine (neutral on nonregulated genes appear black). (c) The pattern of gene upregulation following protracted social isolation was only partially reversed with CREB overexpression, whereas chronic imipramine treatment induced a more complete reversal of the gene expression changes caused by social isolation.
These gene sets were next analyzed to identify specific genes that could contribute to the behavioral phenotypes found for social isolation, chronic imipramine treatment and CREB overexpression in the NAcSh. More specifically, it was hypothesized that genes with common regulation changes resulting from both CREB overexpression and chronic imipramine treatment in isolated animals could contribute to the reversal of anxiety-like symptoms seen under both conditions, whereas those genes that are regulated uniquely by imipramine treatment may be involved in reversing reward-related deficits found in the social isolation model (see abbreviated gene lists in Table 1 and full gene lists in Supplementary Table 1).
Regulation of K+ channels by social isolation
Among the genes that met these criteria were several types of K+ channels; these genes were upregulated in the NAcSh under isolated conditions and this upregulation was blocked by either chronic imipramine treatment or by CREB overexpression in this brain region. Regulation of these same K+ channel genes was noted in previous arrays of NAc in bi-transgenic mice that inducibly overexpressed mCREB in this brain region versus their control littermates33. This is consistent with lower levels of CREB activity being present after social isolation (see Fig. 2). In addition, inducible overexpression of CREB was found to downregulate many of these same channels33.
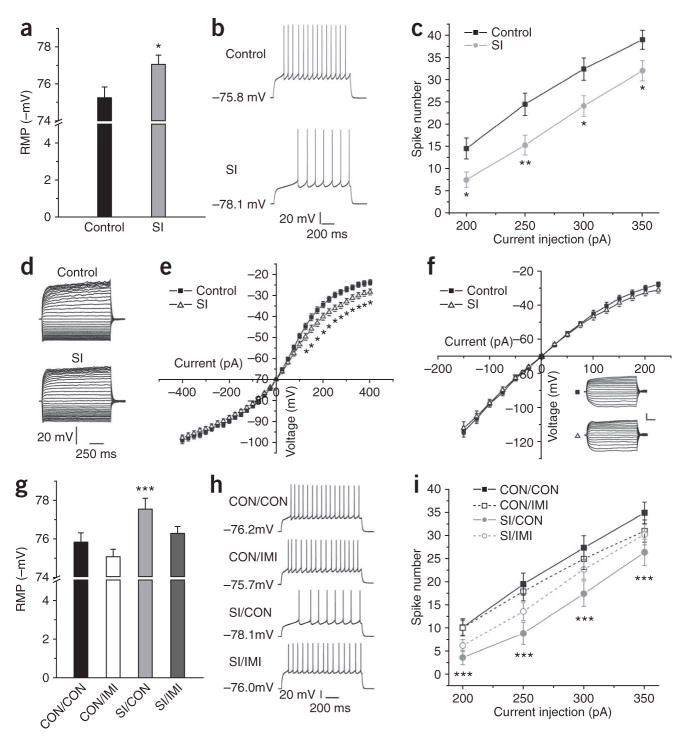
Because K+ channel regulation is a crucial determinant of a neuron’s electrical excitability, the electrophysiological properties of medium spiny neurons in the NAcSh were examined in isolated versus control rats. NAcSh neurons in brain slices from socially isolated animals showed a small, but statistically significant, hyperpolarization of their resting membrane potential (P < 0.05; Fig. 5a), as well as decreased excitability (Fig. 5b,c), which is consistent with an upregulation of K+ channels. Using whole-cell current-clamp recordings, we also found that social isolation had no effect on current-voltage relationships under normal recording conditions (data not shown). However, voltage responses to current injection were decreased when Na+ and Ca2+ channels were blocked (Fig. 5d,e), suggesting that social isolation decreases membrane resistance to K+. We further found that the change in K+-mediated voltage responses was blocked by Ba2+, which inhibits K+ channels, thereby suggesting that K+ channels are an important contributor to the decreased excitability seen after social isolation (Fig. 5f). This increase in K+ conductance and the attendant reduction in NAcSh excitability seen after social isolation, when CREB activity is suppressed in the NAcSh, are consistent with a recent study that directly showed that decreased CREB activity in the NAc has similar effects on NAc neuronal excitability34. Notably, we found that the social isolation-induced hyperpolarization in resting membrane potential and decreased excitability were both reversed by chronic imipramine administration (Fig. 5g–i).
Figure 5.
Effect of social isolation in NAcSh on resting membrane potential (RMP), neuronal excitability and current-voltage relationship. (a) Social isolation significantly reduced RMP (t44 = 2.32, * indicates P < 0.05, n = 5). (b) Sample traces obtained by current injection. (c) Social isolation significantly decreased NAcSh neuronal excitability (t87–89 = 2.23, * indicates P < 0.05, ** indicates P < 0.01 among the range of current injected, n = 8). (d) Sample traces recorded from control and social isolation groups in the presence of Na+ and Ca2+ channel blockers (neurons held at −70 mV). (e) Social isolation significantly decreased membrane input resistance (t26 = 2.39, * indicates P < 0.05 from 125- to 400-pA current injection, n = 4). (f) Ba2+ blocked social isolation–induced effects on membrane input resistance (t = 1.37, P > 0.20, n = 4). Scale bars represent 20 mV and 200 ms for sample traces. (g) Imipramine reversed social isolation–induced changes in RMP (F3,174 = 5.189, P = 0.01, *** indicates significantly different (P < 0.05) from CON/CON, n = 4–5 animals per group). (h) Sample traces induced by current injection. (i) Social isolation–induced decrease in neuronal excitability was reversed by imipramine (F3,172, P < 0.05, n = 4–5 animals per group, *** indicates difference from CON/CON).
Regulation of anxiety, but not anhedonia, by NAcSh K+ channels
Given the evidence that K+ channel expression is induced in the NAcSh after social isolation, we sought to explore whether the behavioral phenotype of isolated rats could be mimicked in non-isolated rats by artificially overexpressing K+ channels and reducing the excitability of NAc neurons. Kir2.1, an inwardly rectifying K+ channel, strongly and reliably decreases NAc neuronal excitability and mimics the effects of decreased CREB activity on these neurons34. We overexpressed Kir2.1 using an HSV vector in the NAcSh of non-isolated rats. This manipulation caused an anxiety-like phenotype in the elevated plus maze (control, 32.7 ± 8.23 s; Kir2.1, 9.67 ± 3.21 s; P = 0.03, n = 9–12) and in the initiation of sexual behavior (control, 204 ± 47.4 s; Kir2.1, 555 ± 115 s; P = 0.011, n = 7–8). However, HSV-Kir2.1 overexpression in the NAcSh had no effect on other isolation-affected behaviors, including anhedonia-related measures such as ejaculation latency, sucrose preference and the number of intromissions to reach ejaculation (data not shown).
The selective effect of Kir2.1 overexpression on anxiety-like symptoms resembles the selective influence of CREB on these behavioral sequelae of social isolation. Our microarray data, along with previous microarray studies33, indicated that manipulation of CREB can alter K+ channel expression, as mentioned earlier. To further determine whether reductions in CREB activity are sufficient for increasing K+ channel expression, we used HSV vectors to overexpress mCREB or β-galactosidase in the NAcSh of non-isolated animals. Using Real-time quantitative PCR (RT-PCR), we found an increase in the expression of Kcnj2 mRNA in mCREB-overexpressing animals compared with β-galactosidase–expressing control animals (β-galactosidase, 1.02 ± 0.0746; mCREB, 1.76 ± 0.248; P = 0.012, n = 8) and a trend for increased levels of Kcnd3 mRNA (β-galactosidase, 1.19 ± 0.137; mCREB, 1.61 ± 0.277; P = 0.07, n = 14–22). In addition, the social isolation condition showed a significant increase in Kcnd3 mRNA levels (control, 1.00 ± 0.0380; social isolation, 1.20 ± 0.0859; P = 0.028, n = 9–10) and trends for increased levels of Kcnj2 (control, 1.02 ± 0.0662; social isolation, 1.38 ± 0.209; P = 0.065, n = 9–10) and Kncs2 (control, 1.04 ± 0.0860; social isolation, 1.26 ± 0.0990; P = 0.062, n = 9–10).
These findings, along with the selective anxiety-like phenotype induced by mCREB overexpression in NAcSh, provide further support for our hypothesis that social isolation increases anxiety-like behaviors via the downregulation of CREB and the subsequent upregulation of certain K+ channels in this brain region.
DISCUSSION
Here, we found that prolonged social isolation of adult animals caused reward-related deficits and an anxiety-like phenotype. Both abnormalities were reversed by chronic, but not acute, imipramine treatment. These findings establish adult social isolation as an animal model of depression- and anxiety-like behavior that responds uniquely to chronic antidepressant administration. The generation of animal models of mood disorders that respond, similar to the human conditions, to chronic antidepressant treatment has been a major goal for this field of research1,35,36. Recent research has shown that novelty-suppressed feeding37 and social defeat3 also show unique responses to chronic administration of antidepressants and both of these models involve a combination of depression- and anxiety-like symptoms as well. Social isolation, as described here, represents an additional model; one that is uniquely related to passive as opposed to active stress and is therefore potentially related to subtypes of human depression and anxiety syndromes that are related to isolation. Use of these various models may lead to better therapeutics for the different subtypes of depression and anxiety caused by active versus passive forms of stress.
The results of our study provide information about the molecular basis of the anxiety-like symptoms induced by social isolation. We found that social isolation decreased CREB activity in the NAcSh, an effect that was reversed by chronic imipramine, and that reduced levels of CREB in social isolation mediated the anxiety-like, but not the anhedonia-like, behaviors seen in the isolation model. Thus, overexpression of CREB in the NAcSh of isolated animals reverses only the anxiety-like phenotype and does not affect the deficits seen in reward-related behavior. Conversely, overexpression of the dominant-negative mutant mCREB in non-isolated animals caused only anxiety-like behavior and did not result in anhedonia-like symptoms. In fact, previous work has shown that mCREB overexpression in the NAcSh of non-isolated animals increases responses to rewarding stimuli and acts similar to an antidepressant, whereas CREB over-expression decreases reward responses and induces depression-like behaviors2,16,17,20. In addition, these overexpression systems modulate anxiety-like behavior in non-isolated animals, with mCREB increasing anxiety and CREB decreasing it2. Our working hypothesis is that CREB activity in the NAcSh during social isolation is downregulated to off-set depressive-like molecular mechanisms; however, this decrease in CREB in the NAcSh comes at the cost of a profound anxiety-like effect. Furthermore, our findings support a model in which social isolation decreases CREB activity in the NAcSh, which mediates the increase in anxiety-like behavior, whereas the restoration of CREB activity induced by chronic antidepressant treatment reverses those anxiety symptoms seen in social isolation.
In contrast, the anhedonia-like phenotype induced by social isolation, which is also reversed by antidepressant treatment, is not mediated by reduced CREB activity in the NAcSh and is presumably mediated by other molecular pathways in this brain region or by other neural circuits. For example, antidepressants have been shown to increase CREB activity in the hippocampus20,38, with CREB over-expression in this region producing antidepressant-like effects39. Therefore, perhaps the anhedonia-like phenotype and the reversal of depressive-like behaviors by imipramine that are observed in the social isolation model are achieved in part through a hippocampal CREB-dependent mechanism. CREB function is also implicated in regulating emotional behavior in several additional circuits, such as amygdala and prefrontal cortex15,20,40, which further underscores the complex mechanisms that are probably involved in anxiety and depression syndromes.
Although we interpreted the increase in ejaculation latency observed in the social isolation model as a deficit in sexual reward, it has not been previously reported as a depression-like phenotype per se. However, other animal models that produce depression-like phenotypes, such as lipopolysaccharide injections or methylphenidate treatment as pups, also increase ejaculation latency24,25. Notably, we found that chronic imipramine administration to non-isolated control animals increased ejaculation latency, similar to the phenotype seen in drug-free isolated animals. This is consistent with both human reports and rodent findings of sexual side effects of antidepressant medications in normal animals and nondepressed humans on antidepressant medications21–23. Together, our findings parallel differences in antidepressant responses seen in normal humans and those with some stress-related disorder. Thus, antidepressants do not produce mood elevating or anxiolytic effects in normal people and sexual deficits caused by depression or anxiety can be alleviated by these treatments in some affected individuals. Likewise, chronic imipramine decreased CREB activity in the NAcSh of normal animals, but increased CREB activity in socially isolated animals. It will be interesting to learn in future studies the molecular basis by which chronic imipramine treatment has opposite effects on CREB activity in the NAcSh, depending on the behavioral history of the animal, as such information could provide insight into the unique effects of long-term antidepressant administration in human populations.
Our microarray findings also led to the investigation of the electrophysiological properties of NAcSh neurons after social isolation. Prolonged isolation increased expression of seven K+ channels, including five voltage-gated K+ channels (Kcna1, Kcnd2 and3, Kcnq3 and Kcns2), an inwardly-rectifying K+ channel (Kcnj4) and a large-conductance calcium-activated K+ channel (Kcnma1). Functionally, these K+ channels contribute to action potential shape (Kcna1, Kcnd3 and Kcnq3), membrane potential hyperpolarization (Kcnj4) and neuronal excitability (Kcnma1). For example, Kcnma1 (also known as SLO1 BK channel) is important in mediating neuronal intrinsic excitability41,42. We found it interesting to note that adaptive changes at the channel level are primarily mediated by K+ channels. No other channels were changed by social isolation with the exception of one Cl− channel. This is similar to findings from the social defeat stress model, in which four K+ channels were upregulated by social defeat in the ventral tegmental area and regulation was not found for any other channels26. These findings may suggest that K+ channels are the major ion channels mediating neuronal plasticity in the brain in both active and passive stress models.
On the basis of the upregulation of several K+ channels in this brain region in socially isolated animals and the reversal of this upregulation by either CREB or imipramine, we hypothesized that dampening the electrical excitability of NAcSh neurons may be a crucial step in the molecular events by which social isolation induces anxiety-like, but not anhedonia-like, symptoms. Indeed, we found that social isolation reduced the excitability of NAcSh neurons, consistent with an upregulation of K+ channel expression. These findings are consistent with our recent demonstration that downregulation of CREB per se reduces NAc neuronal excitability34. Although we did not observe an effect of CREB downregulation on resting membrane potential in this earlier study, this could be a result of the fact that the prior study examined NAc neurons from early postnatal animals and examined short-term effects of CREB downregulation, whereas the social isolation model involved adult animals and prolonged inhibition of CREB activity. Notably, we also found that chronic antidepressant treatment restored the observed deficits in both neuronal excitability and resting membrane potential that were induced by social isolation. This is one of the first studies to investigate electrophysiological mechanisms underlying deficits produced in adulthood social isolation and their reversal by chronic imipramine treatment.
By artificially mimicking the effect of reduced excitability via viral-mediated overexpression of a K+ channel in this region in non-isolated animals, we were able to mimic the increase in anxiety-like, but not anhedonia-like, symptoms induced by social isolation. We then found that downregulation of CREB activity in the NAcSh via overexpression of mCREB was sufficient to increase the expression levels of some of these K+ channels that are upregulated by social isolation. Although this is presumably not the only pathway underlying these behavior abnormalities, our results suggest a molecular pathological pathway by which social isolation, via downregulation of CREB activity and upregulation of K+ channel expression in the NAcSh, induces anxiety-like symptoms. This is of particular interest because CREB is traditionally viewed as a transcriptional activator. In this case, however, it would appear that CREB is acting as a repressor of certain genes, and when its expression was decreased, by either social isolation or mCREB overexpression, an increase in particular K+ channels was observed. Further work is needed to determine whether CREB serves as a direct transcriptional repressor for these genes or regulates them indirectly via other transcription factors. In addition, our microarray analysis of isolated and control animals under CREB and chronic antidepressant conditions identified numerous molecular pathways that may also contribute to the behavioral phenomena observed here and can be investigated in future studies.
In summary, our data provide new insight into the role of CREB in the NAcSh as a crucial regulator of responses to emotional stimuli (Supplementary Fig. 2 online). Prior work has demonstrated that drugs of abuse and active stress induce CREB activity in this region and that this ‘high CREB’ state is associated with a general blunting of emotional responding, including anhedonia-like symptoms and reduced anxiety-like behavior. In contrast, prolonged social isolation during adulthood decreases CREB activity in the NAcSh and this ‘low CREB’ state is associated with emotional hyper-reactivity, including profound anxiety. This role for CREB in the NAcSh as an ‘emotional rheostat’ is consistent with CREB’s role as an electrophysiological rheostat of NAc neuronal excitability, with increased CREB increasing NAc excitability and decreased CREB decreasing it, as has been shown both previously34 and here. Notably, chronic administration of imipramine normalized CREB activity at both extremes: preventing an increase in CREB activity from active stress (data not shown) and increasing it when in the low state (as shown here). In this way, we hypothesize that antidepressants may reverse anhedonia-like symptoms by preventing the induction of CREB activity in the NAcSh during periods of active stress and reversing anxiety-like symptoms when CREB activity is low. Clearly, the situation is far more complex, with anxiety and depression symptoms, as well as sexual behavior, being regulated by numerous molecular mediators not only in the NAc, but in several other brain regions as well1,15,20,27,28,38,39,43–45. Nonetheless, our findings further characterize the long-term sequelae of social isolation and provide insight into the neural and molecular mechanisms that distinguish anxiety and depression symptoms in a chronic stress model.
METHODS
All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas.
Social isolation and imipramine treatment
Sprague-Dawley rats (Charles River Breeding Laboratories) arrived at 7–8 weeks of age and were placed in a 12-h light/12-h dark cycle room (lights on between 7 a.m. and 7 p.m.). They were either housed two animals per cage or isolated one per cage. Testing of the isolated animals began after 10–12 weeks of isolation. In the case of acute imipramine treatment, after 10 weeks of isolation, the animals received either 5 d of oral imipramine (10 mg per kg daily) in their drinking water or chronic imipramine treatment (isolation for 6 weeks with 4 weeks of oral imipramine treatment). Trunk blood levels were taken and measured by high-performance liquid chromatography to ensure clinically relevant levels of the drug (see Supplementary Methods).
Sexual behavior
The sexual behavior of adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (Charles River Breeding Laboratories) was examined as described10 under red light conditions between 8 p.m. and 2 a.m. Males were given a 5-min acclimation period to the testing arena and testing began thereafter by the introduction of a receptive female to the arena. The first series of sexual behavior and the first post-ejaculation interval were then measured24 (see Supplementary Methods for additional details).
Elevated plus maze
Rats were tested for the time spent in the open and closed arms of an elevated plus maze (55 cm from the floor, 12 × 50 cm arms) over 5 min as described2. Testing was carried out under controlled light conditions (15–20 lx) and was scored blindly with regards to housing, imipramine or viral conditions. The experimental procedures for other behavioral tests used here are given in the Supplementary Methods.
Sucrose preference
The sucrose preference test consisted of a modified two-bottle choice procedure, as described previously24, in which the animals were given the choice between water and a sucrose solution after initial habituation to two bottles of water for 5 d. At the start of the experiment, animals were allowed unlimited total access to water in one bottle and ascending concentrations of sucrose (0, 0.25, 0.5, 1 and 2% solutions; wt/vol) in the other bottle for 24 h at each concentration. For animals under isolation and imipramine treatment and for experiments using viral-mediated gene transfer, similar methods were used (described in more detail in the Supplementary Methods).
Viral-mediated gene transfer
Surgery was performed on male Sprague-Dawley rats. AAV or HSV vectors were injected bilaterally (1.5 μl per side) over 7.5 min into the NAcSh (relative to bregma: rat, anterior-posterior = +1.8, lateral = ± 2.4, dorsal-ventral = −6.7 mm below dura, with a 10° angle) as previously described2. At the end of the experiment, the animals that were used in the behavioral tests were killed by perfusion and the injection placements were evaluated for each animal on 40-μm cresyl-violet–stained coronal sections. Only animals with correct bilateral placements were used for analysis. The injected viruses were HSV-mCREB (a dominant-negative mutant of CREB in which phosphorylation at Ser133 is inhibited by an alanine mutation2,18,46), HSV-GFP or HSV-LacZ (encoding control proteins), HSV-Kir2.1 (a wild-type inward-rectifying potassium channel34), AAV-CREB and AAV-GFP. On the basis of the time course of transgene expression in the NAcSh, animals were tested for behavior between 2–4 d after injection of HSV vectors or 3–4 weeks after injection of AAV vectors, when transgene expression is known to be maximal.
CRE-LacZ activity in reporter mice
CRE-LacZ mice were used in which β-galactosidase is expressed under the control of CREs10. The construct, which contains seven CRE consensus sequences in tandem upstream of a minimal somatostatin promoter and the LacZ gene, is flanked by 5′ insulator sequences (see ref. 2). Adult mice were either housed in groups or singly (socially isolated) for 6 weeks and then injected daily with saline or 10 mg per kg of imipramine intraperitoneally for 4 weeks. A second line of CRE-LacZ reporter mice, which supports lower levels of transgene expression under normal conditions, was used for AAV virus validation2,46 (see Supplementary Methods). The mice were killed by perfusion 4 weeks after virus was injected or 4 h post-injection for imipramine experiments. Brain sectioning (40-μm sections) and immunostaining were performed using published procedures2,10. β-galactosidase immunostaining was carried out using a goat antibody to β-galactosidase (1:5,000, Biogenesis), a biotinylated rabbit secondary antibody to goat (1:200) and the biotin-streptavidin technique (ABC kit, Vector Laboratories) with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine as chromogen. The density of positive nuclei was determined bilaterally in the NAcSh over six sections separated by 120 μm for each mouse using the unbiased stereology program Stereoinvestigator (MicroBrightField). The positive cells were counted blindly with regard to the experimental conditions of the mice.
Electrophysiological recordings
All recordings were carried out blind to the experimental conditions of the rats. To minimize possible stress effects on the recordings, we anesthetized the rats and perfused them immediately for 40–60 s with ice-cold aCSF (artificial cerebrospinal fluid), which contained 128 mM NaCl, 3 mM KCl, 1.25 mM NaH2PO4, 10 mM D-glucose, 24 mM NaHCO3, 2 mM CaCl2 and 2 mM MgCl2 (oxygenated with 95% O2 and 5% CO2, pH 7.35, 295–305 mOsm). Acute brain slices containing NAcSh were cut using a microslicer (DTK-1000, Ted Pella) in sucrose-aCSF, which was derived by fully replacing NaCl with 254 mM sucrose, and saturated by 95% O2 and 5% CO2. Slices were maintained in the holding chamber for 1 h at 37 °C. The recording external solution (flow rate = 2.5 ml min−1) consisted of aCSF without NaH2PO4, but with 1 mM kynurenic acid and 100 mM picrotoxin added to block ionotropic glutamate and GABAA receptors, respectively. In the experiments for K+ channel–mediated responses, 1 μM tetrodotoxin and 200 μM Cd2+ were used to block Na+ and Ca2+ channels, respectively.
Whole-cell current-clamp recordings, as described previously34, were carried out at 34°C. Recordings were obtained from medium spiny neurons of NAcSh. Patch pipettes (3–5 M) were filled with an internal solution containing 115 mM potassium gluconate, 20 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 10 mM phosphocreatine, 10 mM HEPES, 2 mM magnesium ATP and 0.5 mM GTP (pH 7.2, 285 mOsm). Whole-cell recordings were made under continuous single-electrode voltage-clamp mode (AxoClamp 2B, Axon Instruments) and converted to Bridge mode for current clamping. Data acquisition was made using DigiData 1322A and pClamp 8 (Axon Instruments). Series resistance was monitored during experiments and Bridge was compensated. Resting membrane potential was measured immediately after whole-cell current-clamp mode in the absence of current injection. Current-voltage relationship in normal aCSF (in the absence of Na+ and Ca2+ channel blockers) was obtained by measuring voltage responses for ~300 ms. The K+ current-voltage relationship was obtained by measuring voltage responses between 1.0 and 1.2 s. The effect of Ba2+ on NAc neuronal physiology was also investigated.
Microarray analysis
Rats were housed alone for 6 weeks for the social isolation experiments, followed by AAV-CREB or AAV-GFP surgeries, or imipramine or control water treatment 4 weeks before tissue collection. After rapid decapitation and brain extraction, punches of NAcSh were taken and frozen until RNA was extracted. Bilateral punches were pooled for two animals, with three independent tissue samples being used per group. RNA was reversed transcribed into cDNA and labeled for microarray analysis as described3. Genes were analyzed by GeneSpring software (Agilent Technologies) and determined to be significant if regulated by at least a 20% (initial experiment) or 30% difference (subsequent experiments), with P < 0.05 adjusted for multiple comparisons.
RT-PCR
HSV-mCREB or HSV-LacZ was injected into the NAcSh as described previously10; 3–4 d later, RNA was extracted from NAcSh punches and cDNA was prepared. Primer sets for Kcns2, Kcnd3 and Kcnj2 were validated and then used on the cDNA generated from NAcSh tissue. All values were normalized to control LacZ samples. For the social isolation experiment, NAcSh punches were taken 10 weeks after isolation, RNA was extracted and cDNA was prepared. All values were normalized to control (double housed) animals.
Statistical analysis
For two group comparisons, student t tests were used. ANOVA was used for experiments that compared effects of housing conditions and drug treatment, and the Bonferroni correction was used for multiple comparisons. Statistics were analyzed using the software packages from Prism (GraphPad Software) and SPSS Statistics (Predictive Analytics Company), and significance was determined at P < 0.05. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m.
Accession codes
ArrayExpress database: All microarray data have been deposited with accession number E-MEXP-1944 (see Supplementary Methods for additional details).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Institute of Mental Health (E.J.N.) and National Alliance of Research for Schizophrenia and Depression (M.-H.H.).
Footnotes
Reprints and permissions information is available online at http://npg.nature.com/reprintsandpermissions/
Note: Supplementary information is available on the Nature Neuroscience website.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
D.L.W. conducted the behavioral, immunohistochemical, cell counting and RT-PCR experiments, surgeries and tissue collection, and wrote the manuscript. M.-H.H. conducted the electrophysiology experiments and contributed to the preparation of the manuscript. D.L.G., T.A.G. and V.V. assisted with surgeries, tissue collection and RT-PCR experiments. S.D.I. assisted with behavioral and electrophysiology experiments. J.-L.C. and D.C.C. assisted with electrophysiology experiments. A. Kirk assisted with the behavioral experiments, immunohistochemistry and surgeries. S.C., A. Kumar and R.L.N. prepared the viral constructs. V.K. and C.A.B. assisted with behavioral experiments. M.B. assisted with behavioral experiments and preparation of the manuscript. C.A.M. conducted microarray experiments and their analysis, and E.J.N. oversaw the design and execution of the overall project and writing of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Nestler EJ, et al. Neurobiology of depression. Neuron. 2002;34:13–25. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00653-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Barrot M, et al. CREB activity in the nucleus accumbens shell controls gating of behavioral responses to emotional stimuli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:11435–11440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.172091899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Berton O, et al. Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress. Science. 2006;311:864–868. doi: 10.1126/science.1120972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mendelson SD, McEwen BS. Autoradiographic analyses of the effects of restraint-induced stress on 5-HT1A, 5-HT1C and 5-HT2 receptors in the dorsal hippocampus of male and female rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1991;54:454–461. doi: 10.1159/000125951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hall FS. Social deprivation of neonatal, adolescent, and adult rats has distinct neurochemical and behavioral consequences. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1998;12:129–162. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v12.i1-2.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Grippo AJ, Cushing BS, Carter CS. Depression-like behavior and stressor-induced neuroendocrine activation in female prairie voles exposed to chronic social isolation. Psychosom Med. 2007;69:149–157. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e31802f054b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Costello J, Kendrick K. Grief and older people: the making or breaking of emotional bonds following partner loss in later life. J Adv Nurs. 2000;32:1374–1382. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2648.2000.01625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Heinrich LM, Gullone E. The clinical significance of loneliness: a literature review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2006;26:695–718. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2006.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ahmed SH, Stinus L, Le Moal M, Cador M. Social deprivation enhances the vulnerability of male Wistar rats to stressor- and amphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1995;117:116–124. doi: 10.1007/BF02245106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Barrot M, et al. Regulation of anxiety and initiation of sexual behavior by CREB in the nucleus accumbens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:8357–8362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500587102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ehlers CL, Walker BM, Pian JP, Roth JL, Slawecki CJ. Increased alcohol drinking in isolate-housed alcohol-preferring rats. Behav Neurosci. 2007;121:111–119. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.121.1.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Deroche V, Piazza PV, Le Moal M, Simon H. Social isolation-induced enhancement of the psychomotor effects of morphine depends on corticosterone secretion. Brain Res. 1994;640:136–139. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91867-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Greco AM, Gambardella P, Sticchi R, D’Aponte D, De Franciscis P. Chronic administration of imipramine antagonizes deranged circadian rhythm phases in individually housed rats. Physiol Behav. 1990;48:67–72. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(90)90262-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stranahan AM, Khalil D, Gould E. Social isolation delays the positive effects of running on adult neurogenesis. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:526–533. doi: 10.1038/nn1668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Blendy JA. The role of CREB in depression and antidepressant treatment. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;59:1144–1150. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Newton SS, et al. Inhibition of cAMP response element-binding protein or dynorphin in the nucleus accumbens produces an antidepressant-like effect. J Neurosci. 2002;22:10883–10890. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-24-10883.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pliakas AM, et al. Altered responsiveness to cocaine and increased immobility in the forced swim test associated with elevated cAMP response element-binding protein expression in nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci. 2001;21:7397–7403. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-18-07397.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Carlezon WA, Jr, et al. Regulation of cocaine reward by CREB. Science. 1998;282:2272–2275. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5397.2272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pandey SC, et al. CREB gene transcription factors: role in molecular mechanisms of alcohol and drug addiction. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005;29:176–184. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000153550.31168.1d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Carlezon WA, Jr, Duman RS, Nestler EJ. The many faces of CREB. Trends Neurosci. 2005;28:436–445. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2005.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.de Jong TR, Veening JG, Waldinger MD, Cools AR, Olivier B. Serotonin and the neurobiology of the ejaculatory threshold. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2006;30:893–907. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2006.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ferguson JM. The effects of antidepressants on sexual functioning in depressed patients: a review. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62 (Suppl 3):22–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rothschild AJ. Sexual side effects of antidepressants. J Clin Psychiatry. 2000;61 (Suppl 11):28–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bolanos CA, Barrot M, Berton O, Wallace-Black D, Nestler EJ. Methylphenidate treatment during pre- and periadolescence alters behavioral responses to emotional stimuli at adulthood. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;54:1317–1329. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(03)00570-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yirmiya R. Endotoxin produces a depressive-like episode in rats. Brain Res. 1996;711:163–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)01415-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Krishnan V, et al. Molecular adaptations underlying susceptibility and resistance to social defeat in brain reward regions. Cell. 2007;131:391–404. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Balfour ME, Yu L, Coolen LM. Sexual behavior and sex-associated environmental cues activate the mesolimbic system in male rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29:718–730. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hull EM, Dominguez JM. Sexual behavior in male rodents. Horm Behav. 2007;52:45–55. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2007.03.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Meisel RL, Mullins AJ. Sexual experience in female rodents: cellular mechanisms and functional consequences. Brain Res. 2006;1126:56–65. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.08.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Conti AC, Blendy JA. Regulation of antidepressant activity by cAMP response element binding proteins. Mol Neurobiol. 2004;30:143–155. doi: 10.1385/MN:30:2:143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tsankova N, Renthal W, Kumar A, Nestler EJ. Epigenetic regulation in psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:355–367. doi: 10.1038/nrn2132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kumar A, et al. Chromatin remodeling is a key mechanism underlying cocaine-induced plasticity in striatum. Neuron. 2005;48:303–314. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.09.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.McClung CA, Nestler EJ. Regulation of gene expression and cocaine reward by CREB and DeltaFosB. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:1208–1215. doi: 10.1038/nn1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dong Y, et al. CREB modulates excitability of nucleus accumbens neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:475–477. doi: 10.1038/nn1661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Duman RS, Monteggia LM. A neurotrophic model for stress-related mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;59:1116–1127. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Berton O, Nestler EJ. New approaches to antidepressant drug discovery: beyond monoamines. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:137–151. doi: 10.1038/nrn1846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dulawa SC, Hen R. Recent advances in animal models of chronic antidepressant effects: the novelty-induced hypophagia test. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2005;29:771–783. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nibuya M, Nestler EJ, Duman RS. Chronic antidepressant administration increases the expression of cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) in rat hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1996;16:2365–2372. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-07-02365.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chen AC, Shirayama Y, Shin KH, Neve RL, Duman RS. Expression of the cAMP response element–binding protein (CREB) in hippocampus produces an antidepressant effect. Biol Psychiatry. 2001;49:753–762. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(00)01114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pandey SC. The gene transcription factor cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein: role in positive and negative affective states of alcohol addiction. Pharmacol Ther. 2004;104:47–58. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bell TJ, et al. Cytoplasmic BK(Ca) channel intron-containing mRNAs contribute to the intrinsic excitability of hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:1901–1906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711796105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Salkoff L, Butler A, Ferreira G, Santi C, Wei A. High-conductance potassium channels of the SLO family. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:921–931. doi: 10.1038/nrn1992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Brown ES, Rush AJ, McEwen BS. Hippocampal remodeling and damage by corticosteroids: implications for mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;21:474–484. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Thome J, et al. cAMP response element-mediated gene transcription is upregulated by chronic antidepressant treatment. J Neurosci. 2000;20:4030–4036. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-11-04030.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Warner-Schmidt JL, Duman RS. Hippocampal neurogenesis: opposing effects of stress and antidepressant treatment. Hippocampus. 2006;16:239–249. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Impey S, et al. Stimulation of cAMP response element (CRE)-mediated transcription during contextual learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:595–601. doi: 10.1038/2830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.