Abstract
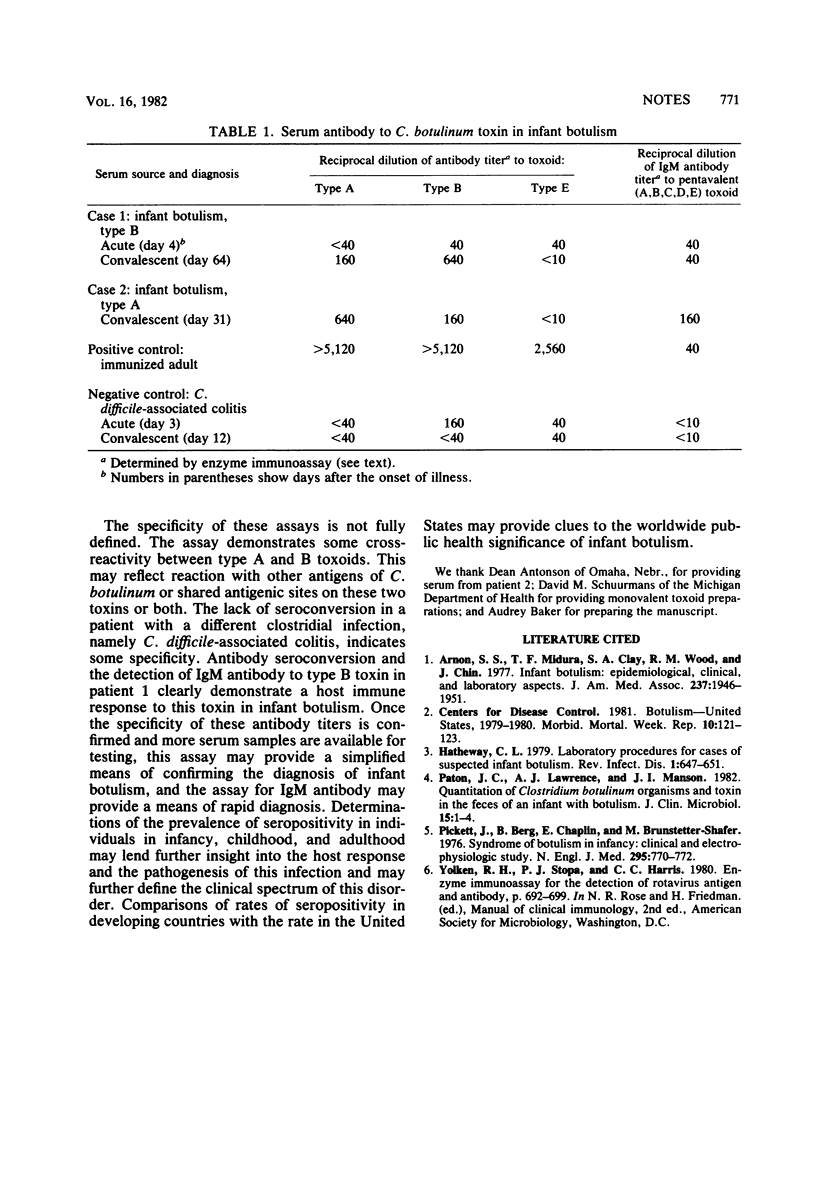
A serum antibody response has not been previously demonstrated after infection with Clostridium botulinum. We developed an enzyme immunoassay for measuring serum antibody to C. botulinum toxins A, B, and E. This assay system detected a specific immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M antibody response to C. botulinum toxin in two patients with infant botulism.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon S. S., Midura T. F., Clay S. A., Wood R. M., Chin J. Infant botulism. Epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory aspects. JAMA. 1977 May 2;237(18):1946–1951. doi: 10.1001/jama.237.18.1946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatheway C. L. Laboratory procedures for cases of suspected infant botulism. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Jul-Aug;1(4):647–651. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.4.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Lawrence A. J., Manson J. I. Quantitation of Clostridium botulinum organisms and toxin in the feces of an infant with botulism. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.1-4.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett J., Berg B., Chaplin E., Brunstetter-Shafer M. A. Syndrome of botulism in infancy: clinical and electrophysiologic study. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 30;295(14):770–772. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609302951407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


