Abstract
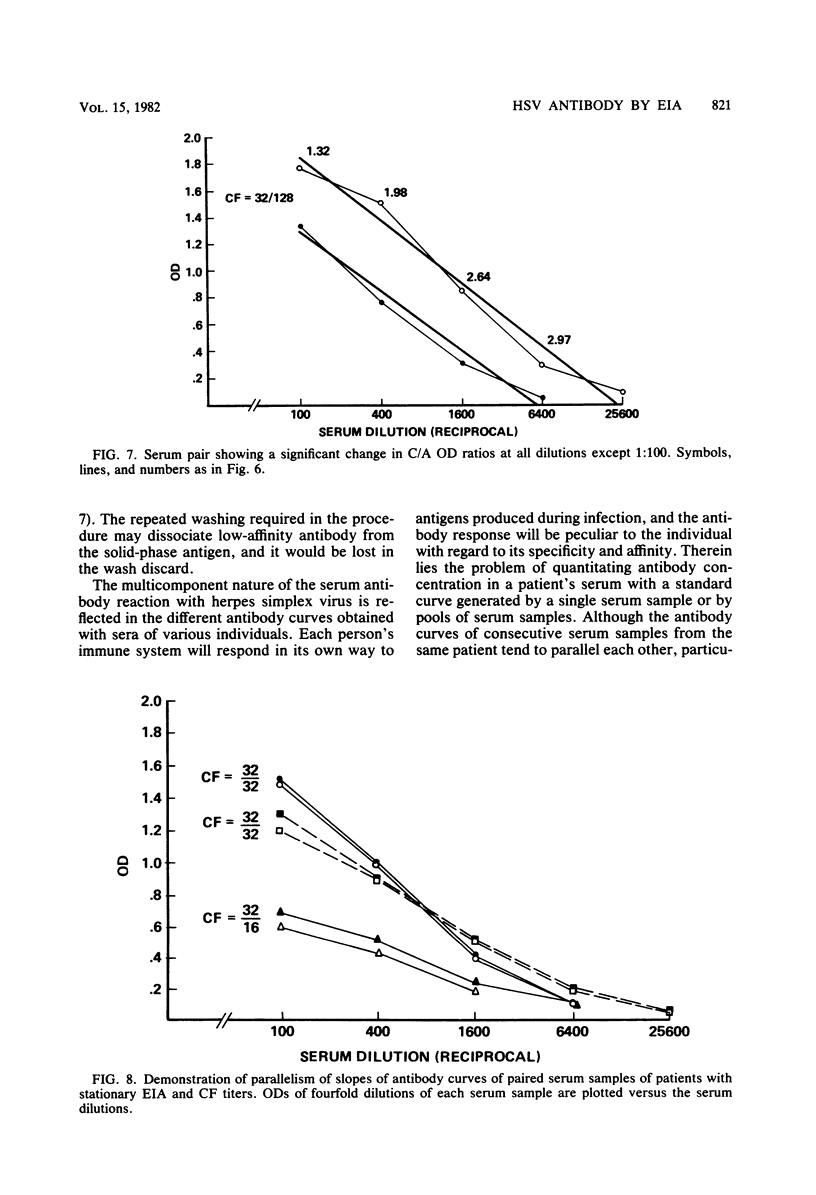
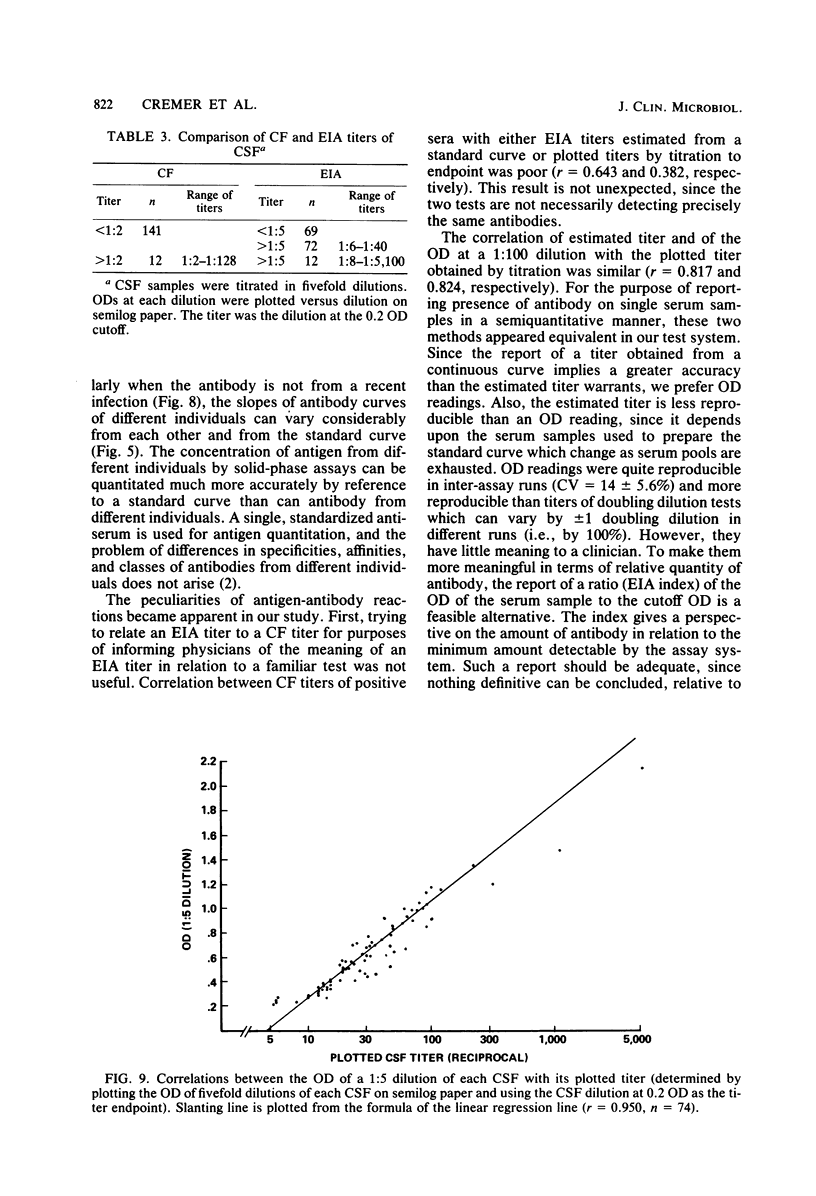
Several methods for evaluating and reporting enzyme immunoassay (EIA) determinations of antibody to herpes simplex virus derived from one dilution of single serum samples were studied. An EIA ratio method for serological evidence of current infection from paired serum samples was also evaluated. Optical density (OD) of the reaction at a 1:100 serum dilution and estimated titers obtained by reference of the OD of the serum dilution to a standard curve were compared to the corresponding plotted EIA titer obtained by titration to endpoint. Neither the OD per se nor the estimated titer was completely predictive of the plotted titer (correlation coefficient [r] of 0.824 and 0.817, respectively), and they provided only a semiquantitative measurement of antibody concentration. For an antibody status report, however, OD would be sufficient if related to the cutoff value as an EIA index (OD of sample divided by cutoff OD for positive specimens). The OD of the EIA reaction at a single dilution (1:5) of cerebrospinal fluid, on the other hand, correlated quite well with the titer obtained by titration (r = 0.950). For serological diagnosis of current infection, the OD ratio of convalescence-phase/acute-phase sera was determined at several dilutions. A ratio of greater than or equal to 1.54 was calculated as a reliable index for a significant rise in antibody concentration and compatible with current infection. By determining the convalescent-phase/acute-phase serum ratio at two dilutions, 1:100 and 1:1,000, the EIA ratio method appeared to be a sensitive as or more sensitive than, complement fixation in diagnosing current infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butler J. E., Feldbush T. L., McGivern P. L., Stewart N. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): a measure of antibody concentration or affinity. Immunochemistry. 1978 Feb;15(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Cremer N. E., Johnson K. P., Fein G., Likosky W. H. Comprehensive viral immunology of multiple sclerosis. III. Analysis of CSF antibodies by radioimmunoassay. Arch Neurol. 1980 Oct;37(10):616–619. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500590040004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson C. V., Riggs J. L., Lennette E. H. Photochemical inactivation of DNA and RNA viruses by psoralen derivatives. J Gen Virol. 1978 Aug;40(2):345–358. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-2-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearst J. E., Thiry L. The photoinactivation of an RNA animal virus, vesicular stomatitis virus, with the aid of newly synthesized psoralen derivatives. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1339–1347. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for cholera serology. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):759–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.759-763.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimo K. O., Marttila R. J., Ziola B. R., Matikainen M. T., Panelius M. Radioimmunoassay of herpes-simplex and measles virus antibodies in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients without infectious or demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Nov;10(4):431–438. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-4-431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfield D. C., Richman D. D., Oxman M. N., Kronenberg L. H. Psoralen inactivation of influenza and herpes simplex viruses and of virus-infected cells. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1216–1226. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1216-1226.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandvik B., Natvig J. B., Wiger D. IgG1 subclass restriction of oligoclonal IgG from cerebrospinal fluids and brain extracts in patients with multiple sclerosis and subacute encephalitides. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(4):427–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Savigny D., Voller A. The communication of ELISA data from laboratory to clinician. J Immunoassay. 1980;1(1):105–128. doi: 10.1080/01971528008055779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


