Abstract
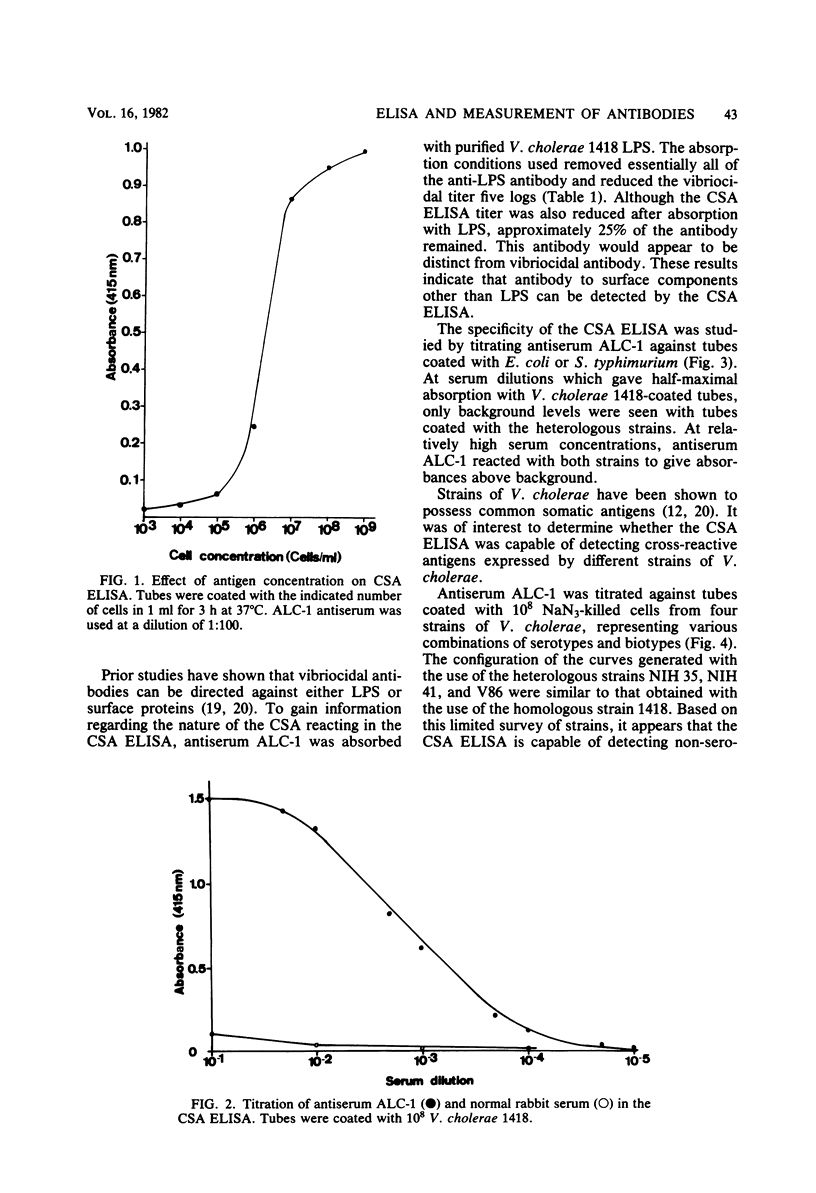
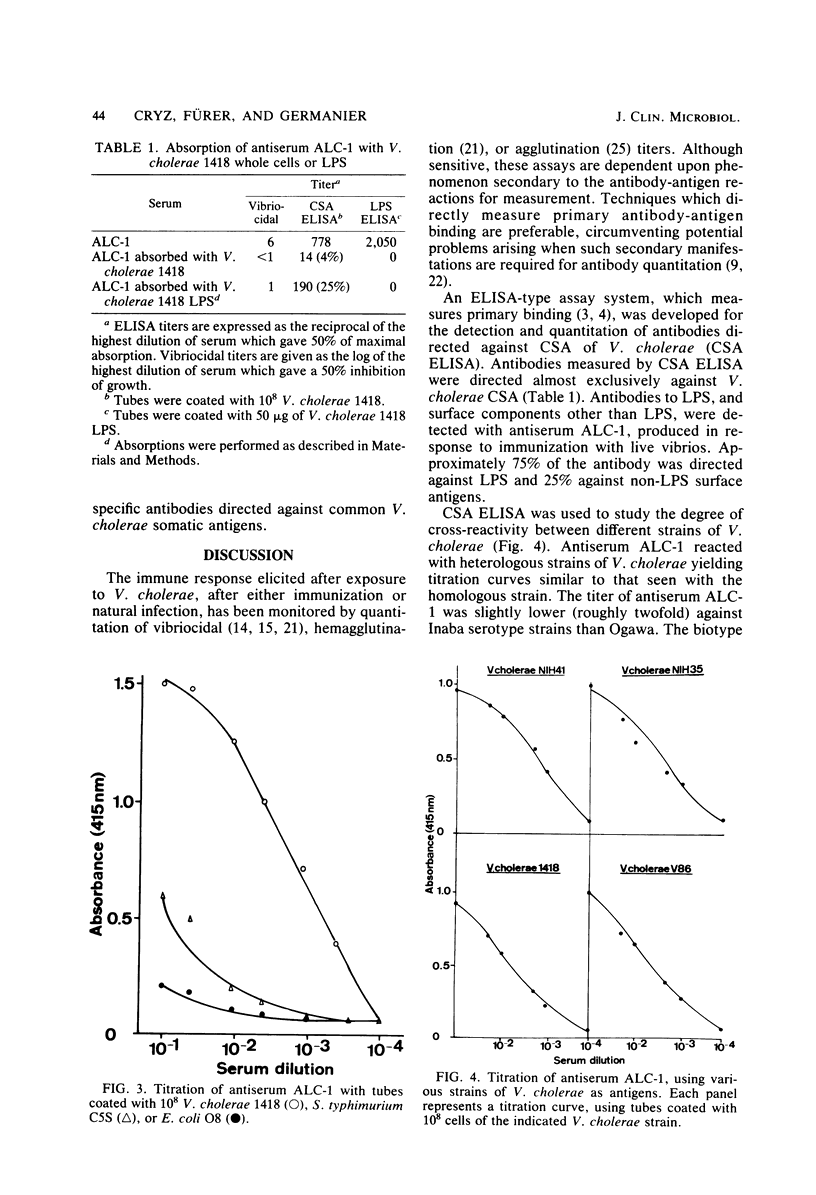
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the measurement of antibodies directed against cell surface antigens of Vibrio cholerae (CSA ELISA) was developed. NaN3-killed whole cells of V. cholerae, adsorbed to polystyrene tubes, were used as immobilized antigens. The assay was capable of detecting antibodies directed against lipopolysaccharide and non-lipopolysaccharide surface antigens. In addition, the CSA ELISA was capable of detecting non-vibriocidal antibody. An antiserum raised in rabbits by immunization with live V. cholerae 1418 (Ogawa, El Tor) was capable of reacting with various heterologous strains of V. cholerae used as immobilized antigens. Therefore, common antigens shared by V. cholerae strains could be detected by using the CSA ELISA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baselski V. S., Medina R. A., Parker C. D. Survival and multiplication of Vibrio cholerae in the upper bowel of infant mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):435–440. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.435-440.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash R. A., Music S. I., Libonati J. P., Craig J. P., Pierce N. F., Hornick R. B. Response of man to infection with Vibrio cholerae. II. Protection from illness afforded by previous disease and vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):325–333. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: observations with purified antigens and the ligated ileal loop model. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):464–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.464-467.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LoSpalluto J. J. Crystalline cholera toxin and toxoid. Science. 1972 Feb 4;175(4021):529–530. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4021.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for cholera serology. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):759–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.759-763.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S. Composition and immunochemical properties of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):382–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.382-389.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J. T., Parker C. D. Identification and preliminary characterization of Vibrio cholerae outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1018–1024. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1018-1024.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nalin D. R., Craig J. P., Hoover D., Bergquist E. J., Waterman D., Holley H. P., Hornick R. B., Pierce N. P., Libonati J. P. Immunity of cholera in man: relative role of antibacterial versus antitoxic immunity. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(1):3–9. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. M., Rahman A. S., Chowdhury A. K., Mosley W. H., Phillips R. A. Report of the 1966-67 cholera vaccine field trial in rural East Pakistan. 3. The lack of effect of prior vaccination or circulating vibriocidal antibody on the severity of clinical cholera. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;40(2):199–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley W. H., Aziz K. M., Rahman A. S., Chowdhury A. K., Ahmed A. Field trials of monovalent Ogawa and Inaba cholera vaccines in rural Bangladesh--three years of observation. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;49(4):381–387. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. T., Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Vibrio cholerae adherence and colonization in experimental cholera: electron microscopic studies. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):527–547. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.527-547.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoh S. H., Rowley D. Protection of infant mice against cholera by antibodies to three antigens of Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):41–47. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoh S. H., Rowley D. Quantitative assay of a protein antigen of vibrio cholerae involved in the vibriocidal action of antibody and complement. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1971 Dec;49(6):605–612. doi: 10.1038/icb.1971.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoh S. H., Rowley D. The antigens of Vibrio cholerae involved in the vibriocidal action of antibody and complement. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):505–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Barua D., Saxena R., Carpenter C. C. Vibriocidal and agglutinating antibody patterns in cholera patients. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):630–640. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Verwey W. F. Protective antigens from El Tor vibrios. 1. The preparation and properties of a purified protective antigen from an El Tor vibrio (Ogawa subtype). Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32(6):809–821. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



