Abstract
The identification of markers for virulent group B streptococci (GBS) could guide prenatal prevention and intervention strategies. We compared the distribution of serotypes and potential pathogenicity islands (PPIs) between invasive and colonizing GBS. Colonizing and invasive strains from The Netherlands and Taiwan were serotyped. We used polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for the amplification of several new PPI markers. Several combinations of PPI-specific markers and serotypes were associated with invasiveness. For Dutch neonatal strains, a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve with serotype and five PPI markers showed an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.963 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.935–0.99). For Taiwanese neonatal strains, serotype and four different PPI markers resulted in an ROC curve with an AUC of 0.894 (95% CI 0.826–0.963). PPI-specific and serological markers can distinguish local neonatal invasive GBS strains from colonizing ones. Apparently, there are clear regional differences in the GBS epidemiology and infection potential of clones.
Introduction
Group B streptococcus (GBS) is an important pathogen with the potential to cause disease in adults with underlying chronic medical conditions, pregnant women, but, above all, in newborns. Early onset neonatal disease (EOD) is acquired by vertical GBS transmission during birth and is characterized by pneumonia and septicemia in the first week of life. Late onset disease (LOD) occurs in infants up to seven months of age and usually involves meningitis. GBS colonization rates up to 35% in healthy pregnant women have been reported, but only 0.5–1% of neonates born from these mothers will finally develop GBS disease [1, 2]. The identification of highly virulent GBS could contribute to our understanding of the pathogenesis of GBS disease and target prevention and intervention strategies.
GBS virulence factors, including the polysaccharide capsule and several gene regulation mechanisms, have been identified, and may all contribute to the complex pathogenesis of GBS disease [3, 4]. Based on the nature of the immunogenic polysaccharide capsule, GBS can be grouped into nine serotypes: Ia, Ib, and II–VIII. Serotype III is recovered significantly more often from cases of meningitis and LOD. At the same time, it is the most prevalent serotype in asymptomatic carriers [5–7]. Previous epidemiological studies have identified virulent clonal types of serotype III by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis (MLEE), restriction digestion pattern (RDP) typing, and multilocus sequence typing (MLST) [8–13]. In vitro studies have demonstrated that these clones have a different level of enzyme activity known to play a role in virulence [14, 15]. The clones also contain genetic material next to known or putative virulence genes that is not present in less virulent serotype III GBS [16]. So, virulence might well be associated with specific GBS subtypes, but based on current microbiological knowledge, unequivocal markers of invasiveness have not been identified [17, 18]. Most known and putative GBS virulence genes are clustered into 14 genetic islands and are considered to be potential GBS-specific potential pathogenicity islands (PPIs) [19, 20]. We studied the epidemiological prevalence of PPI-specific molecular markers and serotypes in invasive neonatal versus colonizing strains. We analyzed well-characterized GBS strains from The Netherlands (Europe) and from a geographically and racially distinct population (Taiwan, Asia).
Materials and methods
Bacterial strains
A total of 136 isolates of GBS from The Netherlands and 202 isolates from Taiwan was included. From The Netherlands, 92 strains were isolated from ante-partum recto-vaginal cultures performed between 1995 and 2004 by the Laboratory of Microbiology at the Medical Center Haaglanden, The Hague, The Netherlands. Forty-four invasive strains were supplied by the Netherlands Reference Laboratory for Bacterial Meningitis at the Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Strains from the same geographical region and episode (1999–2004) as those of the colonizing strains were selected: eight were isolated from blood, 14 from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and 22 from both blood and CSF. In Taiwan, 58 strains were isolated from ante-partum recto-vaginal cultures and 43 invasive neonatal strains were collected between 2000 and 2005: 24 from blood and 19 from blood and CSF. In Taiwan, 101 invasive strains were collected from infections in adults: 50 were isolated from blood only and 51 from blood and another focus (bone, joint, CSF, urine, etc.).
Species confirmation and serotyping
Species confirmation of GBS was performed by Latex agglutination according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Streptex®, Remel Inc., USA). Briefly, five colonies from a 24-h culture at 37°C on 5% sheep blood agar (SBA) were suspended in 400 μl of extraction reagent. After 10 min of incubation at 37°C, 40 μl of the extract was added to a drop of group-specific latex suspension (A, B, C, D, F, and G). Agglutination was read after 1 min. GBS serotyping was performed using the Strep-B-Latex kit (Statens Serum Institut, Denmark). Strains were cultured for 24 h in Todd Hewitt broth. Ten microliters from this culture was mixed with serotypes Ia, Ib, and II–VIII specific latex bead suspension. Agglutination was read after 5 to 10 s.
Polymerase chain reaction
DNA was prepared with the MagNA Pure system (Roche, Lelystad, The Netherlands) using the MagNA Pure LC DNA isolation kit III. For polymerase chain reaction (PCR), primer pairs directed to regions corresponding to 26 genes from 14 putative PPIs were used (Table 1) [20]. Reaction vials were filled with a final volume of 50 μl containing 5 μl 2 mM deoxynucleotide triphosphate bases, 1.0 μl primer pairs, 0.08 μl Taq polymerase (Sigma, Germany), 50 ng/5 μl DNA, and 38.4 μl of distilled water. PCR assays were performed in an ABI thermal cycler (Applied Biosystems, Gouda, The Netherlands) under the following conditions: 25 identical cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 1 min, hybridization at 52°C for 1 min, and extension at 72°C for 1 min. Fifteen microliters of the PCR products was subjected to electrophoresis for 50 min at 100 mA on a 1% agarose gel (Hispanagar, Sphaero Q, Leiden, The Netherlands) in 1× Tris-borate-EDTA (TBE) buffer (89 mM Tris, 89 mM boric acid, 2 mM EDTA). Gels were stained with ethidium bromide and photographed during UV illumination. PCR amplicon sizes were estimated by comparison to a 100 bp DNA ladder (Sigma, Germany).
Table 1.
Gene assignment of putative pathogenicity islands (PPIs) and their characteristics [20]
| Strain NEM 316a | Strain 2603VRb | Putative island | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| gbs0217 gbs0227 |
sag0224 sag0234 |
I | Phage integrase family site-specific recombinase Cro/CI transcriptional regulator Other mobilization genes A homolog of a virulence regulator in S. pyogenes |
| gbs0367 | – | pNEM316-I (island III, VII, and VIII) | Near identical copies of a chromosomally integrated plasmid, designated pNEM316-1 |
| gbs0388 | – | ||
| gbs0628 gbs0660 |
sag0645 sag0685 |
VI | The cyl locus, encoding a virulence factor Transposon genes (Tn5252) A permease gene in NEM316 Protease, endopeptidase and permease genes in 2603VR Core metabolic enzymes |
| gbs1073 | sag1038 | IX | A homolog to a two-component regulatory system |
| gbs1120 gbs1125 gbs1135 |
− − − |
X | A transferase A relaxase Homologs with those in Tn5252 3 LPXTG genes A DNA methyltransferase. |
| gbs1306 gbs1313 |
sag1233 sag1246 |
XII | The lmb gene, encoding laminin binding protein The scpB, encoding C5a peptidase Transposon genes (ISSdyI, Tn5252). Phage and plasmid replication genes in NEM316 The lac operon in Nem316 Heavy metal transporter genes in 2603VR |
| gbs1987 | sag2029 | XIII | Genes with unknown functions in NEM316/2603VR Genes encoding CAMP factor Two proteases Core metabolic enzymes Two transporters A two component regulator |
| − | sag0915 | Tn916 | Mobile element in 2603VR |
aSerotype III
bSerotype V
For the selection of PPI-specific invasion markers, all 26 PCRs were initially performed on five colonizing and five invasive strains, randomly selected from the Dutch collection. If a PCR assay generated a similar result in the two groups of five strains (uniformly positive or negative), we concluded that the contribution of this PCR to discrimination between invasive and non-invasive strains would probably be small; these PCRs were excluded from further evaluation. After this preliminary screening, 14 PCRs were selected and performed for the entire collection, establishing the presence or absence of genetic markers corresponding to the genes of nine PPIs and one transposon for each strain (Table 3).
Table 3.
Prevalence of genetic markers
| PPI | Gene/marker | D N Ia % (n = 44) | D Cb % (n = 92) | T N Ic % (n = 43) | T A Id % (n = 101) | T Ce % (n = 58) | P-valuef D N I vs. D C | P-valuef T N I vs. T C | P-valuef T A I | P-valuef D C vs. T C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | gbs0217/sag0224 | 38,6 | 41.3 | 32.6 | 33 | 27.6 | 0.767 | 0.589 | 0.504 | 0.088 |
| gbs 0227/sag0234 | 43.2 | 72.8 | 32.6 | 82 | 75.9 | 0.001g | <0.001h | 0.339 | 0.680 | |
| III, VII, VIII (pNEM316) | gbs0367 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 0 | 2 | 6.9 | 1.000 | 0.134 | 0.192 | nd |
| gbs0388 | 0 | 3.3 | 4.7 | 1 | 1.7 | 0.551 | 0.573 | 1.000 | nd | |
| VI | gbs628/sag0645 | 56.8 | 68.5 | 65.1 | 67 | 56.9 | 0.183 | 0.404 | 0.188 | 0.150 |
| gbs0660/sag0685 | 81.8 | 92.4 | 79.1 | 82 | 84.5 | 0.082 | 0.482 | 0.709 | 0.126 | |
| IX | gbs1073/sag1038 | 38.6 | 4.3 | 69.8 | 78 | 79.3 | < 0.0001i | 0.272 | 0.872 | <0.0001j |
| X | gbs1120 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 4.7 | 1 | 1.7 | 1.00 | 0.573 | 1.000 | nd |
| gbs1125 | 4.5 | 15.2 | 9.3 | 4 | 8.6 | 0.071 | 1.000 | 0.288 | 0.237 | |
| gbs1135 | 11.4 | 15.2 | 4.7 | 5 | 17.2 | 0.544 | 0.053 | 0.013k | 0.742 | |
| XII | gbs1306/sag1233 | 93.2 | 95.7 | 74.4 | 71 | 84.5 | 0.681 | 0.209 | 0.06 | 0.018l |
| gbs1313/sag1246 | 18.2 | 77.2 | 86.0 | 78 | 82.5 | <0.0001g | 0.655 | 0.492 | `0.411 | |
| XIII | gbs1987/sag2029 | 77.3 | 92.4 | 7.4 | 84 | 84.5 | 0.013g | 0.209 | 0.957 | 0.126 |
| Tn916 | sag915 | 38.6 | 55.4 | 65.1 | 59 | 43.1 | 0.067 | 0.028m | 0.047n | 0.141 |
aDutch neonatal invasive strains
bDutch colonizing strains
cTaiwanese neonatal invasive strains
dTaiwanese adult invasive strains
eTaiwanese colonizing strains
fP-values are calculated for the differences in the prevalence of genetic markers between groups. If the P-value is <0.05, the difference is considered to be significant. Groups of invasive strains are compared with colonizing strains from the same region
gLess prevalent in Dutch neonatal invasive strains
hLess prevalent in Taiwanese neonatal invasive strains
iMore prevalent in Dutch neonatal invasive strains
jMore prevalent in Taiwanese colonizing strains
kLess prevalent in Taiwanese adult invasive strains
lMore prevalent in Dutch colonizing strains
mMore prevalent in Taiwanese neonatal invasive strains
nMore prevalent in adult invasive strains
Data analysis
Isolates were divided into five groups: Dutch neonatal invasive GBS (DNI), Dutch colonizing GBS (DC), Taiwanese neonatal invasive GBS (TNI), Taiwanese adult invasive (TAI), and Taiwanese colonizing GBS (TC). The selective PCR results were analyzed using the SPSS 15.0 software package (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA). Two by two tables were created for virulent and colonizing strains with each serotype and genetic marker. We examined the differences in the prevalence of serotypes and markers in invasive and non-invasive strains by comparing Dutch neonatal invasive with Dutch colonizing GBS, Taiwanese neonatal invasive with Taiwanese colonizing GBS, and Taiwanese adult invasive with Taiwanese colonizing GBS. Chi-quare tests and Fisher’s exact tests were used to assess differences between groups. To limit the number of variables, PCR results for markers with just a few positive results in all groups (<5) were excluded from further statistical analysis. Logistic regression was performed to assess any dependency of one variable to another and to establish the distribution of serotypes and genetic markers combined in colonizing and virulent GBS. Serotype was included as a categorical variable. The Hosmer and Lemeshow test was used to establish the statistical significance of the outcome of the regression analysis. To assess the practical value, a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was calculated with the significant variables to establish the sensitivity and specificity of the model.
Results
Epidemiology of serotype and gene distribution
The distribution of serotypes and PPI markers varied widely between the five groups (Tables 2 and 3). In Dutch and Taiwanese strains, serotype III isolates were more prevalent in neonatal invasive GBS (P < 0.0001). In Dutch strains, serotype II (P = 0.009) and in Taiwanese strains serotype V (P = 0.005) were more prevalent in colonizing GBS. In adult invasive GBS from Taiwan, no serotype was associated with invasiveness or colonization (Table 2). We found two PPI markers to be associated with invasiveness: gbs1073/sag1038, corresponding to PPI IX in Dutch neonatal strains (P < 0.0001), and sag915, corresponding to a transposon (Tn916) in both neonatal (P = 0.028) and adult invasive Taiwanese strains (P = 0.048). Furthermore, marker gbs0227/sag0234 (PPI I) was less prevalent in Dutch (P = 0.001) and Taiwanese invasive neonatal strains (P < 0.001), but not in Taiwanese adult invasive strains. The presence of markers gbs1313/sag1246 (PPI XII) and gbs1987/sag2029 (PPI XIII) was associated with colonization (P < 0.0001 and P = 0.013) only in the Dutch collection of strains (Table 3). Finally, gbs1135 (PPI X) was more prevalent in Taiwanese colonizing strains. The absence of this gene was associated with virulence in Taiwanese adult invasive strains (P = 0.013). When Dutch and Taiwanese colonizing GBS were compared, serotype II, serotype IV, and marker 1306/sag1233 (PPI XII P = 0.049, P = 0.043, P = 0.0001, respectively) were more prevalent among Dutch GBS and marker 1073/sag1038 (PPI IX) among Taiwanese GBS (P < 0.0001) (Tables 2 and 3). Apparently, there are clear regional differences in the GBS epidemiology and infection potential of clones.
Table 2.
Prevalence of serotypes
| Serotype | D N Ia % (n = 44) | D Cb % (n = 92) | T N Ic % (n = 43) | T A Id % (n = 101) | T Ce% (n = 58) | P-valuef D N I vs. D C | P-valuef T N I vs. T C | P-valuef T A I vs. TC | P-valuef D C vs. T C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ia | 13.6 | 26.1 | 11.6 | 18 | 22.4 | 0.101 | 0.161 | 0.482 | 0.611 |
| Ib | 0 | 6.5 | 4.7 | 14 | 8.6 | 0.177 | 0.696 | 0.327 | 0.750 |
| II | 0 | 13.0 | 0 | 6 | 3.4 | 0.009g | 0.506 | 0.711 | 0.049h |
| III | 75.0 | 21.7 | 79.1 | 23 | 32.8 | <0.0001i | <0.0001j | 0.169 | 0.134 |
| IV | 0 | 7.6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.096 | − | 1.000 | 0.043h |
| V | 9.1 | 15.2 | 4.7 | 26 | 25.9 | 0.324 | 0.005k | 0.987 | 0.108 |
| VI | 0 | 7.6 | 0 | 3 | 3.4 | 0.096 | 0.506 | 1.000 | 0.483 |
aDutch neonatal invasive strains
bDutch colonizing strains
cTaiwanese neonatal invasive strains
dTaiwanese adult invasive strains
eTaiwanese colonizing strains
fP-values are calculated for the differences in serotypes between groups. If the P-value is <0.05, the difference is considered to be significant. Invasive strains are compared with colonizing strains from the same region
gLess prevalent in Dutch neonatal invasive strains
hMore prevalent in Dutch colonizing strains
iMore prevalent in Dutch neonatal invasive strains
jMore prevalent in Taiwanese neonatal invasive strains
kLess prevalent in Taiwanese neonatal invasive strains
Invasion markers and serotype analysis
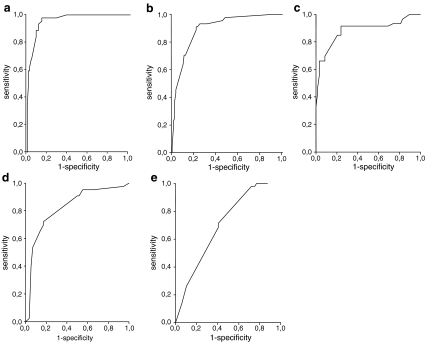
For the Dutch strains, serotype, absence of markers gbs1987/sag2029, gbs227/sag0234, gbs1125, and gbs1313/sag1246, and the presence of marker gbs1073/sag1038 were clearly associated with invasiveness (Tables 2 and 3). The ROC curve showed a large area under the curve (AUC) of 0.963, representing a sensitivity of 97.7% and a specificity of 85.9% in indicating virulence (Fig. 1a). If the algorithm deduced from the ROC curve was used to identify Taiwanese strains, this model correctly identified 79% of the neonatal invasive strains and only 25% of adult invasive strains and 57% of colonizing strains. Therefore, to optimize the selection of markers for the Taiwanese collection of strains, a new model was constructed, comparing both neonatal and adult invasive strains to colonizing strains from the same region. For Taiwanese neonatal strains, serotype and absence of markers gbs1987/sag2029, gbs0227/sag0234, and gbs1135, and the presence of marker sag 915 were independently associated with virulence (Tables 2 and 3). With these variables, the ROC curve showed an AUC of 0.894 and the model potentially predicted invasiveness with a sensitivity of 93% and specificity of 75.9% (Fig. 1c). If the serotype was excluded, the AUC was still 0.89 for the Dutch and 0.81 for the Taiwanese neonatal strains (Fig. 1b, d). The optimal ROC curve constructed for the adult invasive Taiwanese strains generated an AUC of only 0.657 and a low sensitivity (71.4%) and specificity (53.4%) for tracing potential virulence (Fig. 1e). Only a few variables contributed to this model: the presence of marker sag 915, and the absence of markers gbs1306/sag1233 and gbs1135. In contrast to both groups of neonatal invasive strains, serotype was not a relevant variable (Table 2). So, with different sets of markers and serotypes, it was possible to construct a reliable model for the prediction of potential invasiveness for both groups of neonatal but not for adult invasive strains.
Fig. 1.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves including both sensitivity and specificity estimates. Each curve is the regression line that summarizes the overall diagnostic accuracy. AUC = area under the curve, SE = standard error of AUC. a, b Dutch neonatal invasive strains. c, d Taiwanese neonatal invasive strains. e Taiwanese adult invasive strains. In a and c, the included variables are molecular markers and serotype. To establish the influence of markers alone, serotype was left out as a variable in b and d. For adult invasive strains, only one curve was constructed (e) because the serotype was not a relevant variable. a AUC: 0.963, SE: 0.014, 95% CI: 0.935–0.99, cutoff: 0.2055, sensitivity: 97.7%, specificity: 85.9%. Included variables are serotype, gbs1987/sag2029, gbs227/sag0234, gbs1073/sag1038, gbs1125, and gbs1313/sag1246. b AUC: 0.898, SE: 0.028, 95% CI: 0.844–0.952, cutoff: 0.351, sensitivity: 90.9%, specificity: 79.3%. Included variables as in a, except serotype. c AUC: 0.894, SE: 0.035, 95% CI: 0.826–0.963, cutoff: 0.3525, sensitivity: 93%, specificity: 75.9%. Included variables are serotype, gbs1987/sag2029, gbs227/sag0234, gbs1135, and sag915. d AUC 0.823, SE: 0.044, 95% CI:0.738–0.909, cutoff: 0.388, sensitivity: 72.1%, specificity: 82.8%. Variables as in c, except serotype. e AUC: 0.657, SE: 0.046, 95% CI: 0.567–0.747, cutoff: 0.5495, sensitivity: 71.4%, specificity: 53.4%. Included variables are sag915, gbs1306/sag1233, and gbs1135
Discussion
Based on a combination of conventional serotyping and assessment of a set of PCR markers related to GBS PPIs as defined for a collection of strains from The Netherlands and Taiwan, we have been able to characterize the epidemiology of virulent isolates of GBS likely to cause neonatal disease. Previously, Herbert et al. examined the presence of these PPIs in a limited number of invasive and non-invasive strains of GBS, and used PCRs directed at several genes per island as markers [20]. They found that islands I, VI, and XII met the criteria of a true pathogenicity island, but no association was found between the presence of markers corresponding to these islands and invasiveness [20, 21]. Our present study is the first to examine combinations of these markers of PPI and serotype on a large collection of strains, and to compare strains isolated from different groups of patients from different regions [20].
Previously, not a single major GBS virulence factor related to neonatal disease has been identified, and solely comparing the presence or absence of genes encoding virulence factors can not differentiate accurately between epidemic virulent and colonizing strains. This is confirmed by two independent studies that were carried out to establish the frequency of genes coding putative and known GBS virulence factors among invasive and colonizing isolates [22, 23] (Table 4). Others used random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD), exploring a larger part of the genome to compare the genetic structure of colonizing and invasive GBS isolated from neonates with meningitis [24–26] (Table 4). Additionally, two previous French studies using pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) revealed that a subset of isolates recovered from meningitis clustered within three PFGE groups [27, 28]. The authors suggested that it should be possible to characterize the specific markers, define primers, and construct a PCR assay to identify virulent isolates of GBS. However, such a test has not been developed yet. The PPIs we examined harbor known and putative GBS virulence factors, insertion sequences, transposons, and genes of unknown function. (Table 1). We found that in all geographically related neonatal invasive strains, gbs1987/sag2029, corresponding to a true PPI (I), was more prevalent in colonizing rather than invasive GBS isolates. Also, one marker in the Dutch neonatal strains (gbs1073/sag1038, PPI IX) and one marker for a mobile element, sag915(Tn916), in the Taiwanese strains were associated with invasiveness. This probably reflects the complex and multi-factorial nature of GBS virulence and molecular pathogenesis, which is likely to be attributable to multiple genes, polymorphism, and differential expression of these genes and regulation mechanisms [24, 25, 29–32].
Table 4.
Overview of known markers to potentially identify the invasive subgroup, comparing the results of our study with those of previous works
| Ref. | Origin of the strains | Subgroups (n) | Method | Marker -a or +b | P-valuec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neonatal invasive (EOD and LOD) and vaginal and rectal colonizing GBS from The Netherlands and Taiwan | NL invasive (44) NL colonizing (92) |
PCR and serotyping | {ST (II-, III+), gbs1987-, gbs227-, gbs1073+, gbs1125-, gbs1313- } | <0.05 | |
| TW invasive (43) TW colonizing (58) |
{ST (III+, V-), gbs1987-, gbs227-, gbs1135-, sag915+ } | <0.05 | |||
| 22d | Invasive strains from neonates, elderly and pregnant women | Invasive (269) | Selection of known and putative virulence genes, PCR | spb1 + | 0.23 |
| Anal, vaginal, throat, and urine from healthy individuals | Colonizing (152) | bac | ns | ||
| Rib | ns | ||||
| Brp | ns | ||||
| pag - | <0.01 | ||||
| psp | ns | ||||
| 23d | Neonatal meningitis isolates, EOD | Invasive (100) | Selection of known virulence genes, PCR | bca - | 0.002 |
| Colonizing isolates from cervix, vagina, anus | Colonizing (360) | bac | ns | ||
| rib + | 0.09 | ||||
| ST Ia | bca - | 0.03 | |||
| ST | bca + | 0.002 | |||
| 24e | GBS from neonatal CSF (EOD and LOD), vagina pregnant women, and neonatal gastric fluid (colonizing) | Invasive phylogenetic subgroups I, II-ET11, II-ET12 (MLEE) (62) | RAPD, followed by PCR of a tRNA gene cluster | 1,2 kb fragment + | <0.0001 |
| Non-invasive phylogenetic subgroup II (MLEE) (52 | +IS1548 + | <0.0001 | |||
| 25e | CSF neonates 1986–1990 | Invasive phylogenetic subgroups (MLEE) (63) | RAPD, followed by differential display of DNA and PCR of prophagic DNA | DNA fragment F5 + | 0.017 |
| Vagina and gastric fluid neonates (colonizing) | Non-invasive phylogenetic subgroups (MLEE) (46) | DNA fragment F7 + | 0.007 | ||
| DNA fragment F10 + | <0.001 | ||||
| At least one fragment + | 0.002 | ||||
| 26e | GBS from neonatal CSF (EOD and LOD), vagina pregnant women, and neonatal gastric fluid (colonizing) | RAPD group A (virulent clone family) (38) | RAPD, primer A4 | 0.64 kbp fragment | <0.001 |
| Not RAPD gr.A (76) | RAPD, primer AP42 | 1.2 kbp fragment - | <0.001 | ||
| RAPD, primer OPS16 | 2.4 kbp fragment + | <0.001 | |||
| 27f | GBS from neonatal CSF (EOD and LOD), vagina pregnant women, and neonatal gastric fluid (colonizing) | Invasive (54) | PFGE, SmaI restriction | 183 kb fragment + | ns |
| Colonizing (59) | 162 kb fragment + | <0.0001 | |||
| Quadruplet + | 0.009 | ||||
| 28f | Neonatal meningitis isolates, EOD and LOD, all ST III | Invasive (92) | PFGE, SmaI digestion probes of potential virulence genes, and mobile genetic elements | cpsA | ns |
| Ears and gastric fluid healthy neonates | Colonizing (37) | neuA (15kb fragment) + | <0.0001 | ||
| scpB | ns | ||||
| hylB | ns | ||||
| IS1548 | ns | ||||
| GBSi1 + | <0.0001 |
aAbsence of the marker(s) is associated with the specific virulent subgroup. The significance level of this association is expressed by the P-value
bPresence of the marker(s) is associated with the specific virulent subgroup. The significance level of this association is expressed by the P-value
cns means not significant (P > 0.05)
dDistribution of virulence genes among invasive and colonizing GBS. Smith et al. examined the distribution of eight known and putative virulence genes as a function of type of isolate on a heterogeneous collection of strains. With the exception of the pag (phage-associated) gene, appearing more often in colonizing isolates, and the spb1 gene, appearing slightly more often in invasive isolates, no difference was found in the distribution of the selected genes [22]. Manning et al. studied the presence of the rib and the bca and bac genes among colonizing and invasive isolates and found only marginally significant differences in frequency. The calculated sensitivity and specificity of these markers to identify virulent strains is generally low, except for some limited serotype–gene combinations [23]
eDistribution of RAPD fragments among virulent phylogenetically related lineages. With RAPD, Rolland et al. identified a fragment corresponding to a tRNA gene cluster [24]. van der Mee-Marquet et al. identified several prophagic DNA fragments that were significantly more prevalent in strains belonging to invasive MLEE-related subgroups of GBS [25]. Chatellier et al. demonstrated that, with four primers, neonatal invasive strains can be grouped into three predominant RAPD groups, corresponding to the same virulent MLEE lineages as found by van der Mee-Marquet et al. [26]
fPFGE fragments and virulence gene probes, distribution among virulent vs. colonizing (ST III) GBS. Rolland et al., using PFGE, revealed that isolates recovered from meningitis were clustered within three PFGE groups [27]. Bidet et al. found a significant association of a mobile genetic element (GBSi1) and a 15 kb fragment bearing the neuA virulence gene with meningitis isolates [28]
Without understanding the exact link between PPI, serotype, and virulence, our novel markers allow us to epidemiologically differentiate between invasive and colonizing GBS, more so than other methods permitted thus far. However, it has to be emphasized that epidemiological behavior and invasiveness might be closely intertwined. Analysis of GBS strains from additional geographic locales will help to resolve this issue. Optimal PPI markers for epidemiological discrimination vary between the two geographically distinct areas and in subsets of neonatal GBS strains from The Netherlands and Taiwan. After optimizing the markers, our predictive model was still less accurate for the Taiwanese strains, most likely because our initial selection was based on screening of the Dutch strains. Further research exploring the distribution of molecular markers not included in our study in different populations and regions is necessary to give insight into the dynamics of group B streptococci.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
References
- 1.Valkenburg-van den Berg AW, Sprij AJ, Oostvogel PM et al (2006) Prevalence of colonisation with group B Streptococci in pregnant women of a multi-ethnic population in The Netherlands. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 124:178–183. doi:10.1016/j.ejogrb.2005.06.007 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 2.Hansen SM, Uldbjerg N, Kilian M et al (2004) Dynamics of Streptococcus agalactiae colonization in women during and after pregnancy and in their infants. J Clin Microbiol 42:83–89. doi:10.1128/JCM.42.1.83-89.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 3.Manning SD (2003) Molecular epidemiology of Streptococcus agalactiae (group B Streptococcus). Front Biosci 8:s1–s18. doi:10.2741/985 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 4.Doran KS, Nizet V (2004) Molecular pathogenesis of neonatal group B streptococcal infection: no longer in its infancy. Mol Microbiol 54:23–31. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04266.x [DOI] [PubMed]
- 5.Fluegge K, Supper S, Siedler A et al (2005) Serotype distribution of invasive group B streptococcal isolates in infants: results from a nationwide active laboratory surveillance study over 2 years in Germany. Clin Infect Dis 40:760–763. doi:10.1086/427942 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 6.Weisner AM, Johnson AP, Lamagni TL et al (2004) Characterization of group B streptococci recovered from infants with invasive disease in England and Wales. Clin Infect Dis 38:1203–1208. doi:10.1086/382881 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 7.Persson E, Berg S, Trollfors B et al (2004) Serotypes and clinical manifestations of invasive group B streptococcal infections in western Sweden 1998–2001. Clin Microbiol Infect 10:91–796. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.00931.x [DOI] [PubMed]
- 8.Quentin R, Huet H, Wang FS et al (1995) Characterization of Streptococcus agalactiae strains by multilocus enzyme genotype and serotype: identification of multiple virulent clone families that cause invasive neonatal disease. J Clin Microbiol 33:2576–2581 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 9.Musser JM, Mattingly SJ, Quentin R et al (1989) Identification of a high-virulence clone of type III Streptococcus agalactiae (group B Streptococcus) causing invasive neonatal disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:4731–4735. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.12.4731 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Takahashi S, Adderson EE, Nagano Y et al (1998) Identification of a highly encapsulated, genetically related group of invasive type III group B streptococci. J Infect Dis 177:1116–1119. doi:10.1086/517408 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 11.Jones N, Bohnsack JF, Takahashi S et al (2003) Multilocus sequence typing system for group B streptococcus. J Clin Microbiol 41:2530–2536. doi:10.1128/JCM.41.6.2530-2536.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 12.Bisharat N, Jones N, Marchaim D et al (2005) Population structure of group B streptococcus from a low-incidence region for invasive neonatal disease. Microbiology 15:1875–1881. doi:10.1099/mic.0.27826-0 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 13.Lin FY, Whiting A, Adderson E et al (2006) Phylogenetic lineages of invasive and colonizing strains of serotype III group B Streptococci from neonates: a multicenter prospective study. J Clin Microbiol 44:1257–1261. doi:10.1128/JCM.44.4.1257-1261.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Bohnsack JF, Takahashi S, Hammitt L et al (2000) Genetic polymorphisms of group B streptococcus scpB alter functional activity of a cell-associated peptidase that inactivates C5a. Infect Immun 68:5018–5025. doi:10.1128/IAI.68.9.5018-5025.2000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Bohnsack JF, Takahashi S, Detrick SR et al (2001) Phylogenetic classification of serotype III group B streptococci on the basis of hylB gene analysis and DNA sequences specific to restriction digest pattern type III-3. J Infect Dis 183:1694–1697 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 16.Bohnsack JF, Whiting AA, Bradford RD et al (2002) Long-range mapping of the Streptococcus agalactiae phylogenetic lineage restriction digest pattern type III-3 reveals clustering of virulence genes. Infect Immun 70:134–139. doi:10.1128/IAI.70.1.134-139.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 17.Davies HD, Jones N, Whittam TS et al (2004) Multilocus sequence typing of serotype III group B streptococcus and correlation with pathogenic potential. J Infect Dis 189:1097–1102. doi:10.1086/382087 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 18.Hauge M, Jespersgaard C, Poulsen K et al (1996) Population structure of Streptococcus agalactiae reveals an association between specific evolutionary lineages and putative virulence factors but not disease. Infect Immun 64:919–925 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 19.Glaser P, Rusniok C, Buchrieser C et al (2002) Genome sequence of Streptococcus agalactiae, a pathogen causing invasive neonatal disease. Mol Microbiol 45:1499–1513. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03126.x [DOI] [PubMed]
- 20.Herbert MA, Beveridge CJ, McCormick D et al (2005) Genetic islands of Streptococcus agalactiae strains NEM316 and 2603VR and their presence in other Group B streptococcal strains. BMC Microbiol 5:31. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-5-31 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 21.Schmidt H, Hensel M (2004) Pathogenicity islands in bacterial pathogenesis. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:14–56; erratum in (2006) Clin Microbiol Rev 19(1):257. doi:10.1128/CMR.19.1.257.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 22.Smith TC, Roehl SA, Pillai P et al (2007) Distribution of novel and previously investigated virulence genes in colonizing and invasive isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae. Epidemiol Infect 135:1046–1054. doi:10.1017/S0950268806007515 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Manning SD, Ki M, Marrs CF et al (2006) The frequency of genes encoding three putative group B streptococcal virulence factors among invasive and colonizing isolates. BMC Infect Dis 6:116. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-6-116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.Rolland K, Mereghetti L, Watt S et al (2002) tRNA gene clusters at the 3′ end of rRNA operons are specific to virulent subgroups of Streptococcus agalactiae strains, as demonstrated by molecular differential analysis at the population level. Microbiology 148:1493–1499 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 25.van der Mee-Marquet N, Domelier AS, Mereghetti L et al (2006) Prophagic DNA fragments in Streptococcus agalactiae strains and association with neonatal meningitis. J Clin Microbiol 44:1049–1058. doi:10.1128/JCM.44.3.1049-1058.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 26.Chatellier S, Ramanantsoa C, Harriau P et al (1997) Characterization of Streptococcus agalactiae strains by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis. J Clin Microbiol 35:2573–2579 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 27.Rolland K, Marois C, Siquier V et al (1999) Genetic features of Streptococcus agalactiae strains causing severe neonatal infections, as revealed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and hylB gene analysis. J Clin Microbiol 37:1892–1898 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 28.Bidet P, Brahimi N, Chalas C et al (2003) Molecular characterization of serotype III group B-streptococcus isolates causing neonatal meningitis. J Infect Dis 188:1132–1137. doi:10.1086/378517 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 29.Gutekunst H, Eikmanns BJ, Reinscheid DJ (2003) Analysis of RogB-controlled virulence mechanisms and gene repression in Streptococcus agalactiae. Infect Immun 71:5056–5064. doi:10.1128/IAI.71.9.5056-5064.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 30.Rubens CE, Wessels MR, Heggen LM et al (1987) Transposon mutagenesis of type III group B Streptococcus: correlation of capsule expression with virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:7208–7212. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.20.7208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 31.Maeland JA, Brakstad OG, Bevanger L et al (2000) Distribution and expression of bca, the gene encoding the c alpha protein, by Streptococcus agalactiae. J Med Microbiol 49:193–198 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 32.Tettelin H, Masignani V, Cieslewicz MJ et al (2002) Complete genome sequence and comparative genomic analysis of an emerging human pathogen, serotype V Streptococcus agalactiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:12391–12396. doi:10.1073/pnas.182380799 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]