Abstract
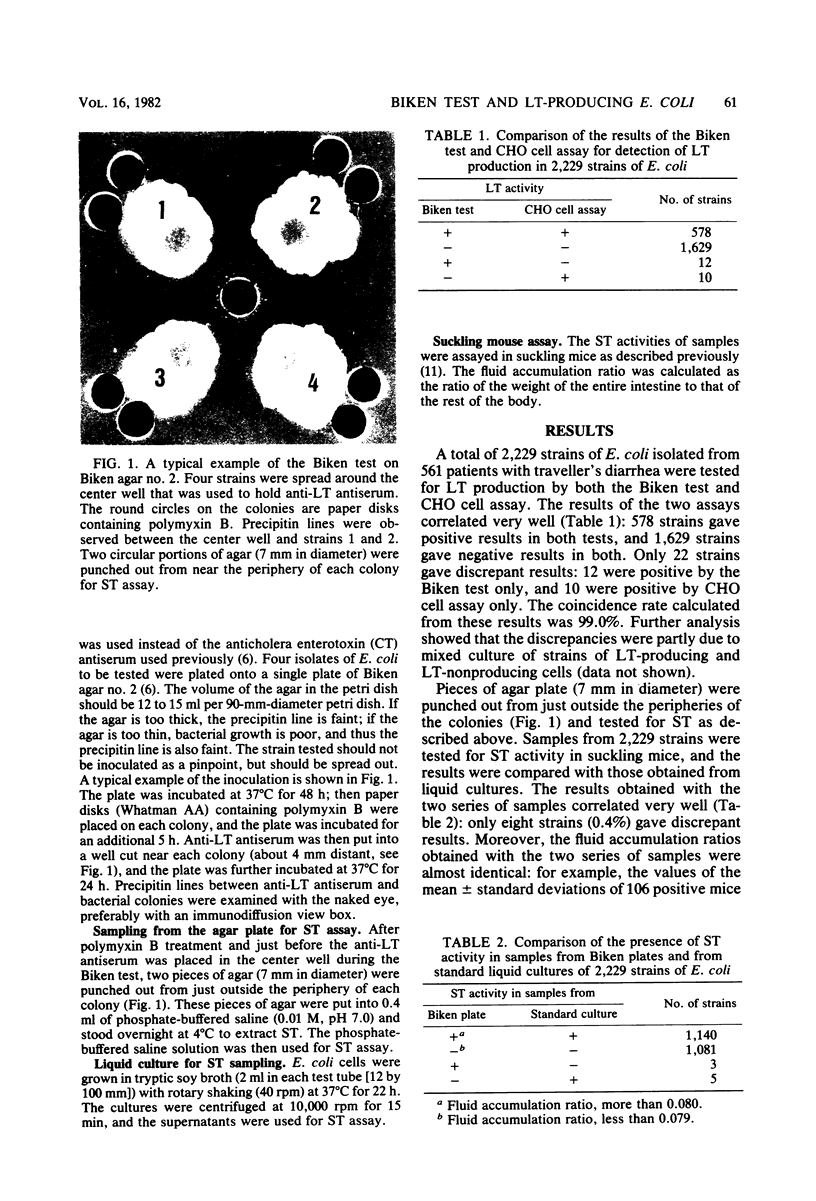
A total of 2,229 strains of Escherichia coli isolated from subjects with traveller's diarrhea were tested for heat-labile enterotoxin production by the Biken test (Honda et al., J. Clin. Microbiol. 13:1--5, 1981). Results of the Biken test showed a 99.0% coincidence with those obtained by Chinese hamster ovary cell assay. The use of antiserum against E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin gave sharper and clearer results than did the use of antiserum against cholera enterotoxin. Samples for heat-stable enterotoxin assay were obtained from the agar plates used for the Biken test, and the heat-stable enterotoxin activities of these samples were compared with those of samples obtained from standard liquid cultures. Results for samples of 2,229 strains from the Biken agar plates and from liquid cultures were almost identical.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D. The recognition of toxicogenic bacterial strains in vitro. Br Med J. 1948 Mar 13;1(4549):493–496. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4549.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Akhtar Q., Glass R. I., Kibriya A. K. A simple assay to detect Escherichia coli producing heat labile enterotoxin: results of a field study of the Biken tests in Bangladesh. Lancet. 1981 Sep 19;2(8247):609–610. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92745-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Shimizu M., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Isolation of a factor causing morphological changes of chinese hamster ovary cells from the culture filtrate of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1028–1033. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1028-1033.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Isolation of special antibodies which react only with homologous enterotoxins from Vibrio cholerae and Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):333–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.333-336.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Tsuji T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Immunological nonidentity of heat-labile enterotoxins from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):337–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.337-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Honda T., Taga S., Miwatani T. In vitro formation of hybrid toxins between subunits of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and those of cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):341–346. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.341-346.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]