Abstract
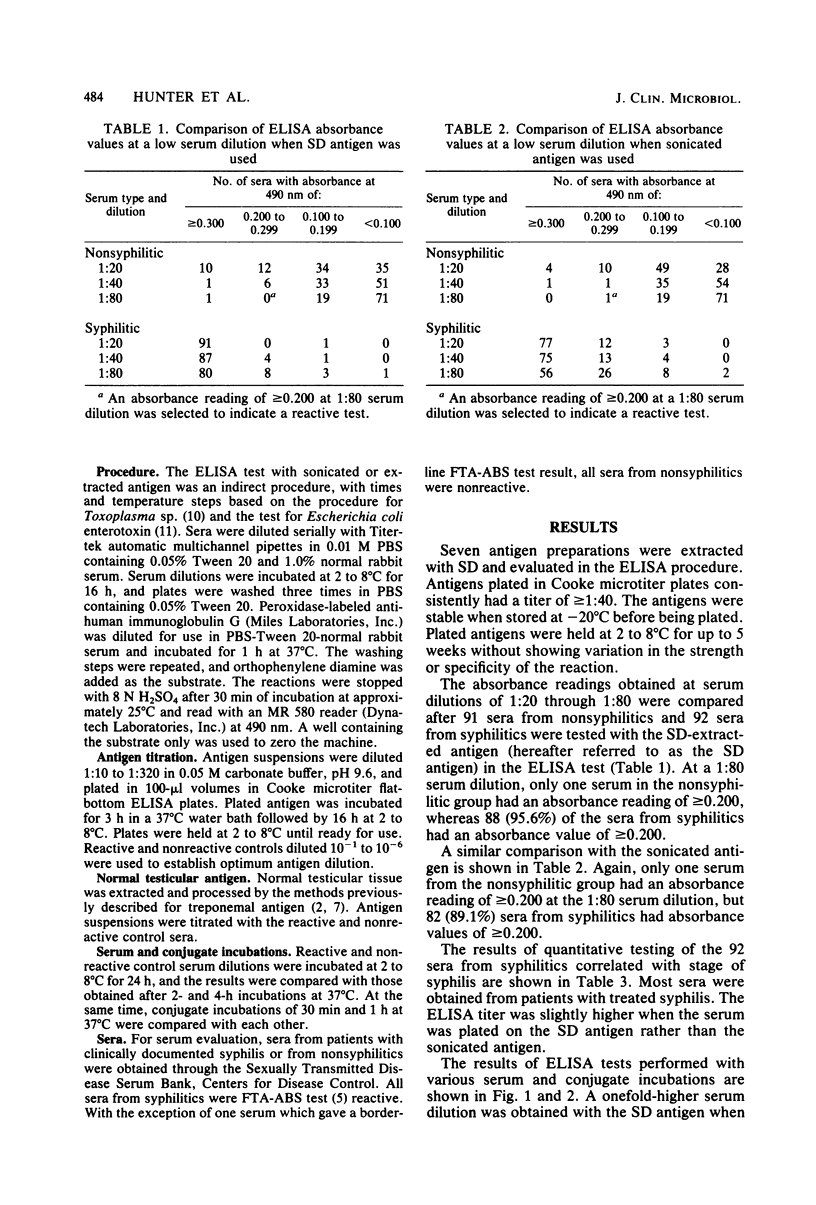
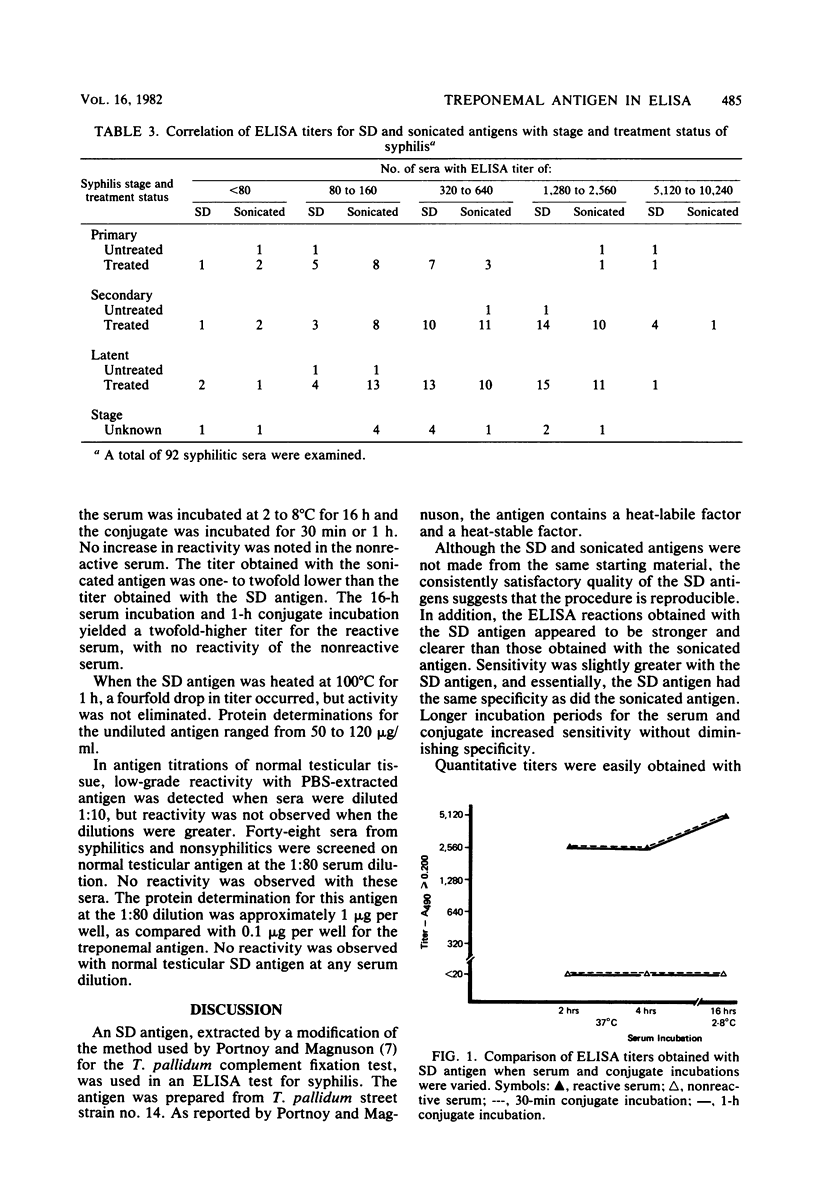
The extraction of Treponema pallidum antigen with sodium desoxycholate, based on a previously described procedure (J. Portnoy and H.J. Magnuson, J. Immuno. 75:348-355, 1955), was used in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test for syphilis. The antigen was prepared from T. pallidum street strain no. 14, and its overall sensitivity and specificity was compared with those of sonicated antigen preparations made with phosphate-buffered saline. The optimum serum dilution for testing and the significant absorbance reading at 490 nm were selected by examination of quantitative dilutions of 91 sera from presumably normal individuals and 92 sera from syphilitics. The time and temperature of serum and conjugate incubations were also examined. With an absorbance reading of greater than or equal to 0.2 at the 1:80 serum dilution, 88 (95.8%) of 92 sera from syphilitics were reactive in the ELISA test with desoxycholate-extracted antigen, and 82 (89.1%) were reactive with the sonicated antigen. Only one nonsyphilitic serum was reactive with each antigen. Greater sensitivity without loss in specificity was obtained with longer serum and conjugate incubations. We concluded that an ELISA test with sodium desoxycholate-extracted antigen is more sensitive than and equally specific to an ELISA with sonicated treponemal antigen.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hunter E. F., Adams M. R., Orrison L. H., Pender B. J., Larsen S. A. Problems affecting performance of the fluorescent treponemal antibody-absorption test for syphilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):163–166. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.163-166.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E. F., Creighton E. T., Lewis J. S. An improved antigen for the FTA-ABS test. Health Lab Sci. 1970 Oct;7(4):237–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob E., Carter T. B., Nauman R. K. Immunological relationship among oral anaerobic spirochetes as detected by indirect microhemagglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):610–613. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.610-613.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob E., Meiller T. F., Nauman R. K. Detection of elevated serum antibodies to Treponema denticola in humans with advanced periodontitis by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Mar;17(2):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb01140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. M., Donowho E. M., Trent D. W., Moody E. E. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for the detection of antibodies to Treponema pallidum. Sex Transm Dis. 1979 Apr-Jun;6(2):43–49. doi: 10.1097/00007435-197904000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTNOY J., MAGNUSON H. J. Immunologic studies with fractions of virulent Treponema pallidum. I. Preparation of an antigen by desoxycholate extraction and its use in complement fixation. J Immunol. 1955 Nov;75(5):348–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope V., Hunter E. F., Feeley J. C. Evaluation of the microenzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with Treponema pallidum antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):630–634. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.630-634.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldkamp J., Visser A. M. Application of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in the serodiagnosis of syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1975 Aug;51(4):227–231. doi: 10.1136/sti.51.4.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls K. W., Bullock S. L., English D. K. Use of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and its microadaptation for the serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):273–277. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.273-277.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Greenberg H. B., Merson M. H., Sack R. B., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):439–444. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.439-444.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


