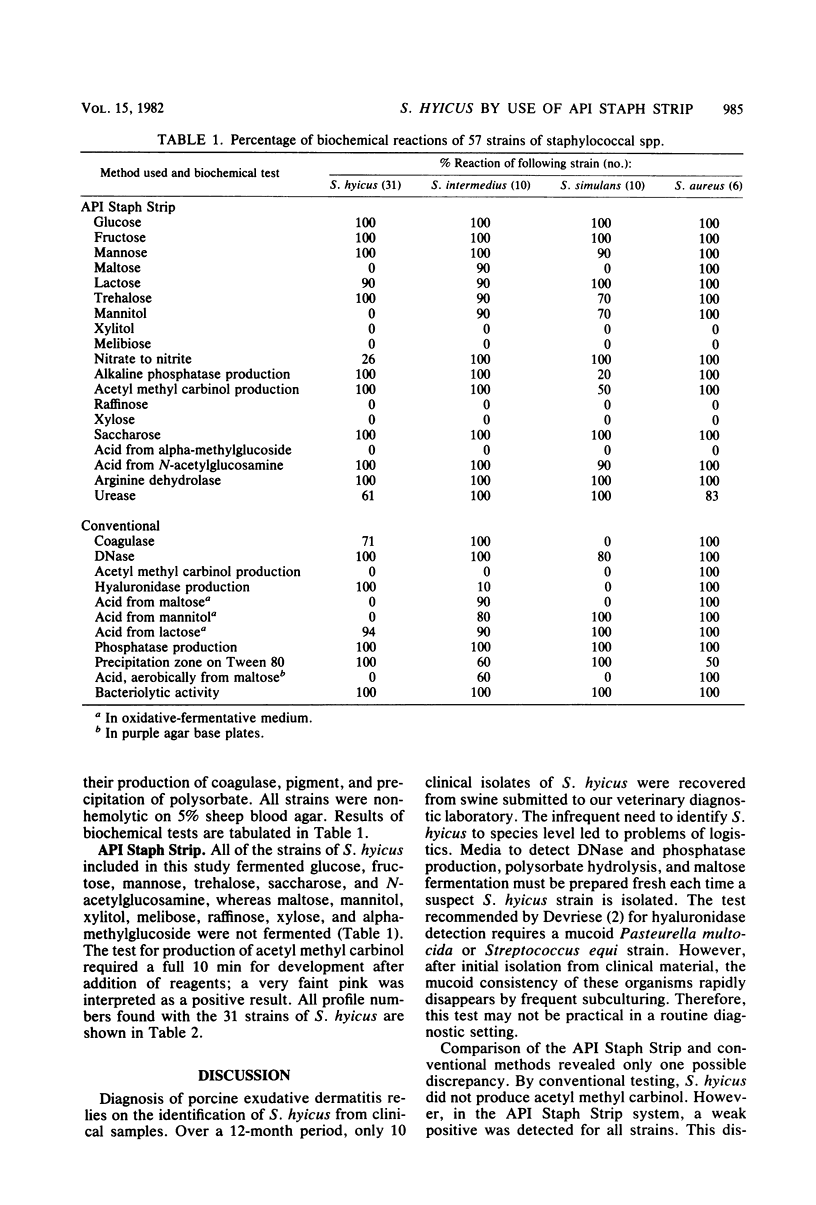
Abstract
The API Staph Strip system (API System S.A., Montalïeu-Vercieu, France) was compared with conventional methods for identification of Staphylococcus hyicus isolated from cases of exudative epidermitis in swine. The API Staph Strip was found to provide unique profile numbers, namely, 6-514-151, 6-514-153, and 6-516-153. These profile numbers are not listed in the API Staph Strip data base. It was found that the use of this miniaturized system is preferable to conventional methods for the identification of the causal agent of swine exudative epidermitis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brun Y., Fleurette J., Forey F. Micromethod for biochemical identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Nov;8(5):503–508. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.5.503-508.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Derycke J. Staphylococcus hyicus in cattle. Res Vet Sci. 1979 May;26(3):356–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A. Isolation and identification of Staphylococcus hyicus. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jun;38(6):787–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R., Hjersing N. Species of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from catheter tips from open-heart surgery patients. Thorax. 1980 May;35(5):359–362. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.5.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofherr L., Lund M. E. Characterization of staphylococci using the API 20E system. Am J Med Technol. 1979 Feb;45(2):127–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. E., Jr, King R. E., Kloos W. E. Isolation of Staphylococcus hyicus subsp hyicus from a pig with septic polyarthritis. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Feb;41(2):274–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satta G., Grazi G., Varaldo P. E., Fontana R. Detection of bacterial phosphatase activity by means of an original and simple test. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Apr;32(4):391–395. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.4.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varaldo P. E., Grazi G., Cisani G., Satta G. Routine separation of staphylococci from micrococci based on bacteriolytic activity production. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):147–148. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.147-148.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarzour J. Y., Belle E. A. Evaluation of three test procedures for identification of Staphylococcus aureus from clinical sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):133–136. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.133-136.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


