Abstract
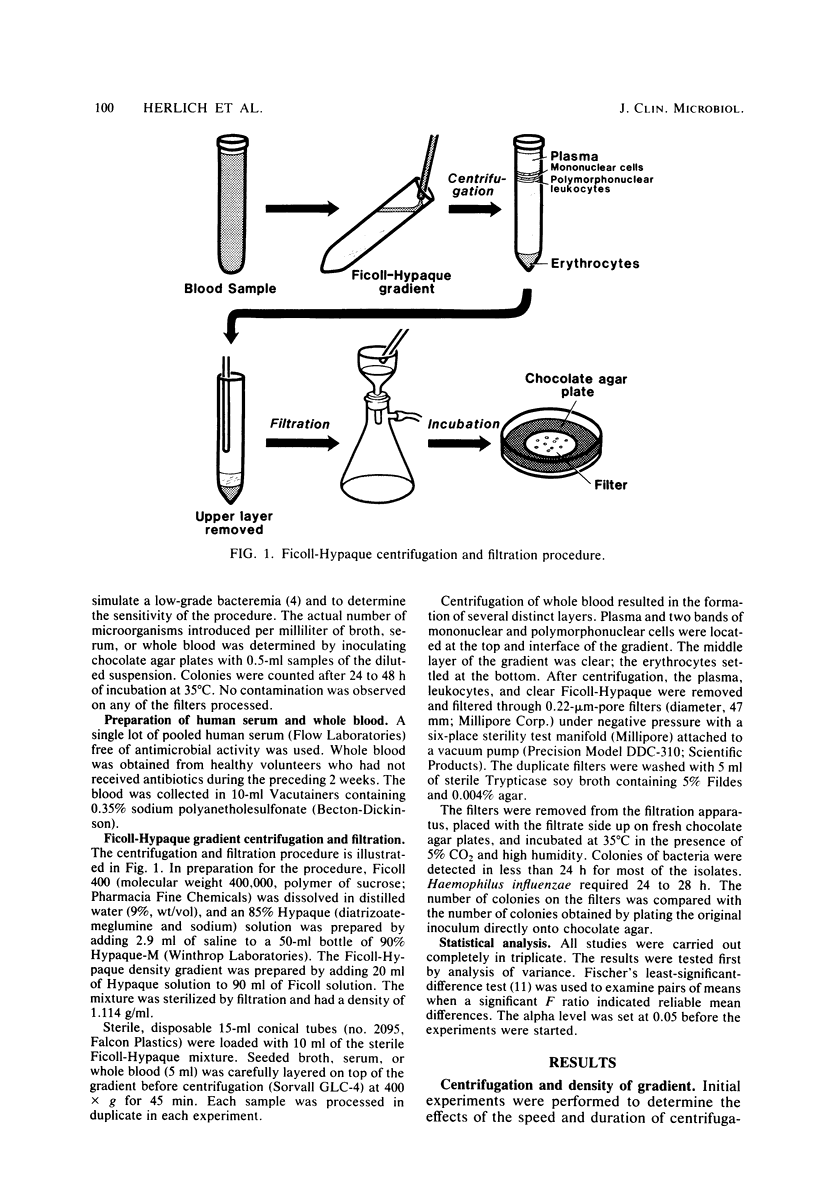
A centrifugation-filtration procedure was developed to expedite the recovery of microorganisms from blood. Fresh whole human blood was inoculated with various aerobic and facultatively anaerobic microorganisms (3 to 18 per ml). The seeded blood was carefully overlaid on a Ficoll-Hypaque gradient (density, 1.114 g/ml) and centrifuged (400 x g) for 45 min at ambient temperature. The entire gradient (plasma, leukocytes, and Ficoll-Hypaque) was removed and filtered through a 0.22-micrometer membrane filter. The filters were then placed on chocolate agar and incubated at 35 degrees C in humidified air containing 5% CO2. No statistically significant differences were detected between the numbers of microorganisms recovered by filtration and by direct culture of the original inoculum. Most microorganisms were detected within 18 h after filtration. This system has excellent sensitivity and negligible toxicity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babu J. P., Schell R. F., Le Frock J. L. Evaluation of twenty-three blood culture media. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):288–292. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.288-292.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn G. L., Smith K. New centrifugation blood culture device. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):52–54. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.52-54.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Komorowski R. A. Evaluation of the Sterifil lysis-filtration blood culture system. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):500–504. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.500-504.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., White M. L., Ziment I., Winn W. R. Rapid diagnosis of bacteremia. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Sep;18(3):458–463. doi: 10.1128/am.18.3.458-463.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan R. L., Schuette W. H., Zierdt C. H., MacLowry J. D. Rapid automated disgnosis of bacteremia by impedance detection. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):51–57. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.51-57.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller F., Feldmann K., Abshagen U., Hennemann H., Barz R. Diagnostic haemoperfusion for rapid detection of bacteremia. First clinical results of a comparison with the conventional blood culture technique. Klin Wochenschr. 1981 May 4;59(9):425–429. doi: 10.1007/BF01695896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner R. A quantitative evaluation of three blood culture systems. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Feb;57(2):220–227. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/57.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell R. F., Le Frock J. L., Babu J. P., Robinson D. B. Recovery of Haemophilus influenzae from twenty-three blood culture media. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):84–87. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.84-87.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanaszek P. M. Rapid bacteremia diagnosis using field monitor membrane filtration. Am J Med Technol. 1971 Mar;37(3):97–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan N. M., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Practical aerobic membrane filtration blood culture technique: clinical blood culture trial. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):37–43. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.37-43.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan N. M., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Practical aerobic membrane filtration blood culture technique: development of procedure. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):30–36. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.30-36.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd Evaluation of two commercially available media for detection of bacteremia. Appl Microbiol. 1972 May;23(5):956–959. doi: 10.1128/am.23.5.956-959.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. R., White M. L., Carter W. T., Miller A. B., Finegold S. M. Rapid diagnosis of bacteremia with quantitative differential-membrane filtration culture. JAMA. 1966 Aug 15;197(7):539–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



