Abstract
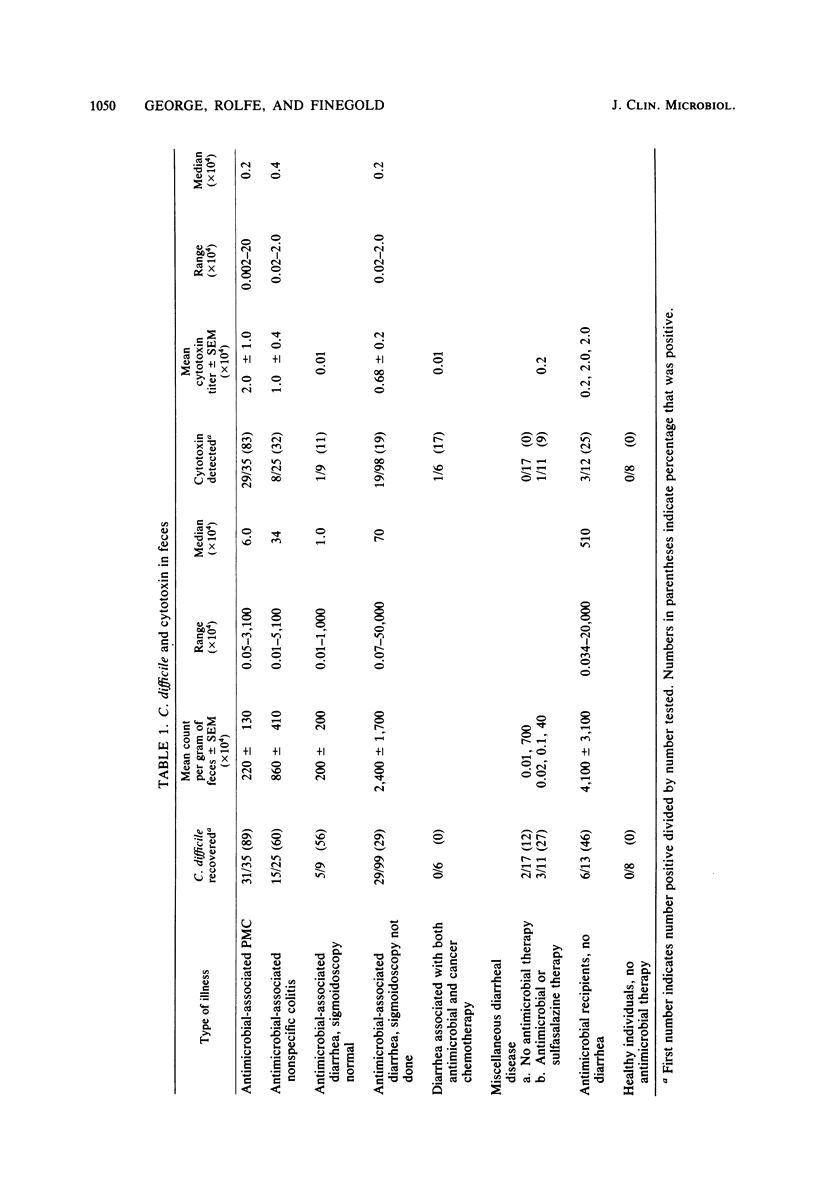
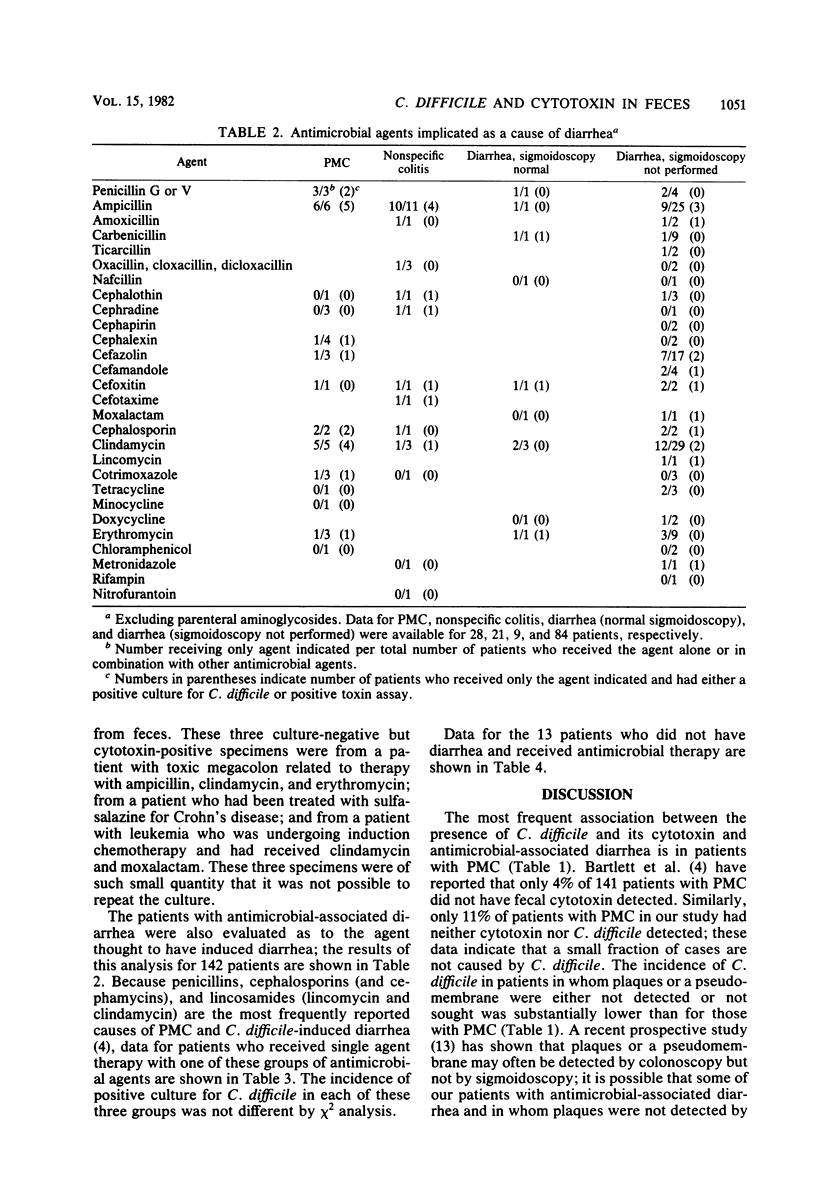
Fecal specimens from 223 subjects were evaluated for the presence of Clostridium difficile by use of a selective medium developed in our laboratory and for the presence of C. difficile cytotoxin. C. difficile and cytotoxin were detected in 89 and 83%, respectively, of patients with antimicrobial agent-associated pseudomembranous colitis (PMC). In patients in whom PMC was not documented, C. difficile and cytotoxin were present in only 37 and 21%, respectively. C. difficile and cytotoxin were also recovered from the feces of 6 and 3, respectively, of 13 antimicrobial recipients who did not have diarrhea. Although C. difficile appears to be a major cause of PMC, it is not responsible for at least some two-thirds of cases of antimicrobial agent-associated diarrhea in which PMC is not documented. Neither the recovery of C. difficile nor the detection of its cytotoxin should be considered diagnostic for C. difficile-induced disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett J. G., Chang T., Taylor N. S., Onderdonk A. B. Colitis induced by Clostridium difficile. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):370–378. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.2.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Onderdonk A. B., Cisneros R. L., Kasper D. L. Clindamycin-associated colitis due to a toxin-producing species of Clostridium in hamsters. J Infect Dis. 1977 Nov;136(5):701–705. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.5.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Taylor N. S., Chang T., Dzink J. Clinical and laboratory observations in Clostridium difficile colitis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Nov;33(11 Suppl):2521–2526. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.11.2521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Tedesco F. J., Shull S., Lowe B., Chang T. Symptomatic relapse after oral vancomycin therapy of antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Gastroenterology. 1980 Mar;78(3):431–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekety R., Silva J., Toshniwal R., Allo M., Armstrong J., Browne R., Ebright J., Rifkin G. Antibiotic-associated colitis: effects of antibiotics on Clostridium difficile and the disease in hamsters. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):386–397. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.2.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George R. H., Symonds J. M., Dimock F., Brown J. D., Arabi Y., Shinagawa N., Keighley M. R., Alexander-Williams J., Burdon D. W. Identification of Clostridium difficile as a cause of pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J. 1978 Mar 18;1(6114):695–695. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6114.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Rolfe R. D., Finegold S. M. Treatment and prevention of antimicrobial agent-induced colitis and diarrhae. Gastroenterology. 1980 Aug;79(2):366–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Sutter V. L., Citron D., Finegold S. M. Selective and differential medium for isolation of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.214-219.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Sutter V. L., Goldstein E. J., Ludwig S. L., Finegold S. M. Aetiology of antimicrobial-agent-associated colitis. Lancet. 1978 Apr 15;1(8068):802–803. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)93001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Mikawa M., Nakashio S., Takabatake M., Okado I., Yamakawa K., Serikawa T., Okumura S., Nishida S. Isolation of Clostridium difficile from the feces and the antibody in sera of young and elderly adults. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(4):345–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä K., Hjelt L., Sipponen P. Colonoscopy in the diagnosis of antibiotic-associated colitis. A prospective study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1981;16(4):465–468. doi: 10.3109/00365528109181999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R., Willey S., Bartlett J. G. Isolation rates and toxigenic potential of Clostridium difficile isolates from various patient populations. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jul;81(1):5–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


