Abstract
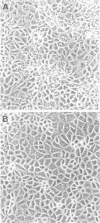
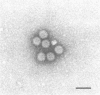
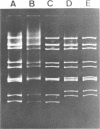
One strain of human rotavirus subgroup 1 (KUN) and one strain of subgroup 2 (MO) were isolated with the MA104 cell line, a fetal rhesus monkey kidney cell line. Their subgroup specificities and RNA patterns were identical to those of rotaviruses present in stools before cultivation. Distinct cytopathic effects consisting of obscure cell boundaries, cell fusion, cell rounding, cell detachment, and lytic foci were recognized at passage 3 of MO and passage 6 of KUN. No differences in cytopathic changes were found between the two isolates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Espejo R. T., Avendaño L. F., Muñoz O., Romero P., Eternod J. G., Lopez S., Moncaya J. Comparison of human rotaviruses isolated in Mexico City and in Santiago, Chile, by electrophoretic migration of their double-stranded ribonucleic acid genome segments. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):342–348. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.342-348.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes I. H. Viral gastroenteritis. Prog Med Virol. 1979;25:1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Cline W. L., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Banks C. E., James H. D., Jr, Flores J., Chanock R. M. Antigenic characterization of human and animal rotaviruses by immune adherence hemagglutination assay (IAHA): evidence for distinctness of IAHA and neutralization antigens. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):415–425. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.415-425.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Cline W. L., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M., Arrobio J. O., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Kalica A. R. Recent advances in the aetiology of viral gastroenteritis. Ciba Found Symp. 1976;(42):273–309. doi: 10.1002/9780470720240.ch16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno T., Suzuki H., Imai A., Ishida N. Reovirus-like agent in acute epidemic gastroenteritis in Japanese infants: fecal shedding and serologic response. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):259–266. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsuzawa T., Konno T., Suzuki H., Ebina T., Ishida N. Two distinct electrophoretic migration patterns of RNA segments of human rotaviruses prevalent in Japan in relation to their serotypes. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(3):271–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inaba Y., Shinozaki T., Fujii R., Matumoto M. Isolation of human rotavirus in cell cultures: brief report. Arch Virol. 1981;69(2):155–160. doi: 10.1007/BF01315159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa T., Urasawa S., Taniguchi K. Sequential passages of human rotavirus in MA-104 cells. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(10):1025–1035. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., James W. D., Pittman A. L., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Definition of human rotavirus serotypes by plaque reduction assay. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):110–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.110-115.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James W. D., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Human rotavirus type 2: cultivation in vitro. Science. 1980 Jan 11;207(4427):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.6243190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]