Abstract
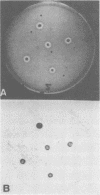
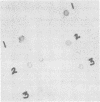
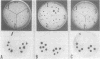
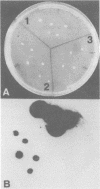
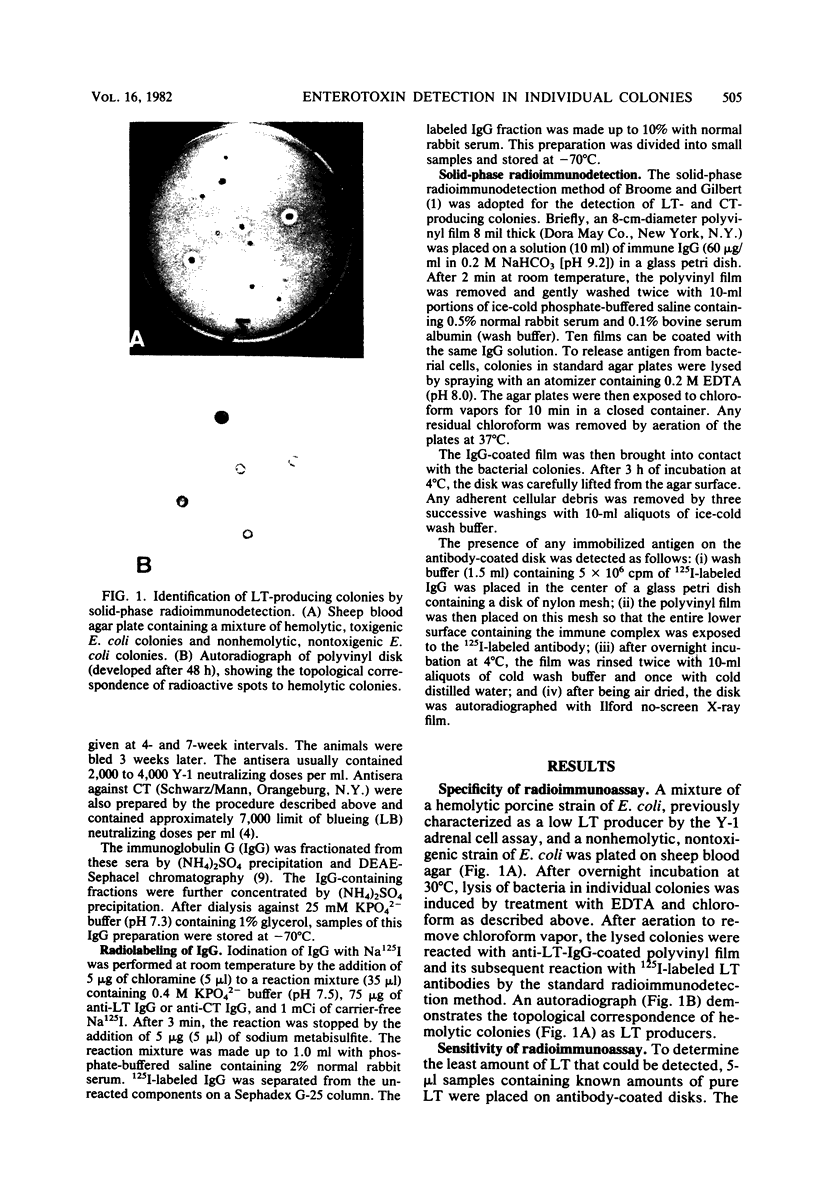
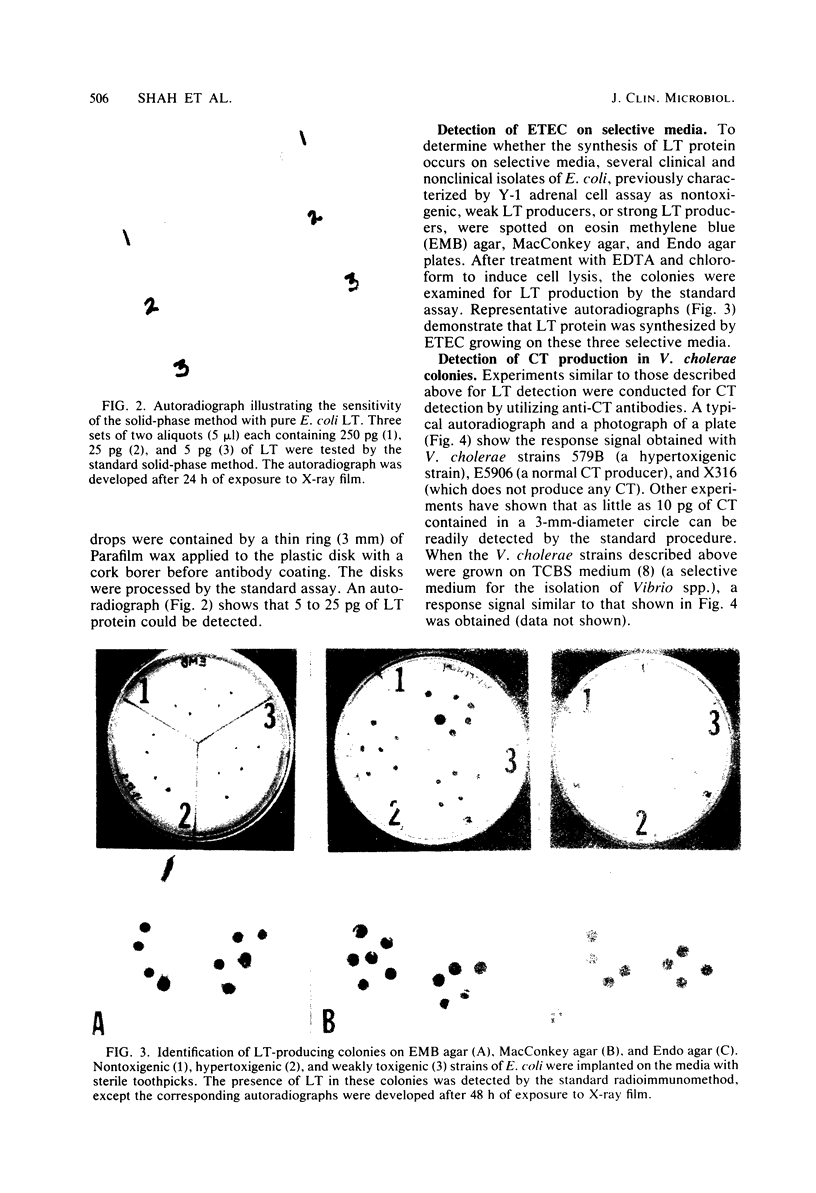
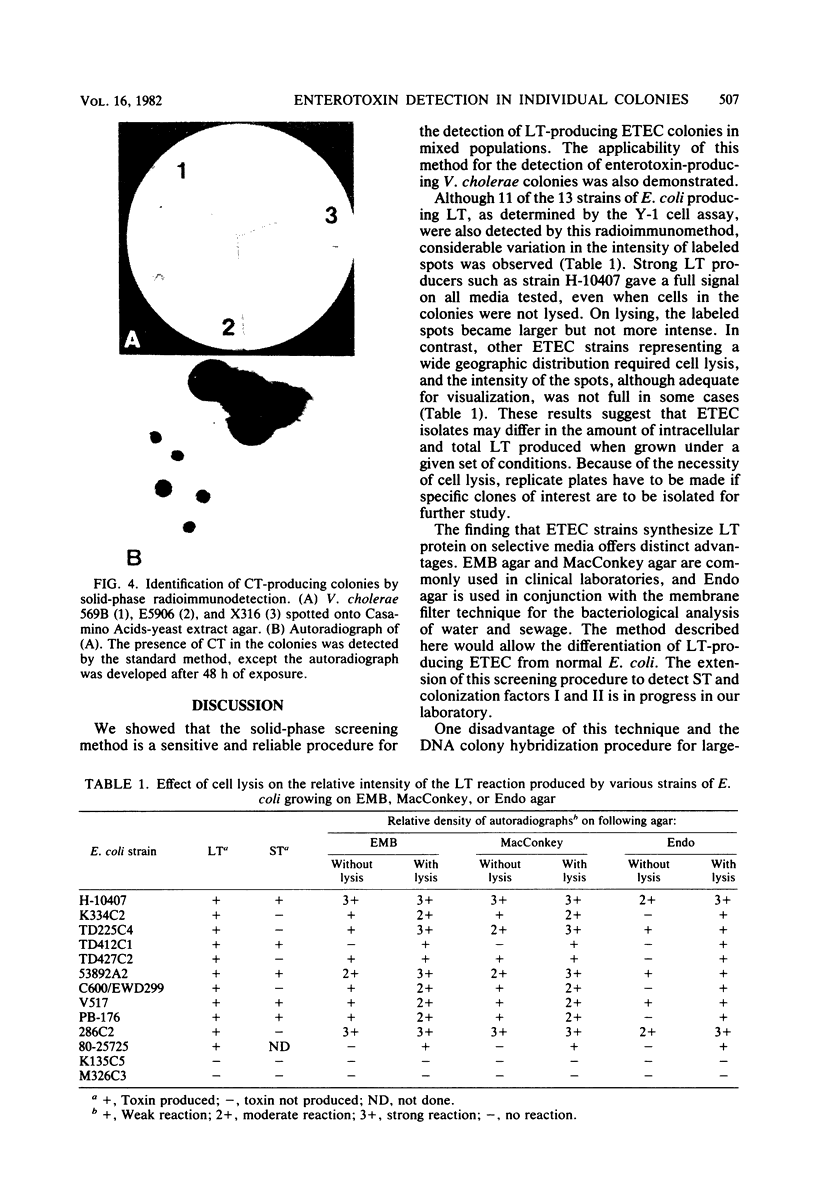
A solid-phase sandwich assay that was able to differentiate heat-labile-enterotoxin-producing colonies of Escherichia coli and choleratoxin-producing colonies of Vibrio cholerae from nontoxigenic colonies is described. Flexible polyvinyl chloride plastic film coated with antibody molecules was allowed to react with partially lysed bacterial colonies in a standard petri dish. The immobilized antigen on the plastic film was then labeled with radioiodinated antibody. Autoradiography identified antigen-containing colonies. As little as 5 to 25 pg of pure toxin contained in a 3- to 4-mm-diameter circle was reliably detected by this method. The synthesis of heat-labile enterotoxin and choleratoxin by cells growing on selective media such as eosin methylene blue agar, MacConkey agar, Endo agar, and thiosulfate-citrate-bile salts-sucrose agar was demonstrated. The method appears to be suitable for large-scale surveys.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broome S., Gilbert W. Immunological screening method to detect specific translation products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2746–2749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderon R. L., Levin M. A. Quantitative method for enumeration of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):130–134. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.130-134.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., DuPont H. L. Hemagglutination patterns of enterotoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli determined with human, bovine, chicken, and guinea pig erythrocytes in the presence and absence of mannose. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):336–346. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.336-346.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOBAYASHI T., ENOMOTO S., SAKAZAKI R., KUWAHARA S. [A NEW SELECTIVE ISOLATION MEDIUM FOR THE VIBRIO GROUP; ON A MODIFIED NAKANISHI'S MEDIUM (TCBS AGAR MEDIUM)]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1963 Nov;18:387–392. doi: 10.3412/jsb.18.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. M. Immunoaffinity chromatography of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:723–731. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34094-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bartlett A., Bidwell D. E. Enzyme immunoassays with special reference to ELISA techniques. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;31(6):507–520. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.6.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]