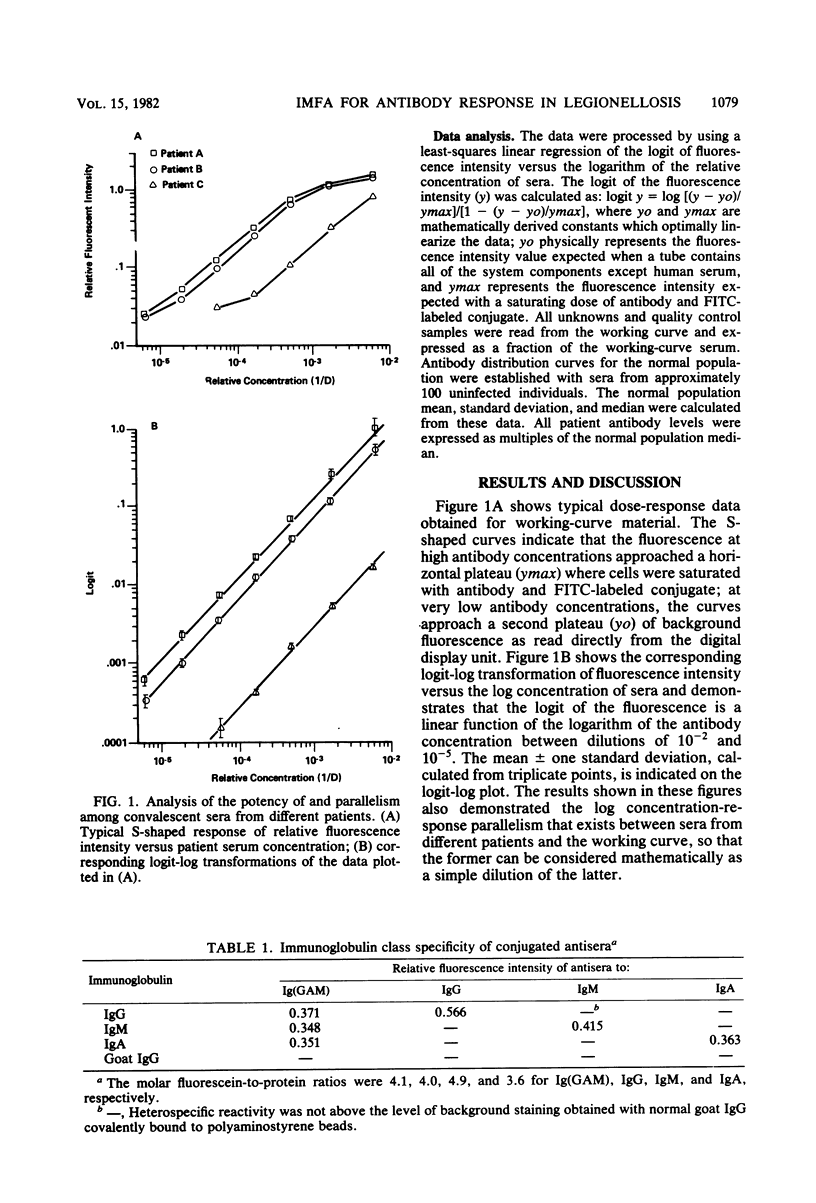
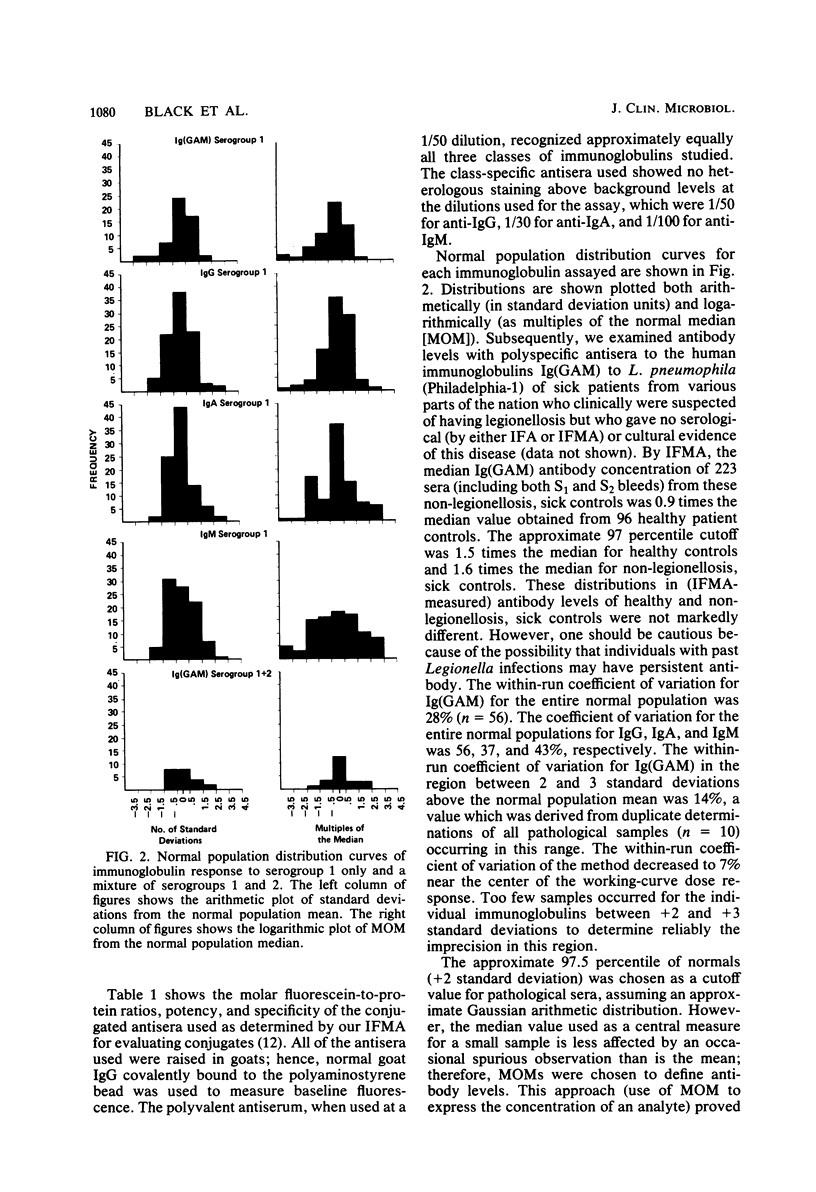
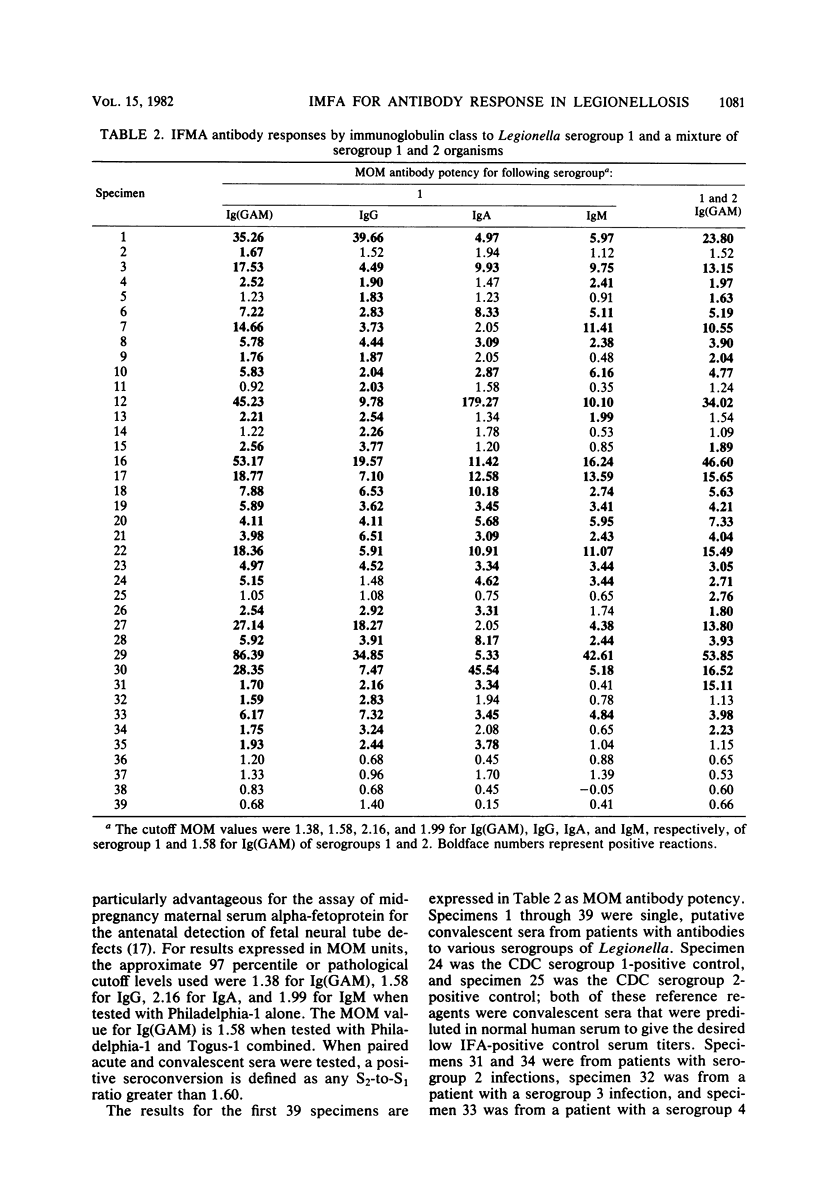
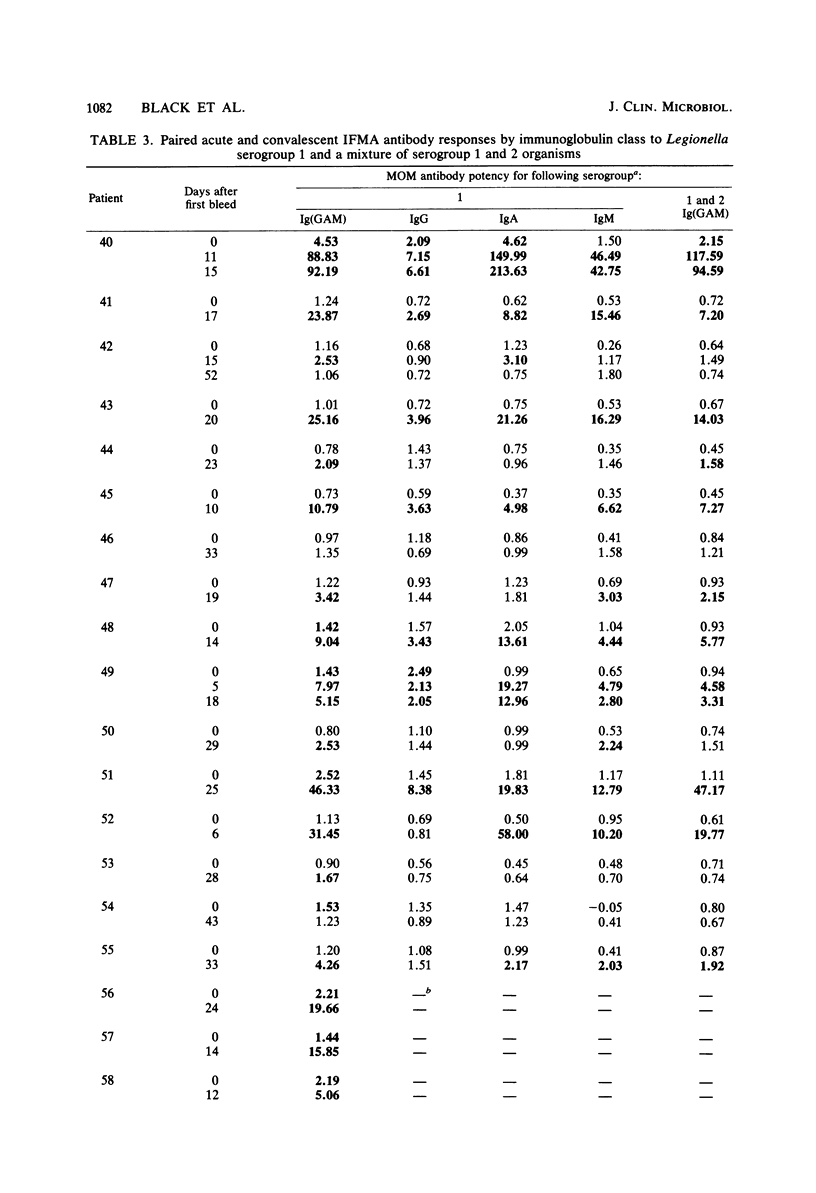
Abstract
A solid-phase immunofluorometric assay was used to qualitatively characterize and precisely measure human immunoglobulin class-specific antibody responses in legionellosis. Stable antigen preparations consisted of cells grown at 25 degrees C that were killed, fixed with Formalin vapors, washed, and lyophilized. Working-curve material consisted of dilutions of selected convalescent sera. Linear regressions of logit transformations of relative fluorescence intensities versus the logarithm of the relative concentrations of sera were determined to give immunoglobulin class-specific antibody levels from uninfected and infected individuals. Each fluorescence intensity obtained with immunoglobulin class-specific antibody was converted to a multiple of the median fluorescence intensity obtained with sera from uninfected individuals. A presumptive-positive acute-phase legionellosis serum was defined for each immunoglobulin class by a multiple of the normal median fluorescence intensity that was greater than the multiple of the normal median from approximately 97% of the uninfected population.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgett M. W., Fairfield S. J., Monthony J. F. A solid phase fluorescent immunossay for the quantitation of the C4 component of human complement. J Immunol Methods. 1977;16(3):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deelder A. M., Ploem J. S. An immunofluorescence reaction for Schistosoma manosoni using the defined antigen substrate spheres (DASS) system. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Mar;4(2):239–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England A. C., 3rd, McKinney R. M., Skaliy P., Gorman G. W. A fifth serogroup of Legionella pneumophila. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):58–59. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Weaver R. E., Mackel D. C., Smith H. W. Primary isolation media for Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.320-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Porschen R. K., Edelstein P. H., Bissett M. L., Harris P. P., Bondell S. P., Steigerwalt A. G., Weaver R. E., Ein M. E., Lindquist D. S. Legionella longbeachae species nova, another etiologic agent of human pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jun;94(6):739–743. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-6-739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Thomason B. M., Harris P. P., Thacker L., Lewallen K. R., Wilkinson H. W., Hebert G. A., Moss C. W. Recognition of a new serogroup of Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):103–107. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.103-107.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Wilkinson H. W., Sommers H. M., Fikes B. J., Sasseville K. R., Yungbluth M. M., Wolf J. S. Legionella pneumophila serogroup six: isolation from cases of legionellosis, identification by immunofluorescence staining, and immunological response to infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.395-401.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. J., Kendal A. P., Webster R. G., Feorino P. M., Reimer C. B. Detection of monoclonal influenza antibodies synthesized in culture by hybridoma cells with a solid-phase indirect immunofluorometric assay. J Virol Methods. 1980;1(5):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(80)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. J., Reimer C. B., Wells T. W., Black C. M. Quantitative characterization of specificity and potency of conjugated antibody with solid-phase, antigen bead standards. J Immunol Methods. 1980;34(4):315–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soini E., Hemmilä I. Fluoroimmunoassay: present status and key problems. Clin Chem. 1979 Mar;25(3):353–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundeen J. T., Krakauer R. S. A quantitative assay for low levels of IgM by solid-phase immunofluorescence. J Immunol Methods. 1979;26(3):229–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90248-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald N. J., Cuckle H., Brock J. H., Peto R., Polani P. E., Woodford F. P. Maternal serum-alpha-fetoprotein measurement in antenatal screening for anencephaly and spina bifida in early pregnancy. Report of U.K. collaborative study on alpha-fetoprotein in relation to neural-tube defects. Lancet. 1977 Jun 25;1(8026):1323–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


