Abstract
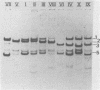
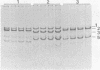
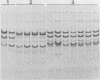
Thirty to fifty percent of group B and group C Neisseria meningitidis carrier isolates are not serotypable with existing outer membrane protein typing sera. A typing system based on differences in the outer membrane protein profiles after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) was therefore developed as an adjunct to existing serotyping methods. Although most N. meningitidis strains contain several outer membrane proteins visible by SDS-PAGE, there are only one to three predominant proteins. The SDS-PAGE profiles of these major proteins were used to establish 10 different PAGE types. Greater than 95% of all meningococcal isolates, regardless of serogroup, fit into 1 of the 10 PAGE types. The outer membrane protein profile of individual strains after SDS-PAGE was constant when outer membrane fractions were prepared from the same strain on several different days. A comparison of gel profiles of meningococcal isolates obtained from different sites of the same patient revealed no significant differences among both major and minor proteins for isolate sets thus far examined. Characterization of strains by PAGE type can be a valuable epidemiological tool in addition to serotyping and in the absence of specific serotype antisera.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):668–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Frasch C. E., Mocca L. F., Rose F. B., Gonzalez R. Rapid serogroup identification of Neisseria meningitidis by using antiserum agar: Prevalence of serotypes in a disease-free military population. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):302–307. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.302-307.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Frasch C. E., Robbins J. B., Feldman H. A. Serogroup identification of Neisseria meningitidis: comparison of an antiserum agar method with bacterial slide agglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 May;7(5):410–414. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.5.410-414.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Peppler M. S., Frasch C. E., Mocca L. F., McGrath P. P., Washington G. Adherence of isolates of Neisseria meningitidis from patients and carriers to human buccal epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):556–568. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson D., Olcén P. Rapid serotyping of groups A, B, and C meningococci by rocket-line immunoelectrophoresis and co-agglutination. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Feb;32(2):136–142. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Chapman S. S. Classification of Neisseria meningitidis group B into distinct serotypes. I. Serological typing by a microbactericidal method. Infect Immun. 1972 Jan;5(1):98–102. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.1.98-102.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Chapman S. S. Classification of Neisseria meningitidis group B into distinct serotypes. II. Extraction of type-specific antigens for serotyping by precipitin techniques. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):127–133. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.127-133.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Gotschlich E. C. An outer membrane protein of Neisseria meningitidis group B responsible for serotype specificity. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):87–104. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., McNelis R. M., Gotschlich E. C. Strain-specific variation in the protein and lipopolysaccharide composition of the group B meningococcal outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):973–981. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.973-981.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Mocca L. F. Strains of Neisseria meningitidis isolated from patients and their close contacts. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):155–159. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.155-159.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Zollinger W. D. Lipopolysaccharide serotyping of Neisseria meningitidis by hemagglutination inhibition. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):471–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.471-475.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. I., Frasch C. E., Shapera R. M. Meningococcal colonization and infection in children and their household contacts. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 May;109(5):563–571. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman J. T., Hopman C. T., Zanen H. C. Immunochemical characterization of Neisseria meningitidis serotype antigens by immunodiffusion and SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis immunoperoxidase techniques and the distribution of serotypes among cases and carriers. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):465–473. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman J. T., de Marie S., Zanen H. C. Variability of low-molecular-weight, heat-modifiable outer membrane proteins of Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):642–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.642-648.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose H. D., Lenz I. E., Sheth N. K. Meningococcal pneumonia. A source of nosocomial infection. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Apr;141(5):575–577. doi: 10.1001/archinte.141.5.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel J. E., Quan A. Homogeneity of protein serotype antigens in Neisseria meningitidis group A. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):623–627. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.623-627.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E., Mocca L. F. Five structural classes of major outer membrane proteins in Neisseria meningitidis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):69–78. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.69-78.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E. Outer-membrane protein and lipopolysaccharide serotyping of Neisseria meningitidis by inhibition of a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):424–433. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.424-433.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]