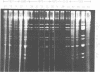
Abstract
We succeeded in isolating human rotaviruses from the feces of gastroenteritis patients by using roller cultures of primary cynomolgus monkey kidney cells with trypsin in the maintenance medium but without concentration and trypsin treatment of the inocula at each passage level. These cells were found to be more sensitive than MA-104 cells (derived from fetal rhesus monkey kidney) for the propagation of human rotaviruses. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the genome RNA revealed that there were small differences in the migration pattern of the segments among all the strains isolated from 1976 to 1981. The cultivation of human rotaviruses in primary cell cultures might aid in developing a liver rotavirus vaccine.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrey M. B., Murphy A. M. Letter: Rotavirus growth in bovine monolayers. Lancet. 1976 Apr 3;1(7962):753–753. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)93136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banatvala J. E., Totterdell B., Chrystie I. L., Woode G. N. In-vitro detection of human rotaviruses. Lancet. 1975 Oct 25;2(7939):821–821. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)80057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Davidson G. P., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Virus particles in epithelial cells of duodenal mucosa from children with acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1281–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92867-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza J., Gorziglia M., Gil F., Römer H. Multiplication of human rotavirus in cultured cells: an electron microscopic study. J Gen Virol. 1980 Apr;47(2):461–472. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-47-2-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Matsuno S., Kono R. Difference in antibody reactivity between complement fixation and immune adherence hemagglutination tests with virus antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):241–246. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.241-246.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Inouye S., Kono R. Plaque assay of neonatal calf diarrhea virus and the neutralizing antibody in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.1-4.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Nagayoshi S. Quantitative estimation of infantile gastroenteritis virus antigens in stools by immune adherence hemagglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Mar;7(3):310–311. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.3.310-311.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishima T., Nagayoshi S., Ozaki T., Isomura S., Suzuki S. Letter: Immunofluorescence of human reovirus-like agent of infantile diarrhoea. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):695–696. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92517-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdham D. R., Purdham P. A., Evans N., McNeish A. S. Letter: Isolation of human rotavirus using human embryonic gut monolayers. Lancet. 1975 Nov 15;2(7942):977–977. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90386-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Holmes I. H. Comparison of the genomes of simian, bovine, and human rotaviruses by gel electrophoresis and detection of genomic variation among bovine isolates. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):839–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.839-846.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanekata T., Yoshida Y., Oda K. Detection of rotavirus from faeces by reversed passive haemagglutination method. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Sep;32(9):963–963. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.9.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inaba Y., Shinozaki T., Fujii R., Matumoto M. Isolation of human rotavirus in cell cultures: brief report. Arch Virol. 1981;69(2):155–160. doi: 10.1007/BF01315159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soenarto Y., Sebodo T., Ridho R., Alrasjid H., Rohde J. E., Bugg H. C., Barnes G. L., Bishop R. F. Acute diarrhea and rotavirus infection in newborn babies and children in Yogyakarta, Indonesia, from June 1978 to June 1979. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):123–129. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.123-129.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuker G., Oshiro L. S., Schmidt N. J. Antigenic comparisons of two new rotaviruses from rhesus monkeys. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):202–203. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.202-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa T., Urasawa S., Taniguchi K. Sequential passages of human rotavirus in MA-104 cells. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(10):1025–1035. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Gill V. W., Sereno M. M., Kalica A. R., VanKirk D. H., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Letter: Probable in-vitro cultivation of human reovirus-like agent of infantile diarroea. Lancet. 1976 Jan 10;1(7950):98–99. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James W. D., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Human rotavirus type 2: cultivation in vitro. Science. 1980 Jan 11;207(4427):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.6243190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]