Abstract
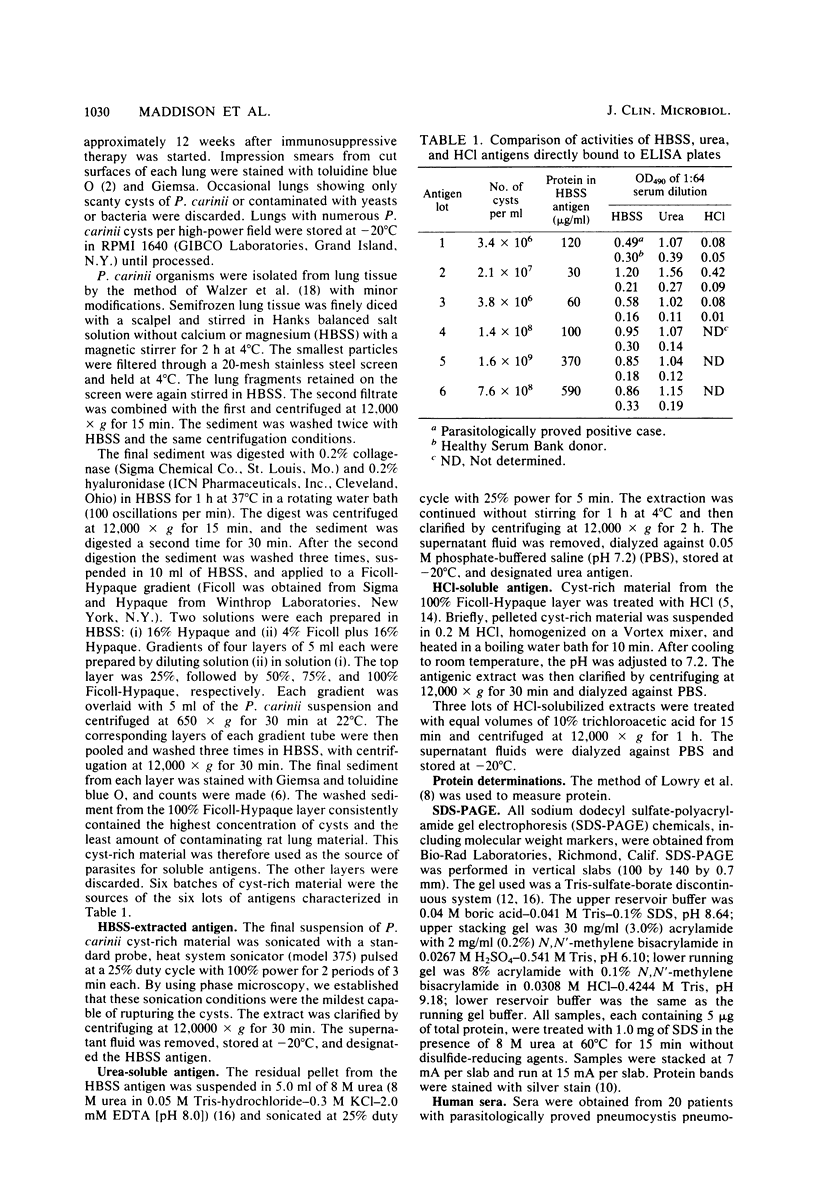
Cyst-rich suspensions of Pneumocystis carinii were obtained by differential and gradient centrifugation from heavily infected rat lungs. After preparation of an aqueous-soluble extract of the cyst-rich material, the insoluble residue was extracted with 8 M urea. Small amounts of infected human lung tissue and uninfected rat and human lung were processed similarly. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showed that both human and rat infected lung extracts contained a large protein (greater than 200,000 daltons). This component was not present in extracts of uninfected lung. In addition, an HCl-soluble extract was prepared from the cyst-rich suspension from infected rat lung. The urea-extracted antigen was most reactive in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Rabbit antiserum against the HCl-soluble antigen detected circulating antigen in patients' sera in a counterimmunoelectrophoresis assay.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett A., Bidwell D. E. Enzyme immunoassays for parasitic diseases. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1976;70(2):98–106. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(76)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHALVARDJIAN A. M., GRAWE L. A. A NEW PROCEDURE FOR THE IDENTIFICATION OF PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII CYSTS IN TISSUE SECTIONS AND SMEARS. J Clin Pathol. 1963 Jul;16:383–384. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.4.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg K., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Serological studies of actionomyces israelii by crossed immunoelectrophoresis: standard antigen-antibody system for A. israelii. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):387–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.387-397.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsoe G. H., Weller T. H. Immunodiagnosis of infection with Schistosoma mansoni: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibody to circulating antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5715–5717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison S. E., Hayes G. V., Slemenda S. B., Norman L. G., Ivey M. H. Detection of specific antibody by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and antigenemia by counterimmunoelectrophoresis in humans infected with Pneumocystis carinii. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1036–1043. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1036-1043.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. D., Pifer L. L., Sale G. E., Thomas E. D. The value of Pneumocystis carinii antibody and antigen detection for diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia after marrow transplantation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Dec;120(6):1283–1287. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.6.1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr, Glossmann H. Molecular weight determination of membrane protein and glycoprotein subunits by discontinuous gel electrophoresis in dodecyl sulfate. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:92–102. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman L., Kagan I. G. Some observations on the serology of Pneumocystis carinii infections in the United States. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.317-321.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Stagno S., Woods D. Pneumocystis carinii infection: evidence for high prevalence in normal and immunosuppressed children. Pediatrics. 1978 Jan;61(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Brasfield D. M., Tiller R. E. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in young immunocompetent infants. Pediatrics. 1980 Jul;66(1):56–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Tao Y., Maddison S. E. Systematic fractionation of Schistosoma mansoni urea-soluble egg antigens and their evaluation by the single-tube, kinetic-dependent, enzyme-linked, immunosorbent assay (K-ELISA). J Parasitol. 1981 Jun;67(3):340–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E., Yoneda K., Stahr B. J. Pneumocystis carinii: new separation method from lung tissue. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Jun;47(3):356–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]