Abstract
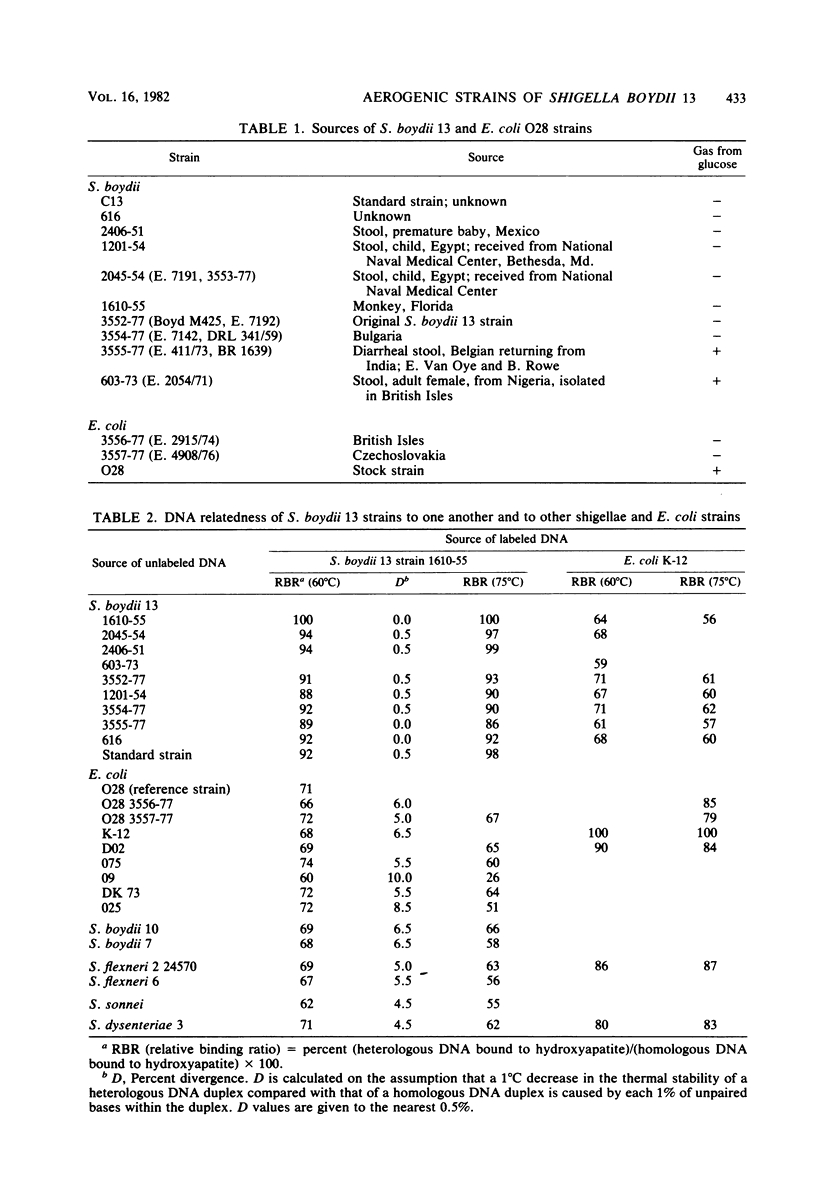
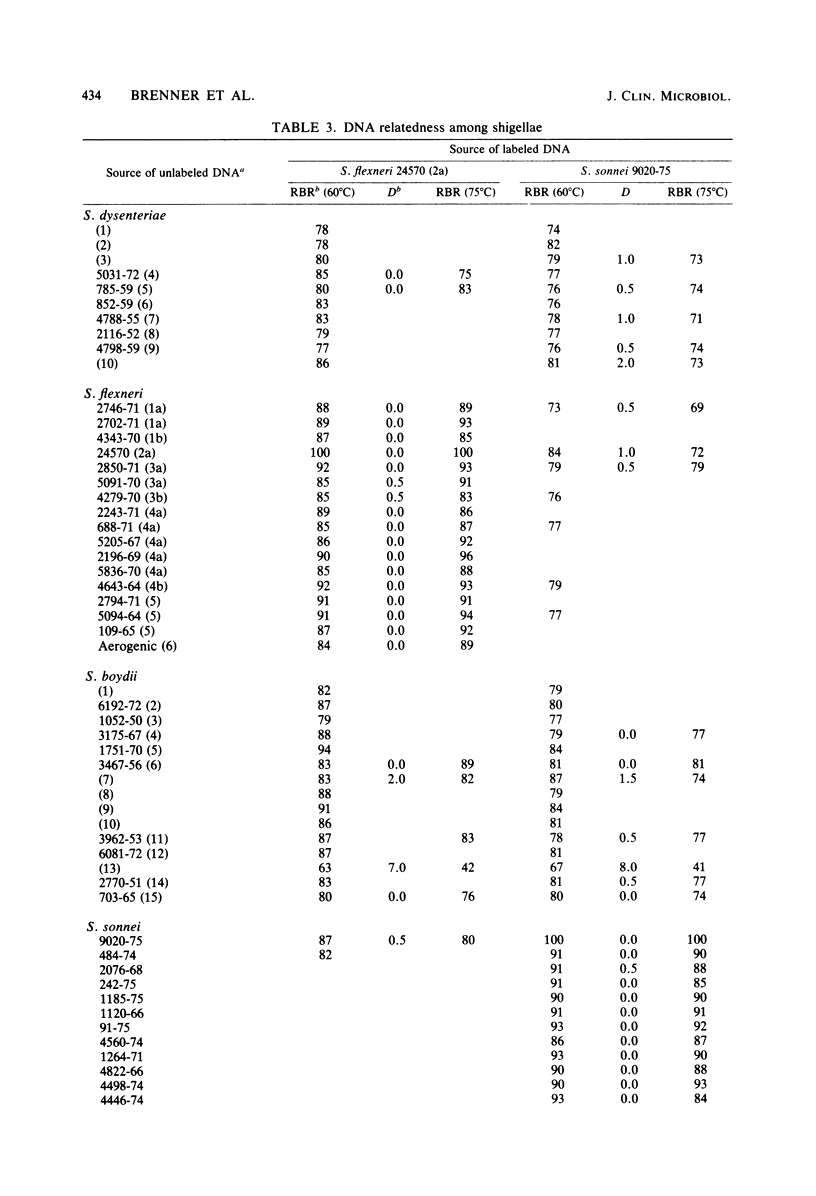
Shigella boydii 13 strains are separable from other Shigella and Escherichia coli strains on the basis of DNA relatedness. From this observation, it was possible to confirm the existence of aerogenic S. boydii 13 strains. DNA relatedness studies also showed that strains of E. coli and strains representing all other serotypes of Shigella, including provisional strains, belong to the same genetic species.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Johnson K. E., Citarella R. V., Falkow S. Polynucleotide sequence relationships among members of Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):637–650. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.637-650.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Skerman F. J., Falkow S. Polynucleotide sequence divergence among strains of Escherichia coli and closely related organisms. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):953–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.953-965.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman F. W., Farmer J. J., 3rd Salmonella typhi: identification, antibiograms, serology, and bacteriophage typing. Am J Med Technol. 1978 Dec;44(12):1149–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STYPULKOWSKA H. NIETYPOWY SZCZEP SHIGELLA DYSENTERIAE 3 IZOLOWANY NA TERENIE POLSKI. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 1964;16:147–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



