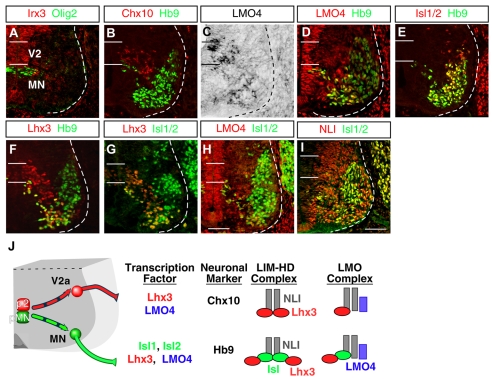
Fig. 1.
Combinatorial expression of transcription factors in ventral spinal neurons. (A-I) Expression of Irx3, Olig2, Chx10, Hb9, Lmo4, Isl1/2, Lhx3 and NLI in E11.5 mouse cervical spinal cord. MNs and V2a INs each express unique combinations of these factors. Expression of Lmo4 is assessed by both in situ hybridization (C) and immunohistochemistry (D,H). The locations of ventricular progenitor cells for MNs (pMN) and V2a INs (p2) are marked by two horizontal lines. Dashed lines indicate the boundary of the spinal cord. (J) The schematic diagram shows that the pMN domain generates motoneurons (MN, green), whereas p2 cells give rise to V2a INs (red). A summary of the combinatorial expression profile of transcription factors is shown along with neuronal-subtype markers and predicted higher-order regulatory complexes based on known protein-protein interactions. Scale bars: in I, 50 μm for A-C,E,I; in H, 40 μm for D,F-H.