Abstract
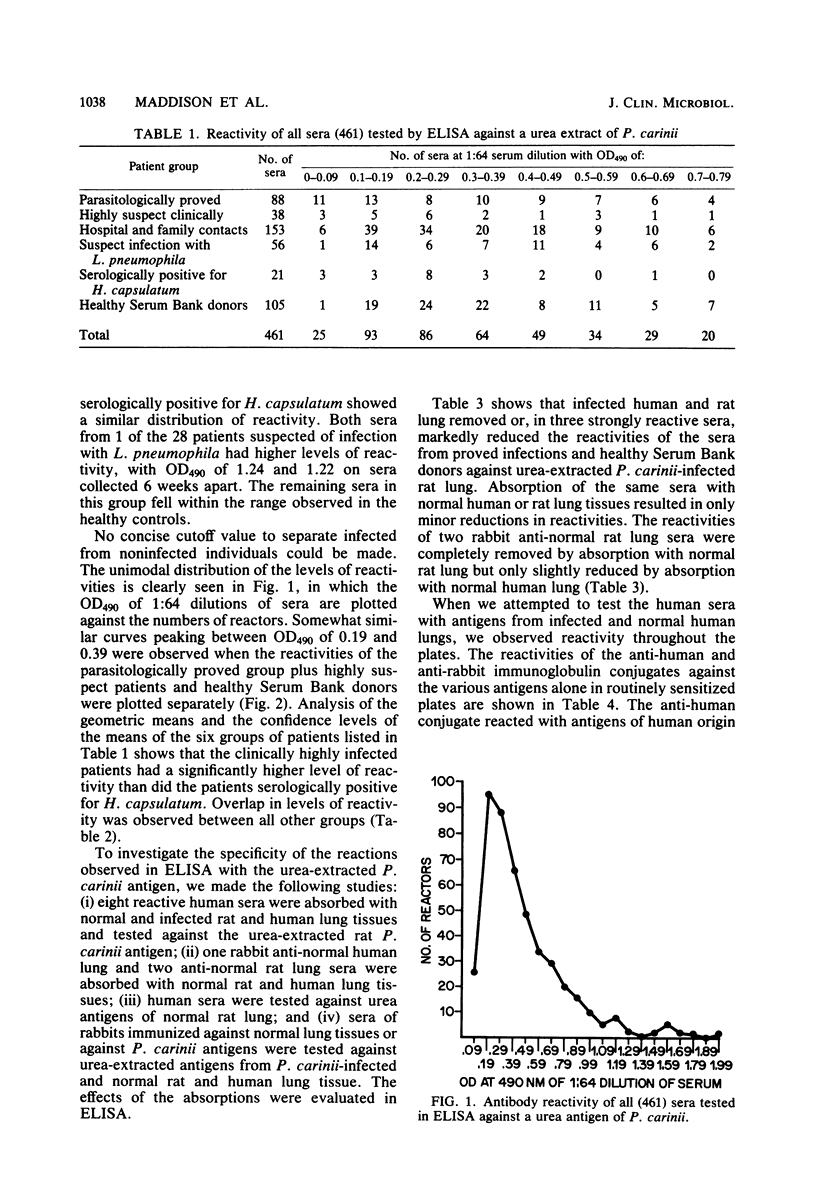
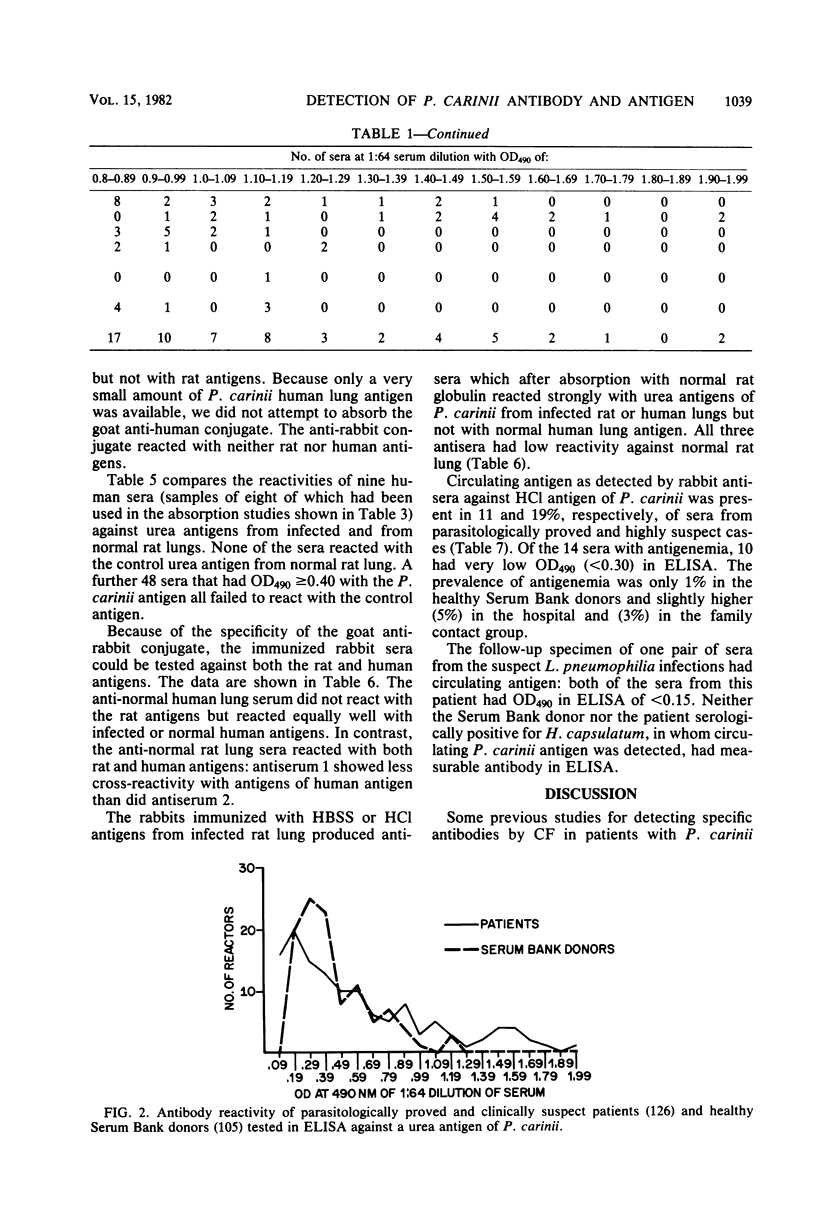
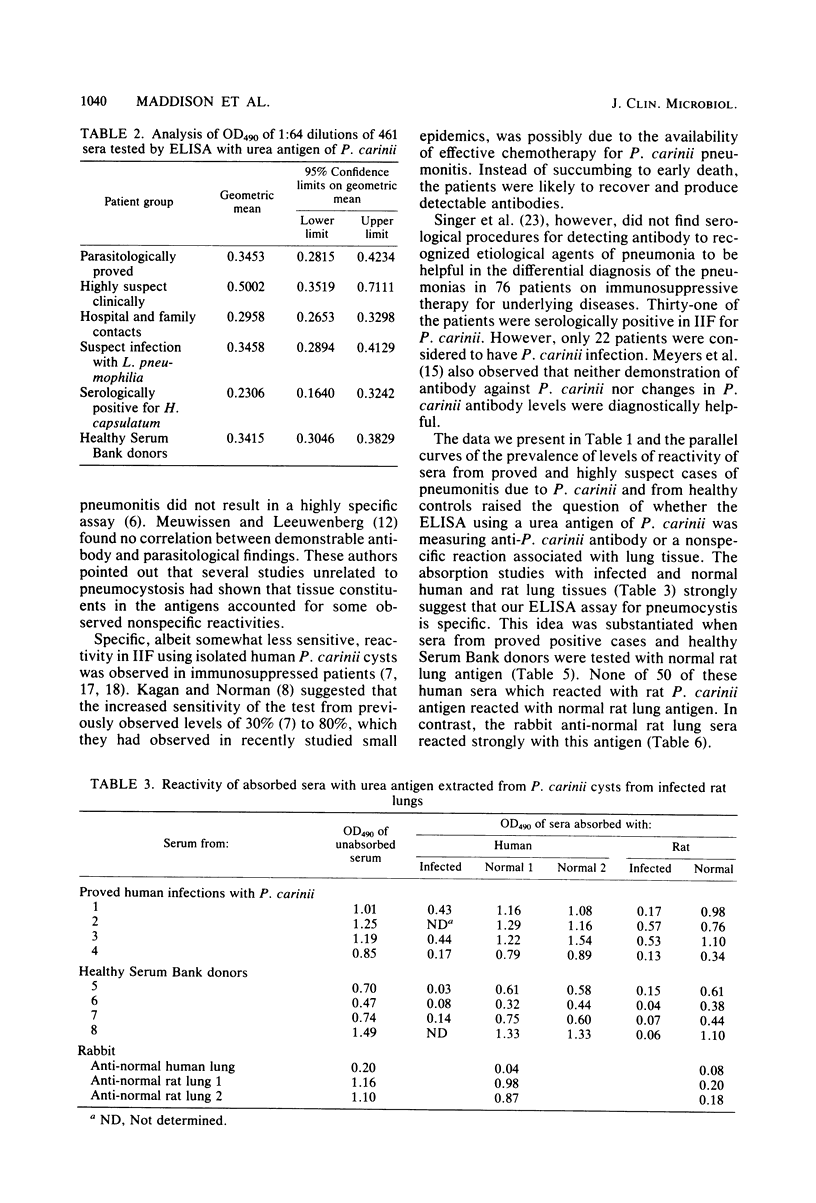
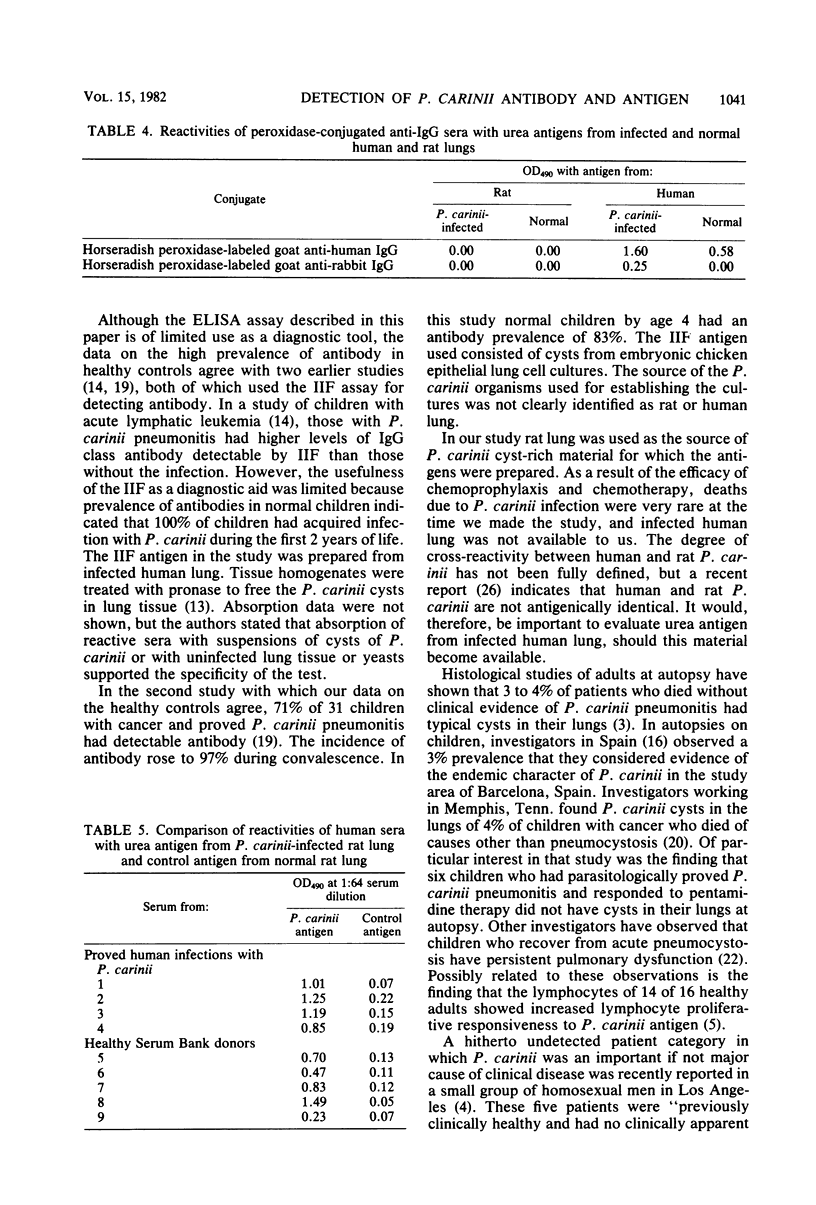
A urea-soluble extract of cyst-rich material from rat lung heavily infected with Pneumocystis carinii was evaluated in an enzyme-linked immunosorption assay for antibody in 461 human sera. The highest level of reactivity occurred in sera submitted for serodiagnosis from proved or highly suspect cases. However, the range of reactivities in these groups, many of whom were on immunosuppressive therapy, was very wide. A more restricted lower range of reactivity was observed in both hospital-family contacts and healthy Serum Bank donors. Because of the overlap in levels of reactivity between the pneumocystosis and control groups, no concise cutoff value to separate infected from noninfected individuals could be made. Specificity of the reactions was shown by absorption of patients' and control sera with uninfected and P. carinii-infected human and rat lung tissue. The data support the concept that P. carinii is highly prevalent as a latent agent in the general population and is provoked to cause clinically manifest disease in the compromised host. Detection of circulating antigen appeared to be specific and possibly a useful adjunct to diagnosis, as 10 of the 14 proved or highly suspect patients with antigenemia did not have measurable antibody to P. carinii.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benex J. A propos du diagnostic immun-logique des affections à Pneumocystis carinii. Le test d'agglutination au latex. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1973 Jan-Feb;66(1):32–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutz W., Jennings-Khodadad E., Post C., Kohout E., Nazarian I., Esmaili H. Marasmus and Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in institutionalised infants. Observations during an endemic. Z Kinderheilkd. 1974;117(4):241–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00440491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterly J. A. Pneumocystis carinii in lungs of adults at autopsy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968 May;97(5):935–937. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1968.97.5.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrod H. G., Valenski W. R., Woods D. R., Pifer L. L. The in vitro response of human lymphocytes to Pneumocystis carinii antigen. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):59–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Current status of laboratory diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1975 Sep;6(2):145–170. doi: 10.3109/10408367509151568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan I. G., Norman L. G. Serology of pneumocystosis. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1976 Oct;43:121–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan I. G., Norman L. The laboratory diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Health Lab Sci. 1977 Jul;14(3):155–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre C. R., Sulzer A. J., Norman L. G. Serial propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in cell line cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1204–1206. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1204-1206.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison S. E., Hayes G. V., Ivey M. H., Tsang V. C., Slemenda S. B., Norman L. G. Fractionation of Pneumocystis carinii antigens used in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies and in the production of antiserum for detecting Pneumocystis carinii antigenemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1029–1035. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1029-1035.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H. Infections with Pneumocystis carinii. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1976 Oct;43:133–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H., Leeuwenberg A. D. A micro-complement fixation test applied to infection with Pneumocystis carinii. Trop Geogr Med. 1972 Sep;24(3):282–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H., Leeuwenberg A. D., Heeren J., Stumpel A. New method for study of infections with Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):209–210. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H., Tauber I., Leeuwenberg A. D., Beckers P. J., Sieben M. Parasitologic and serologic observations of infection with Pneumocystis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. D., Pifer L. L., Sale G. E., Thomas E. D. The value of Pneumocystis carinii antibody and antigen detection for diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia after marrow transplantation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Dec;120(6):1283–1287. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.6.1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moragas A., Vidal M. T. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. First autopsy series in Spain. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1971 Apr;26(1):71–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman L., Kagan I. G. A preliminary report of an indirect fluorescent antibody test for detecting antibodies to cysts of Pneumocystis carinii in human sera. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Aug;58(2):170–176. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/58.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman L., Kagan I. G. Some observations on the serology of Pneumocystis carinii infections in the United States. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.317-321.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Stagno S., Woods D. Pneumocystis carinii infection: evidence for high prevalence in normal and immunosuppressed children. Pediatrics. 1978 Jan;61(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. A., Hughes W. T. Histopathology of Pneumocystis carinii infestation and infection in malignant disease in childhood. Hum Pathol. 1974 Nov;5(6):737–752. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(74)80043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind D., Faris T. D., Hill R. B., Jr Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Studies on the diagnosis and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Nov;65(5):943–956. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-65-5-943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer C., Armstrong D., Rosen P. P., Walzer P. D., Yu B. Diffuse pulmonary infiltrates in immunosuppressed patients. Prospective study of 80 cases. Am J Med. 1979 Jan;66(1):110–120. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90490-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Brasfield D. M., Tiller R. E. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in young immunocompetent infants. Pediatrics. 1980 Jul;66(1):56–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIVELL O. Ein neues stabiles Antigen für die Serodiagnose der interstitiellen plasmazellulären Pneumonie junger Säuglinge und Frühgeburten. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1955 Sep 16;80(37):1357–1357. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1116202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Comparison of rat, mouse, and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):449–449. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



