Abstract
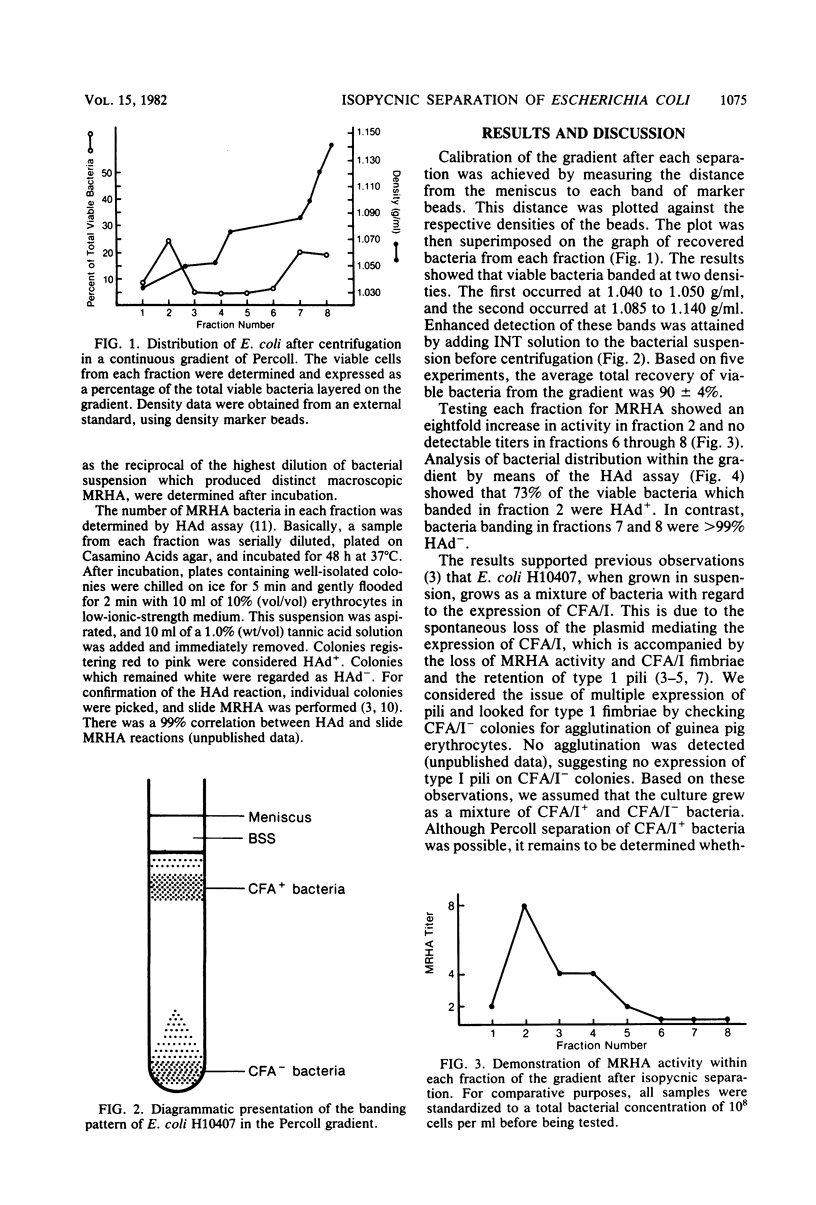
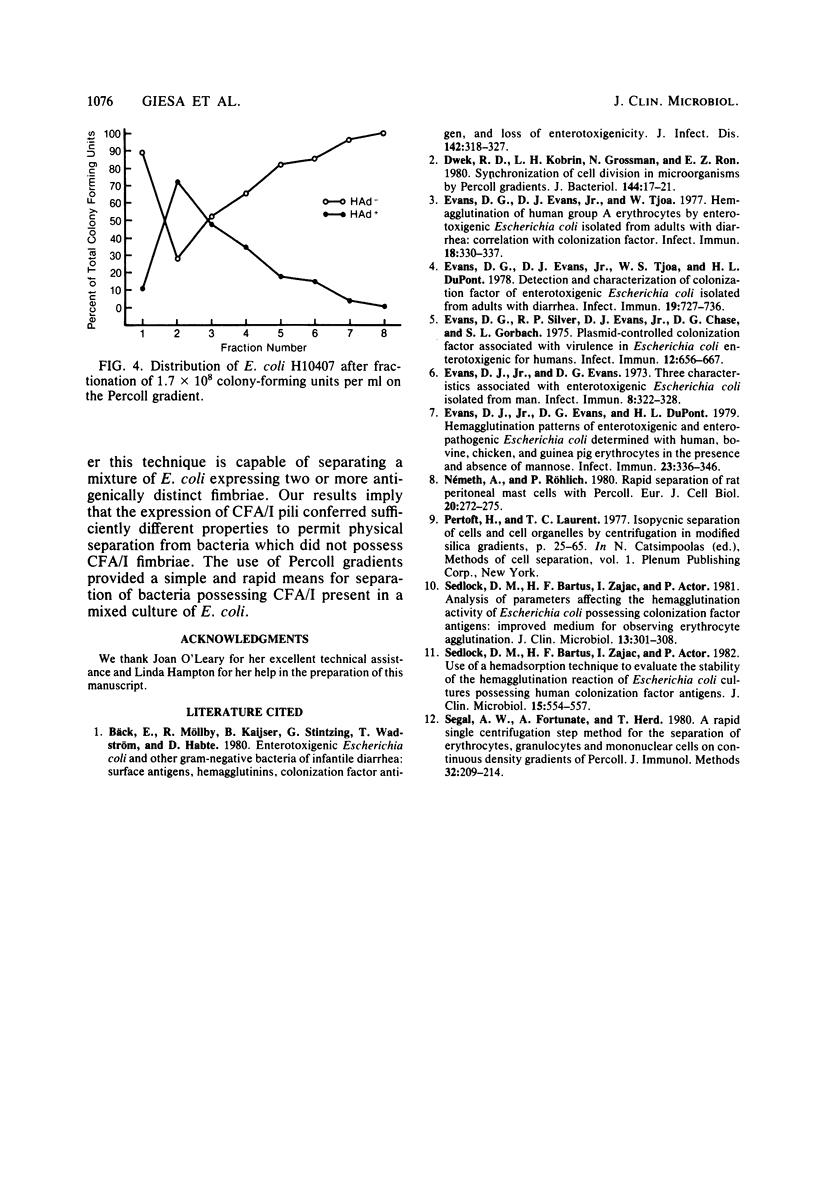
A culture of Escherichia coli possessing colonization factor antigen I was subjected to isopycnic separation on Percoll gradients. The results demonstrated successful division of the culture into two populations: (i) bacteria which cause mannose-resistant hemagglutination and (ii) bacteria which lack the ability to hemagglutinate in the presence of mannose.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bäck E., Möllby R., Kaijser B., Stintzing G., Wadström T., Habte D. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria of infantile diarrhea: surface antigens, hemagglutinins, colonization factor antigen, and loss of enterotoxigenicity. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):318–327. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwek R. D., Kobrin L. H., Grossman N., Ron E. Z. Synchronization of cell division in microorganisms by percoll gradients. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):17–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.17-21.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. S., DuPont H. L. Detection and characterization of colonization factor of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):727–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.727-736.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. Hemagglutination of human group A erythrocytes by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea: correlation with colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):330–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.330-337.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., DuPont H. L. Hemagglutination patterns of enterotoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli determined with human, bovine, chicken, and guinea pig erythrocytes in the presence and absence of mannose. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):336–346. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.336-346.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G. Three characteristics associated with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):322–328. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.322-328.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Németh A., Röhlich P. Rapid separation of rat peritoneal mast cells with Percoll. Eur J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;20(3):272–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedlock D. M., Bartus H. F., Zajac I., Actor P. Analysis of parameters affecting the hemagglutination activity of Escherichia coli possessing colonization factor antigens: improved medium for observing erythrocyte agglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):301–308. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.301-308.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedlock D. M., Bartus H. F., Zajac I., Actor P. Use of a hemadsorption technique to evaluate the stability of the hemagglutination reaction of Escherichia coli cultures possessing human colonization factor antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):554–557. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.554-557.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Fortunato A., Herd T. A rapid single centrifugation step method for the separation of erythrocytes, granulocytes and mononuclear cells on continuous density gradients of Percoll. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(3):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



