Abstract
Studies in skeletal muscle demonstrate that elevation of plasma FFAs increases the sphingolipid ceramide. We aimed to determine the impact of FFA oversupply on total sphingolipid profiles in a skeletal muscle model. C2C12 myotubes were treated with palmitate (PAL). Lipidomics analysis revealed pleiotropic effects of PAL on cell sphingolipids not limited to ceramides. 13C labeling demonstrated that PAL activated several branches of sphingolipid synthesis by distinct mechanisms. Intriguingly, PAL increased sphingosine-1-phosphate independently of de novo synthesis. Quantitative real-time PCR demonstrated that PAL increased sphingosine kinase 1 (SK1) mRNA by approximately 4-fold. This was accompanied by a 2.3-fold increase in sphingosine kinase enzyme activity. This upregulation did not occur upon treatment with oleate, suggesting some level of specificity for PAL. These findings were recapitulated in the diet-induced obesity mouse model, in which high-fat feeding increased SK1 message in skeletal muscle over 2.3-fold. These data suggest that the impact of elevated FFA on sphingolipids reaches beyond ceramides and de novo sphingolipid synthesis. Moreover, these findings identify PAL as a novel regulatory stimulus for SK1.
Keywords: free fatty acid, sphingolipid, ceramide, skeletal muscle, insulin resistance, diabetes, obesity, lipotoxicity
Recent years have witnessed a rise in the incidence of obesity, which precipitates serious health problems, including cardiovascular disease, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes (1–5). Though mechanistic information remains scarce, data indicate that alterations in lipid metabolism may link obesity to its pathological sequelae. Specifically, obesity may increase the rate of lipolysis in adipocytes, thereby elevating plasma nonesterified, or free, fatty acids (FFAs) (6). This condition increases fatty acid supply to peripheral tissues, resulting in overproduction of bioactive lipids and subsequent disruption of cell homeostasis (7, 8). The effects of elevated FFAs on skeletal muscle are diverse and include disruption of insulin signaling (9, 10), increase in muscle proteolysis and amino acid catabolism (11), aberrant gene regulation, and induction of inflammatory responses (12).
Sphingolipids represent a key class of bioactive lipids with diverse biological activities. Data indicate that sphingolipids, including sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) and ceramide-1-phosphate (C1P), promote inflammation, mitogenesis, and other cell programs (13–16), while ceramides generally promote senescence and/or apoptosis (16, 17). Studies in human skeletal muscle as well as models including mouse muscle and cultured murine myotubes demonstrate that elevated FFAs, such as in obesity, precipitate increases in cell and/or tissue sphingolipid content (2, 18, 19). Specific attention has been paid to increases in ceramide, which is thought to mediate inhibition of insulin signaling by a mechanism dependent on protein phosphatase 2A (10).
Sphingolipid synthesis commences with condensation of serine and palmitate (PAL; derived from palmitoyl-CoA) through the action of serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT), a multisubunit enzyme inhibitable by the fungal toxin myriocin. Intriguingly, the Km of SPT for palmitoyl-CoA has been determined at 0.2 mM, consistent with normal tissue levels of this fatty acid (20, 21). This situation likely leaves SPT activity highly subject to fluctuations in PAL, such as occurs in obesity-induced elevation of circulating FFA, which can increase plasma PAL concentrations to well over 2 mM. These data have led to the hypothesis that regulation of flux through SPT occurs largely via kinetic effects due to changes in substrate availability, which has been demonstrated in both mammalian (20) and yeast systems (22). On the other hand, sphingolipid metabolic pathways represent a highly interconnected web of interactions such that changing concentrations of one lipid often cause profound effects on concentrations of many lipids throughout the pathway (23). Thus, though bulk ceramide increases upon PAL treatment have been demonstrated, effects of elevated PAL supply on other lipids in the pathway have yet to be determined. Moreover, specific ceramide species, distinguishable by the length and/or saturation of their N-acyl chains, have not been determined under conditions of elevated plasma fatty acid supply.
Since various sphingolipids, including diverse ceramide species (24), S1P (25), C1P (26), and complex sphingolipids, including sphingomyelin and glycosphingolipids (27, 28), each play distinct cellular roles, we aimed to determine the impact of PAL oversupply on tissue sphingolipid profiles. These data revealed pleiotropic effects of PAL on cell sphingolipids not limited to ceramides. Labeling and inhibitor studies demonstrated that PAL activates several branches of sphingolipid synthesis by distinct mechanisms, including serving as substrate, activation of sphingolipid catabolism and/or recyling, and increasing message and activity of sphingosine kinase 1 (SK1).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Mouse C2C12 myoblasts and DMEM were from ATCC (Manassas, VA); the DMEM with 4 mM l-glutamine is modified by ATCC to contain 4.5% glucose, 1.5% g/l sodium bicarbonate, and 1.0 mM sodium pyruvate. PAL, myriocin, and fatty-acid-free BSA were from Sigma-Aldrich (Milwaukee, WI); oleate was from Matreya (Pleasant Gap, PA). FBS and horse serum were from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). U-13C palmitic acid was from Cambridge Isotope Laboratories (Andover, MA).
Cell culture
Mouse C2C12 myoblasts were maintained at 37°C in DMEM containing 10% FBS. When the cells become confluent, the media were supplemented with 10% horse serum instead of FBS for myotube formation. After 4 days of differentiation, myotubes were formed and were used for experiments (29).
Diet-induced obesity mouse model
Mice were induced to obesity as described previously (30). In short, 8-week-old C57BL/6J male mice (The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME) were placed on special diets for 16 weeks. These diets were either high-fat (12492; Research Diets, New Brunswick, NJ), in which 60% of the total calories were derived from fat (soybean oil and lard), or an isocaloric low-fat diet (D12450B), in which 10% of the total calories were derived from fat.
PAL treatment
PAL was administered to cells as a conjugate with fatty-acid-free BSA prepared using methods described previously (18). Briefly, PAL was dissolved in ethanol and diluted 1:100 in 1% FBS-DMEM containing 2% (w/v) fatty-acid-free BSA, followed by a 5 min sonication and 15 min incubation at 55°C, cooled at room temperature, and administrated to myotubes. The myotubes were incubated with serum-free DMEM for 3 h and then treated with PAL at concentrations and times indicated, with or without cotreatment with 0.1 μM myriocin, an inhibitor of de novo sphingolipid synthesis. Samples were taken for lipid extraction and RNA isolation for quantitative real-time PCR.
LC/MS measurement
Except for the labeling experiments, analysis of sphingolipids was performed on a Thermo Finnigan TSQ 7000 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer, operating in a multiple reaction monitoring positive ionization mode as described (31).
PAL labeling and sphingolipid quantification
Cells were treated with BSA-conjugated uniformly labeled 13C-PAL exactly as described above. Lipids were extracted and subjected to analysis according to methods described previously (32).
RNA isolation and quantitative real-time PCR assay
Total RNA from C2C12 myotubes and mouse hind limb skeletal muscle isolated postmortem was isolated using the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). The first-strand cDNA was synthesized from 5 µg of total RNA using the SuperScript™ first-strand synthesis system for the RT-PCR kit from Invitrogen. The primers used were specific for mouse SK1 (forward 5′-ACAGTGGGGCACCTTCTTTC-3′ and reverse 5′-CTTCTGCACCAGTGTAGAGGC-3′), mouse SK2 (forward 5′-GACAGAACGACAGAACCATGC-3′ and reverse 5′-AGTCTGGCCGATCAAGGAG-3′), and mouse β-actin (forward 5′-CATGAAGTGTGACGTTGACATCCG-3′ and reverse 5′-GAGCAGTAATCTCCTTCTGCATCC-3′). Quantitative real-time PCR was performed on an iCycler system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA) in a reaction volume of 25 μl, including 12.5 μl of iQ™SYBR Green Supermix from Bio-Rad Laboratories, 2 μl of cDNA template, 1 μl of a primer mixture, and 9.5 μl of water. The signals derived from amplification of β-actin were used as internal controls. The initial denaturation was 3 min at 95°C, followed by 40 cycles of a 10 s melting at 95°C, and a 10 s annealing/extension at 55°C. The final step was a 55°C incubation for 1 min. Reactions were performed in triplicate. The results were analyzed using Q-gene software, which expresses data as mean normalized expression. Mean normalized expression is directly proportional to the amount of mRNA of the target gene relative to the amount of mRNA of the reference gene (β-actin).
SK activity assay
SK activity was determined as described previously with minor modifications (33). After treatment with 1.25 mM PAL for the indicated times, C2C12 myotubes were washed twice with cold PBS, scraped, and lysed with a Dounce homogenizer (40 strokes) in SK1 buffer containing 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 1 mM EDTA, 0.5 mM deoxypyridoxine, 15 mM NaF, 1 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 1 mM sodium orthovanadate, 40 mM β-glycerophosphate, 0.4 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 10% glycerol, 0.5% Triton X-100, and complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). Protein concentrations were determined using Micro BCATM protein assay reagent (Pierce Biotechnology, Rockford, IL). Sixty micrograms of protein was incubated in 100 µl of reaction mixture containing sphingosine (50 μM in 4 mg/ml fatty-acid-free BSA), 32P-ATP (5 µCi, 1 mM dissolved in 10 mM MgCl2), and SK1 buffer for 30 min at 37°C. The reaction was terminated by the addition of 10 µl of 1 N HCl and 400 µl of chloroform/methanol/HCl (100:200:1, v/v/v), vortexed vigorously, and allowed to stand at room temperature for 10 min. Subsequently, 120 µl of chloroform and 120 µl of 2 M KCl were added, and samples were centrifuged at 3,000 g for 5 min. Two hundred microliters of the organic phase was transferred to new glass tubes and dried. Samples were dissolved in chloroform/methanol/HCl (100:200:1, v/v/v). Lipids were then resolved on silica TLC plates using 1-butanol/methanol/acetic acid/water (8:2:1:2, v/v/v/v) as solvent system and visualized by autoradiography. The radioactive spots corresponding to S1P were scraped from the plates and quantified by liquid scintillation. Background values were determined in negative controls in which sphingosine was not added to the reaction mixture.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as means ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by two-tailed Student's t-test with a value of P < 0.05 considered significant.
RESULTS
Exogenous PAL serves as substrate for SPT and increases cellular dihydrosphingosine
To obtain a comprehensive view of cell sphingolipid profiles under conditions of excess PAL, lipid extracts from PAL-treated C2C12 myotubes were subjected to high-throughput LC/MS analysis as previously described (31). The first step in de novo sphingolipid synthesis occurs through the enzyme SPT, which resides in the endoplasmic reticulum and condenses serine with palmitoyl-CoA to generate 3-ketodihydrosphingosine. This transient intermediate then undergoes rapid reduction to dihydrosphingosine (DHSph), the first readily detectable product of de novo sphingolipid synthesis. LC/MS measurements indicated that PAL increased DHSph >5-fold (Fig. 1A), suggesting that PAL increased de novo sphingolipid synthesis.
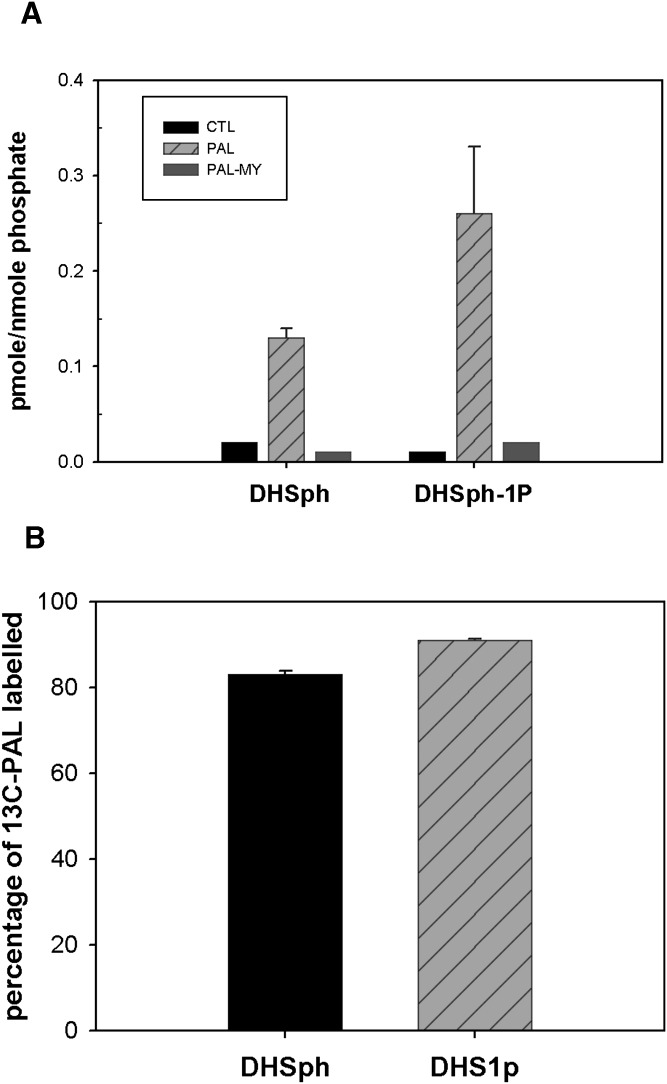
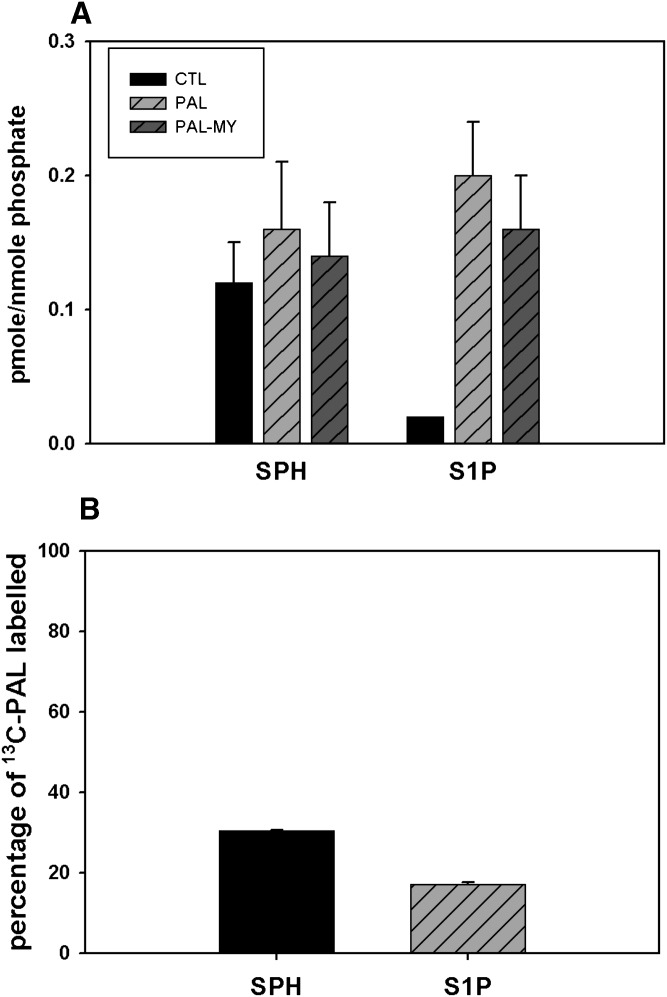
Fig. 1.
PAL increases cellular DHSph and DHSph-1-P. Mouse C2C12 myoblasts were cultured and differentiated into multinucleate myotubes as described in Materials and Methods. A: Cells were treated with 1.25 mM PAL with or without 0.1 μM myriocin. Lipid profiles were determined by LC/MS as described in Materials and Methods. Data are means ± SEM (n = 6) of four experiments. For both DHSph and DHSph1p, CTL versus PAL, P < 0.05; PAL versus PAL-MY, P < 0.05. B: Cells were treated with 1.25 mM uniformly labeled 13C- PAL. The percentage of 13C-PAL labeled in DHSph and DHSph-1-P was determined by LC/MS analysis. Data are means ± SEM (n = 3). CTL, control; MY, myriocin.
The Km of SPT for palmitoyl-CoA has been determined at ∼0.2 mM, in line with intracellular concentrations (20). This situation likely leaves SPT activity subject to changes from minor alterations in substrate concentration and, thus, current thinking holds that a major route of PAL-induced changes in sphingolipids derives from its use as substrate for SPT. On the other hand, PAL-induced DHSph production could also potentially result from hydrolysis of dihydroceramides by ceramidase enzymes (34). To distinguish between these two routes of DHSph production, a specific inhibitor of SPT, myriocin (35), was included in PAL treatment media. Results indicated that myriocin reduced PAL-induced DHSph to slightly lower than basal levels in untreated cells (Fig. 1A). These data indicate that PAL-induced DHSph indeed derived from de novo sphingolipid synthesis through SPT.
DHSph undergoes either N-acylation to dihydroceramide by dihydroceramide synthases (CerS) or phosphorylation to dihydrosphingosine-1 phosphate (DHSph-1-P) by SK. LC/MS measurements indicated that DHSph-1-P increased similarly in magnitude to DHSph (Fig. 1A), indicating that the pool of DHSph resulting from PAL treatment may undergo phosphorylation. Moreover, myriocin also attenuated PAL-induced DHSph-1-P production under these conditions.
Fatty acids play numerous cellular roles, including serving as an energy source through mitochondrial oxidation, mediating transcription by binding to nuclear receptors, and/or serving as substrates for production of lipid mediators. Though data indicating PAL-induced DHSph production was inhibited by myriocin confirmed that PAL treatment increases sphingolipid synthesis through SPT, they did not address potential routes by which this increase occurs. Therefore, to determine whether PAL became incorporated into the DHSph produced upon PAL treatment, cells were treated with uniformly labeled 13C-PAL to distinguish metabolic products of exogenously added PAL from metabolites derived through other routes. These data indicated that >80% of DHSph had incorporated the exogenously added 13C-PAL and, moreover, that the labeled DHSph served as substrate to produce DHSph-1-P (Fig. 1B). Moreover, incorporation of label into these species was completely attenuated by cotreatment with myriocin (data not shown). Together, these data confirm that exogenous PAL serves as substrate for SPT and thus drives DHSph production through de novo sphingolipid synthesis.
Ceramide production from exogenous PAL exhibits chain length specificity
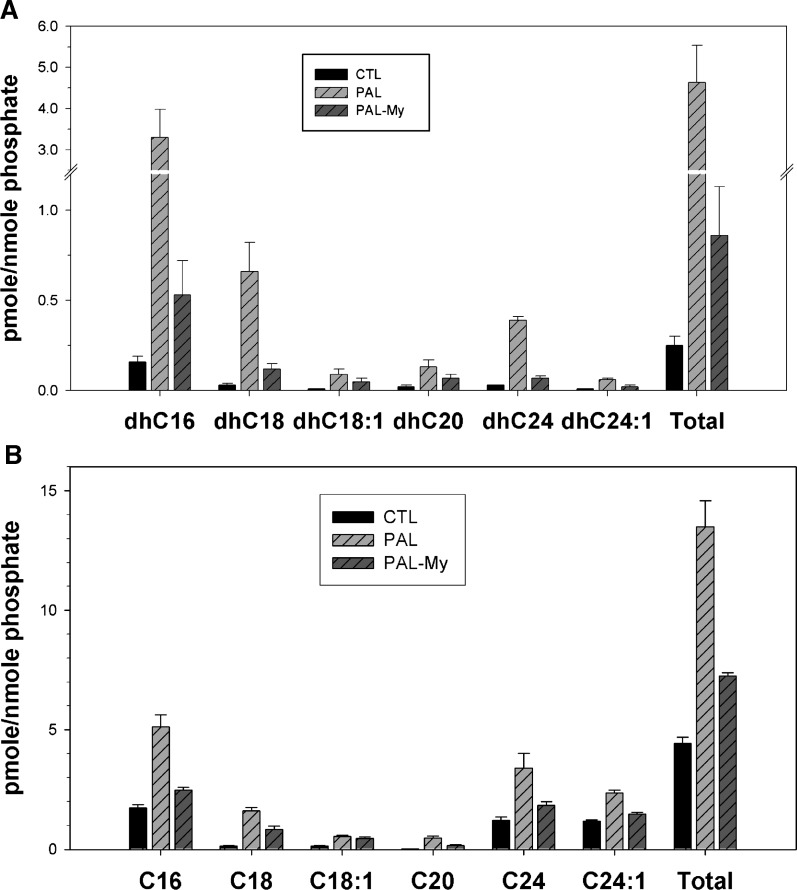
In addition to its phosphorylation to produce DHSph-1-P, a key fate of DHSph occurs through its N-acylation to form dihydroceramides, which can undergo desaturation to produce ceramides of various N-acyl chain lengths (Scheme 1). Importantly, although PAL and/or FFA treatment has been demonstrated to increase the ceramide content of rat and human skeletal muscle as well as C2C12 myotubes (2, 9, 19), the chain lengths of ceramides have never been determined in these systems. Since recent studies indicate different functional roles for different ceramide species (24, 36, 37), determining ceramides produced under these conditions may shed light on sphingolipid-dependent pathology associated with excess PAL. Indeed, LC/MS data revealed specificity in dihycroceramide profiles. For example, dihydroC16-cer, dihydroC18-cer, dihydroC24-cer, and dihydroC24:1-ceramide demonstrated the greatest changes upon PAL treatment, increasing by 16.8-, 7.5-, 14-, and 4-fold, respectively (Fig. 2A). These data suggest a preference for production of C16 and C24 ceramides in C2C12 myotubes treated with PAL. While the increase in C16 ceramides might result from increased C16 fatty acid (i.e., PAL), the specific increase in C24 ceramide was unexpected and may reflect cellular CerS isoform expression profiles (Scheme 1).
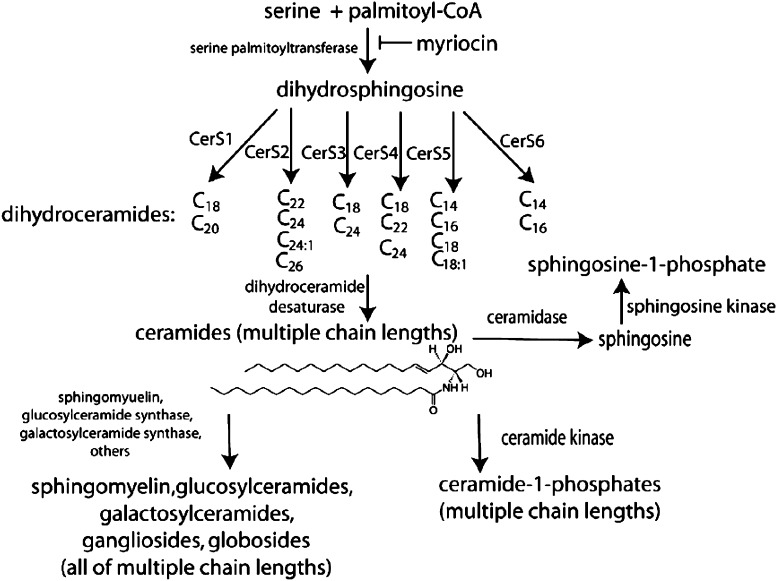
Scheme 1.
Complexity of sphingolipid biosynthetic pathways. Palmitoyl-CoA serves as substrate for the initial and rate-limiting step in de novo sphingolipid synthesis to form dihydrosphingosine, followed by acylation of dihydroceramide synthase (CerS) to generate ceramide. There are six isoforms of CerS, which play a specific action in formation of specifi c chain-length of ceramide. Ceramide can be converted to other interconnected bioactive lipid species. Ceramide can be phosphorylated by ceramide kinase to generate C1P, or can serve as a substrate for the synthesis of glycosphingolipids or sphingomyelin. Ceramide can be metabolized by ceramidases to produce sphingosine, which in turn is phosphorylated by sphingosine kinase to yield S1P, or, by a mechanism termed the ‘salvage’ pathway, undergoes CerS-mediated re-acylation back to ceramide.
Fig. 2.
Chain length specificity of dihydroceramides and ceramide production from exogenous PAL. C2C12 myotubes were treated with 1.25 mM PAL with or without myriocin for 14 h. Lipid profiles were determined by LC/MS measurements. A: N-acyl chain lengths of dihydroceramides. B: N-acyl chain lengths of ceramides. Data are means (n = 6) ± SEM of four experiments. In all length of dihydroceramides and ceramides as well as totals, CTL versus PAL, P < 0.05; PAL-MY versus PAL, P < 0.05. CTL, control; MY, myriocin; CER, ceramide; DHC, dihydroceramide.
PAL treatment increases C1P in a chain-length-specific manner
Ceramide can be phosphorylated by the recently cloned enzyme ceramide kinase (CERK). CERK belongs to the diacylglycerol kinase superfamily and uses ceramide to produce C1P (38). In addition to a purported role in activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 and inflammation (39), a recent study indicated an important role for CERK in the control of C1P, ceramide, and dihydroceramide levels (40).
To determine whether PAL altered C1P, these species were measured as described in Materials and Methods. The data indicated that the large majority of the C1P occurred with an N-acyl chain length of 18 carbons (see supplementary Fig. I). This may reflect either specificity of CERK and/or specificity of ceramide transport protein(CERT), which may transfer ceramide to the location of ceramide kinase (41). These data may also provide an explanation for the relatively low amounts of C18 ceramide detected upon PAL treatment (Fig. 2B), i.e., C18 ceramide may undergo preferential conversion to C1P.
13C-PAL labeling reveals complex routes for PAL-induced ceramide synthesis
As mentioned above, dihydroceramides undergo desaturation to generate ceramides. However, ceramides may also result from hydrolysis of complex lipids including glycosphingolipids and sphingomyelin or the salvage pathway of reacylation of SPH derived from ceramide hydrolysis. Therefore, differences between dihydroceramide and ceramide profiles after PAL treatment may indicate that PAL activates other routes of ceramide production in addition to de novo synthesis. Importantly, myriocin should not directly inhibit ceramide generated via these routes. In general, PAL treatment increased ceramides bearing N-acyl chain lengths similar to those incorporated into dihydroceramide, i.e., the greatest changes were observed in C16, C18, C24, and C24:1 species (Fig. 2B). Intriguingly, however, while myriocin nearly completely blocked dihydroceramides produced upon PAL treatment, ceramides demonstrated slightly less susceptibility to inhibition with myriocin, indicating that some ceramide species may derive from routes of synthesis not requiring SPT activity.
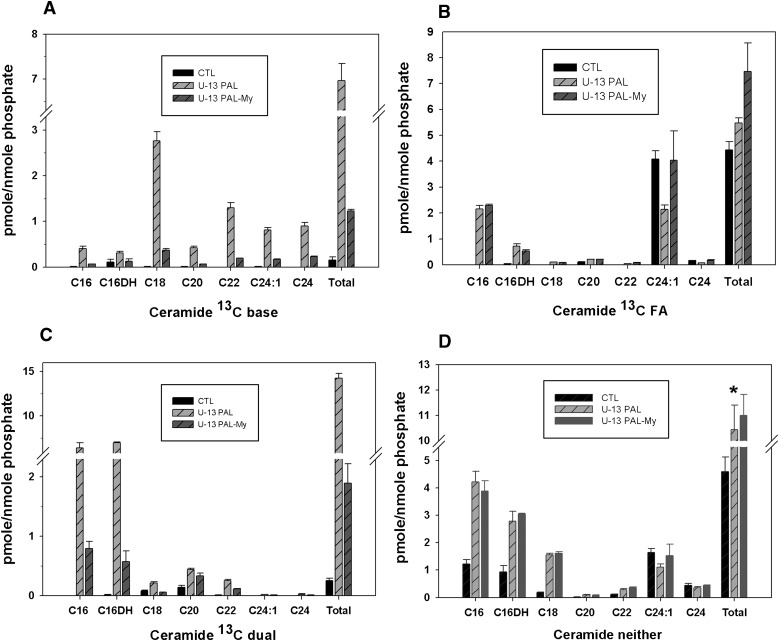
To distinguish between ceramides derived from these different routes, cells were treated with 13C-PAL. Labeling ceramides followed by LC/MS analysis allowed determination of where the 13C-PAL becomes incorporated as substrate, including distinguishing whether the label is incorporated in the DHSph backbone (base), in the N-acyl chain, in both chains of ceramide (dual), or in neither chain of ceramide (neither). This strategy revealed significant labeling in the base (Fig. 3A), as may be expected given the specificity of SPT for PAL (42). Consistent with this finding, base labeling was largely attenuated by myriocin. Significant labeling also occurred in the N-acyl chain (FA) with the majority as C16, consistent with incorporation of PAL into the fatty acid chain without significant fatty acid elongation through endogenous mechanisms (Fig. 3B). As expected, myriocin did not inhibit this incorporation, which is carried out by CerS rather than SPT (Scheme 1). Moreover, the lack of incorporation of label into the base of these indicated that the base likely derived from existing DHSph or sphingosine (SPH). However, basal DHSph levels were approximately 15 pmole/nmole phosphate (data not shown), only 25% of that needed to generate the >5 pmol/nmole phosphate of ceramides labeled in the fatty acid chain. These findings are consistent with the notion that PAL treatment may stimulate the salvage pathway of ceramide synthesis, which occurs through deacylation of ceramides followed by reacylation with a different N-acyl chain length fatty acyl-coA. Importantly, while distinct roles for ceramide produced through the salvage pathway are emerging, very few stimuli are known (43). These data indicate that PAL may serve to stimulate this pathway.
Fig. 3.
Labeling studies indicate diverse mechanisms for PAL-induced ceramide production. C2C12 myotubes were treated with 1.25 mM uniformly labeled 13C- PAL with or without 0.1 μM myriocin. After 14 h treatment, the lipid fraction was extracted from cell pellets and subjected to LC/MS analysis. The label became incorporated in the dihydrosphingosine backbone (base) (A), in the N-acyl chain (B), in both chains of ceramide (dual) (C), or in neither chain of ceramide (neither) (D). Data are expressed as means (n = 3) ± SEM. For all N-acyl chain lengths and for total ceramide, CTL versus PAL, P < 0.05; PAL-MY versus PAL, P < 0.05. CTL, control; MY, myriocin. FA, N-acyl chain.
Ceramide species where label incorporated into both the base and the fatty acid chains were measured, and, as expected, these species were both inhibitable with myriocin and shifted toward C16 ceramides (Fig. 3C). Intriguingly, a portion of ceramides occurring upon PAL treatment did not contain label in either the base or the N-acyl chain (Fig. 3D), indicating they did not derive from SPT or salvage using the exogenous PAL, but rather, their production likely resulted from PAL-induced hydrolysis of complex sphingolipids, i.e., glucosylceramides or existing sphingomyelin. On the other hand, they could be derived from de novo synthesis with endogenous fatty acids, which would require SPT; however, myriocin did not block production of these species, supporting the conclusion that these species derive from hydrolysis of complex lipids. In total, approximately 6 pmole/nmole phosphate of ceramide occurred as unlabeled; we also observed a decrease in sphingomyelin upon treatment with PAL in the amount of approximately 15 pmole/nmole phosphate (see supplementary Fig. IIA), whereas no decrease in any glycosphingolipids was observed (see supplementary Fig. IIB). Together, these data indicate that PAL treatment may activate sphingomyelinase to produce some ceramide from sphingomyelin that existed in cells previous to PAL treatment. Importantly, however, SPT-dependent species (labeled in the base or both base and N-acyl chain) comprised the majority (75%) of total ceramide mass increase upon PAL treatment, the increase in unlabeled ceramide species comprise approximately 25%, underscoring the importance of de novo sphingolipid synthesis through SPT as a key player in increasing cell ceramide content upon PAL treatment.
PAL upregulates SK, which can be prevented by oleate
In addition to its phosphorylation or incorporation into complex sphingolipids, a key fate of ceramide occurs upon its cleavage to produce SPH. SPH serves as the metabolic precursor for S1P, a potent lipid signaling molecule with several well-defined cellular activities key for skeletal muscle development, repair, and function (44, 45). LC/MS measurements of SPH indicated levels of this compound remained stable in response to each treatment. Specifically, SPH levels exhibited little change upon PAL treatment and no change in the presence of myriocin (Fig. 4A). On the other hand, PAL treatment induced a 4-fold change in S1P (Fig. 4A). Intriguingly, myriocin had no effect on levels of this key molecule, indicating its increase by PAL occurred independently of de novo sphingolipid synthesis. This conclusion drew further support through data from 13C-PAL labeling studies. Specifically, in contrast to DHSph and DHSph-1-P (Fig. 1B), both SPH and S1P were comprised mainly of 12C-PAL (Fig. 4B), The percentage of total SPH and S1P that contain 13C-PAL are only approximately 30% and 17%, respectively, showing incorporated exogenous 13C-PAL. These data indicate that they did not derive primarily from exogenously added PAL, but rather, other mechanisms.
Fig. 4.
PAL increased S1P independently of de novo sphingolipid synthesis. A: C2C12 myotubes were treated with 1.25 mM PAL for 14 h. SPH and S1P were determined by LC/MS measurements. Data are means (n = 6) ± SEM of four experiments. In SPH, PAL versus CTL, P > 0.05; PAL-MY versus PAL, P > 0.05; in S1P, PAL versus CTL, P < 0.05; PAL-MY versus PAL, P > 0.05. B: C2C12 myotubes were treated with 1.25 mM uniformly labeled 13C- PAL with or without 0.1 μM myriocin described as in Materials and Methods. The lipid fraction was extracted from cell pellets and subjected to LC/MS analysis. The graph shows the percentage of DHSph and DHSPh-1-P containing the 13C-PAL label. Data are means (n = 3) ± SEM. CTL, control; MY, myriocin.
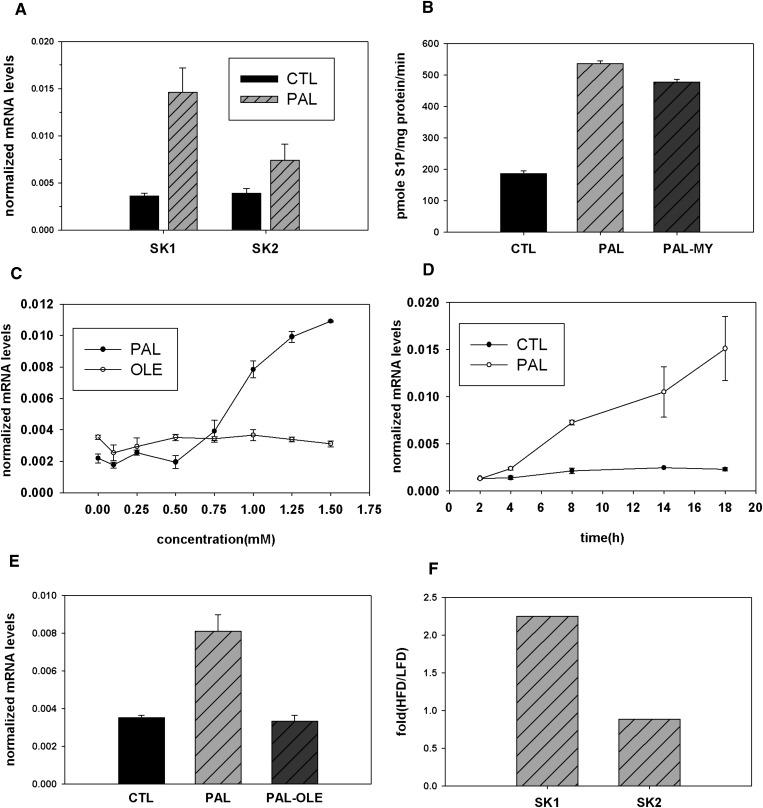
The increase of S1P upon PAL treatment, coupled with the lack of inhibition of S1P by myriocin and lack of incorporation of exogenous PAL into S1P, raised the possibility that in addition to serving as substrate for de novo synthesis, PAL may direct its own fate via regulation of sphingolipid metabolic enzymes. Quantitative real-time PCR experiments demonstrated the key enzymes producing S1P, SK1 and SK2, increased upon PAL treatment by approximately 4- and 2-fold, respectively (Fig. 5A). The increase of SK1 message occurred in a dose- and time-dependent manner (Fig. 5, C and D). PAL did not alter the expression of the reference gene encoding β-actin (data not shown). Furthermore, PAL treatment increased SK enzyme activity by 2.3-fold (Fig. 5B). Myriocin did not attenuate this activity increase, indicating this effect occurs independently of PAL-induced de novo sphingolipid synthesis. Together these data suggest a role for PAL in regulation of S1P levels through increasing SK message and activity.
Fig. 5.
PAL upregulates SK. A: C2C12 myotubes were treated with 1.25 mM PAL for 14 h. SK1 and SK2 mRNA expression was determined by quantitative real-time PCR. Data are presented as means (n = 5) ± SEM. For SK1, CTL versus PAL, P < 0.05; for SK2, CTL versus PAL, P > 0.05. B: C2C12 myotubes were treated with 1.25 mM PAL with or without 0.1 μM myriocin for 14 h, and SK1 enzyme activity was determined. Data are mean (n = 2) ± SEM; t-test, two-sample assuming equal variances, CTL versus PAL, P < 0.01; PAL versus PAL-MY, P < 0.05. C: C2C12 myotubes were treated with PAL or oleate at the indicated concentrations for 14 h, and SK1 mRNA expression was determined by quantitative real-time PCR. D: C2C12 myotubes were treated with 1.25 mM PAL at the indicated time course, and SK1 mRNA expression was determined by quantitative real-time PCR. E: C2C12 myotubes were treated with 1.25 mM PAL with or without 0.75 mM oleate for 14 h, and SK1 mRNA expression was determined by quantitative real-time PCR. Data are mean (n = 3) ± SEM. For PAL versus CTL, P < 0.05; PAL-OLE versus PAL, P < 0.01. F: Mice were placed on a high-fat diet or isocaloric low-fat control diet for 16 weeks. Hind limb skeletal muscle was isolated postmortem, and tissue homogenates were used for SK message level. Data are mean (n = 3) ± SEM. CTL, control; OLE, oleate, MY, myriocin; HFD, high-fat diet; LFD, low-fat diet.
Production of the sphingoid backbone of sphingolipids can be regulated by the availability of saturated fatty acids, which have generally been regarded to be more pathogenic than unsaturated ones (46, 47); plasma FFAs are largely composed of the saturated fatty acid PAL (C16:0) and the unsaturated oleate (C18:1) (48). To test if PAL demonstrated specificity in induction of SK1 message, the cells were treated with PAL or oleate. The results indicated PAL specifically increased SK1 mRNA expression at concentrations as low as 0.75 mM, while oleate showed no significant increase at up to 1.5 mM (Fig. 5C). Real-time PCR measurements indicated that oleate prevents PAL-induced upregulation of SK1 message (Fig. 5E). Thus, the increase in SK1 demonstrates some specificity for PAL, which is generally considered more pathogenic than oleate, which, according to recent data, may protect against PAL-induced lipotoxic effects (46, 47, 49).
Diet-induced obesity increases SK1 message in mice
To determine whether the induction of SK1 bore relevance to a disease model, the diet-induced obesity model was used. In this model, mice are placed on a high-fat diet and subsequently become obese and display pathological sequelae of obesity, including insulin resistance and elevated plasma FFA similar to the metabolic syndrome in humans (50). Accordingly, mice were placed on a high-fat diet or isocaloric low-fat control diet for 14 weeks, by which time elevation in plasma FFA is observed (51). Hind limb skeletal muscle was isolated postmortem, and tissue homogenates were used for determinations of SK message level. Indeed, compared with controls, high-fat-diet-fed mice exhibited a 2.3-fold increase in message for SK1 (Fig. 5F). In contrast with the cell culture model, SK2 changed very little. These data indicate that PAL-mediated induction of SK1 occurs in an animal model of metabolic disease and, thus, may have functional relevance to obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
DISCUSSION
Obesity and/or disordered adipocyte function raise levels of circulating FFA (52–54). This elevation promotes deposition of fatty acids into peripheral tissues, where they undergo incorporation into various lipid species, including signaling lipids, such as diacylglycerol and sphingolipids (55, 56). The aberrant production of bioactive lipids is thought to mediate pathologies associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. Herein, we have characterized the effect of PAL and/or a high-fat diet on sphingolipid pools in skeletal muscle cells. In rodent models of obesity, plasma FFAs (of which PAL is the major component) increase from below 0.5 mM, for nonobese animals, to over 2 mM. Prior to initiating these experiments, we did a PAL dose response on C2C12 myotubes and measured cell survival by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-Yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay and common apoptotic markers (data not shown). We found that 1.25 mM PAL was consistent with the pathological in vivo FFA concentrations in obese animals, while still permitting survival of cells in culture. Thus, experiments were performed at this concentration. However, we also performed a time course for lipidomic assay from 0.5, 2, 4, 6, 14, and 24 h. Trends in lipid increases showed little kinetic variation (see supplementary Figs. II and III). Maximal changes occurred at 14 h and tapered off at later time points; thus, 14 h treatments were used in subsequent experiments. The data from C2C12 myotubes indicate that PAL caused broad changes in sphingolipid pools. These changes included specific increases in ceramides, most notably C24, C24:1, and C16. Though labeling studies indicated that PAL stimulated ceramide production through the salvage pathway as well as complex sphingolipid hydrolysis, most PAL-induced ceramide demonstrated inhibition by myriocin, indicating that the largest effects of PAL on sphingolipid profiles occurs via its use as substrate for de novo sphingolipid synthesis.
In general, saturated fatty acids, including PAL (C16:0) and stearate (C18:0), give rise to greater pathology than unsaturated FFA, including oleate (C18:1) (46, 47, 49). In fact, a recent study indicated that, while PAL caused insulin resistance, cotreatment with oleate could restore insulin sensitivity in C2C12 myotubes (46). Interestingly, the FFA-mediated induction of SK1 occurred only upon PAL treatment, and oleate caused no appreciable increase in SK1 message. This may suggest that SK1 and S1P mediate pathological roles of FFA and/or that SK1 induction may occur in response to FFA-induced muscle damage. Moreover, cotreatment of cells with PAL and oleate resulted in returning SK1 message levels to normal. These data suggest that the effect of PAL on message level may play a role in saturated FA-mediated skeletal muscle pathology.
S1P plays several key roles in skeletal muscle repair and differentiation of myoblasts to myotubes. Work by the Bruni group has demonstrated a major requirement for S1P in the process of differentiation from myocytes to myotubes (45). Thus, we assayed expression of markers of myotube differentiation under these conditions. In fact, we found that PAL treatment did not change two of the markers and significantly reduced the expression of a key marker, myogenin (see supplementary Fig. V). We hypothesize that, under these conditions, the toxic effect of ceramides and/or other metabolites of PAL significantly outweigh the potential prodifferentiation actions of S1P. Moreover, prodifferentiation activities of S1P were demonstrated during the myoblast to myotube transition, whereas the current studies have been performed in differentiated myotubes. This suggests that functions of S1P in skeletal muscle depend on the differentiation state of the tissue.
The increase in SK1 message observed under conditions of high PAL was recapitulated in the diet-induced obesity mouse model. These mice exhibit elevation of plasma FFA concomitant with inception of pathologies similar to the metabolic syndrome in humans. These pathologies include insulin resistance (9, 10), aberrant gene regulation (11), and inflammation (12). The aberrant SK1 expression in skeletal muscle of these mice may suggest that sphingolipids may link elevation of plasma FFA to some of these deleterious sequelae. We hypothesize that S1P is probably not involved in insulin signaling but may mediate other deleterious effects of FFA on skeletal muscle, for example, inflammation. One particularly attractive hypothesis includes a role for S1P in FFA-induced skeletal muscle inflammation, as this lipid has been implicated in numerous inflammatory processes (13, 15, 57). However, further investigation will be required to determine and/or identify a role for FFA induction of SK in skeletal muscle inflammation. On the other hand, though there are no previously identified functions for S1P downstream from plasma FFA elevation, several key roles for S1P in normal muscle are known, including differentiation of myoblasts to myotubes and recruitment of fibroblasts to replace damaged myotubes (as reviewed in Refs. 45 and 58). Thus, induction of SK1 and S1P increase in skeletal muscle may serve a protective role in muscle repair under these potentially damaging conditions.
Though bulk ceramide has been demonstrated to cause insulin resistance via modulation of Akt2 phophorylation via ceramide-activated protein phosphatase PP2A (59), many other signaling targets for ceramides are currently known, including PP1, PKC isoforms, KSR, RAF, JNK, RAC, p38, cathepsin D, and Rb (as reviewed in Ref. 60). Moreover, distinct cellular functions for ceramides with specific N-acyl chain lengths are beginning to emerge (61). Thus, several important questions remain. First, which ceramide species mediate skeletal muscle insulin resistance? Studies presented here may implicate either C16 and/or C24 ceramides in this process. Moreover, do ceramides of other chain lengths, and/or other sphingolipids including C1P and SPH, play additional deleterious roles in skeletal muscle exposed to excess FFA? Answering these questions may allow future targeting of specific enzymes of sphingolipid biosynthesis to ameliorate FFA-induced skeletal muscle toxicity.
Lipidomic data revealed no decreases in glycosphingolipids (see supplementary Fig. IIA), but statistically significant decreases occurred in sphingomyelins (see supplementary Fig. IIB) in amounts more than sufficient to account for the catabolically derived ceramides. Thus, we now conclude that these unlabeled ceramides, which increase upon PAL treatment, derive from sphingomyelin hydrolysis. To address potential mechanism(s) by which this occurs, we determined message levels and found no increases in neutral sphingomyelinase message (data not shown). While few mechanisms of nSMase2 activation are known, oxidative stress has been shown to increase nSMase2 activity (62). We propose that the increased oxidative stress associated with PAL treatment may cause the activation of nSMase2, thus decreasing sphingomyelin and producing unlabeled ceramides.
In conclusion, elevated PAL precipitates broad changes in sphingolipid profiles, including increasing levels of many sphingolipid species with known signaling properties. Moreover, in addition to use as substrate for SPT, PAL acts through other routes to increase SK1 and S1P. These observations may shed light on potential mechanisms of FFA-induced skeletal muscle dysfunction.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the assistance of Alexa Orr for technical advice on the SK activity assay and Jason L. Gandy for technical assistance in real-time PCR. We would also like to thank Dr. Ashley Snider for providing SK PCR primers, Christopher Clarke for valuable discussion, and Sarah Brice for comments on the manuscript. We would like to acknowledge Dr. Lina Obeid for a thorough reading of the manuscript and helpful suggestions. Except for the labeling studies, LC/MS lipid measurements were performed at the Lipidomics Core Facility at the Medical University of South Carolina.
Footnotes
Abbreviations:
- C1P
- ceramide-1-phosphate
- CERK
- ceramide kinase
- CerS
- ceramide synthase, DHSph, dihydrosphingosine
- DHSph-1-P
- dihydrosphingosine-1-phosphate
- PAL
- palmitate
- S1P
- sphingosine-1-phosphate
- SK
- sphingosine kinase
- SPH
- sphingosine
- SPT
- serine palmitoyltransferase
This work was supported by funding from the Department of Veteran's Affairs and the National Institutes of Health COBRE in Lipidomics and Pathobiology at the Medical University of South Carolina to L.A.C.
The online version of this article (available at http://www.jlr.org) contains supplementary data in the form of five figures.
REFERENCES
- 1.Shah C., Yang G., Lee I., Bielawski J., Hannun Y. A., Samad F. 2008. Protection from high fat diet-induced increase in ceramide in mice lacking plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 283: 13538–13548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Adams J. M., II, Pratipanawatr T., Berria R., Wang E., DeFronzo R. A., Sullards M. C., Mandarino L. J. 2004. Ceramide content is increased in skeletal muscle from obese insulin-resistant humans. Diabetes. 53: 25–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lee J. S., Pinnamaneni S. K., Eo S. J., Cho I. H., Pyo J. H., Kim C. K., Sinclair A. J., Febbraio M. A., Watt M. J. 2006. Saturated, but not n-6 polyunsaturated, fatty acids induce insulin resistance: role of intramuscular accumulation of lipid metabolites. J. Appl. Physiol. 100: 1467–1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Summers S. A. 2006. Ceramides in insulin resistance and lipotoxicity. Prog. Lipid Res. 45: 42–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Straczkowski M., Kowalska I., Baranowski M., Nikolajuk A., Otziomek E., Zabielski P., Adamska A., Blachnio A., Gorski J., Gorska M. 2007. Increased skeletal muscle ceramide level in men at risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 50: 2366–2373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Samad F., Hester K. D., Yang G., Hannun Y. A., Bielawski J. 2006. Altered adipose and plasma sphingolipid metabolism in obesity: a potential mechanism for cardiovascular and metabolic risk. Diabetes. 55: 2579–2587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Holland W. L., Summers S. A. 2008. Sphingolipids, insulin resistance, and metabolic disease: new insights from in vivo manipulation of sphingolipid metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 29: 381–402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Holland W. L., Knotts T. A., Chavez J. A., Wang L. P., Hoehn K. L., Summers S. A. 2007. Lipid mediators of insulin resistance. Nutr. Rev. 65: S39–S46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Holland W. L., Brozinick J. T., Wang L. P., Hawkins E. D., Sargent K. M., Liu Y., Narra K., Hoehn K. L., Knotts T. A., Siesky A., et al. 2007. Inhibition of ceramide synthesis ameliorates glucocorticoid-, saturated-fat-, and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 5: 167–179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schmitz-Peiffer C., Craig D. L., Biden T. J. 1999. Ceramide generation is sufficient to account for the inhibition of the insulin-stimulated PKB pathway in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells pretreated with palmitate. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 24202–24210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhou Q., Du J., Hu Z., Walsh K., Wang X. H. 2007. Evidence for adipose-muscle crosstalk: opposing regulation of muscle proteolysis by adiponectin and fatty acids. Endocrinology. 148: 5696–5705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Richardson D. K., Kashyap S., Bajaj M., Cusi K., Mandarino S. J., Finlayson J., DeFronzo R. A., Jenkinson C. P., Mandarino L. J. 2005. Lipid infusion decreases the expression of nuclear encoded mitochondrial genes and increases the expression of extracellular matrix genes in human skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 280: 10290–10297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Alvarez S. E., Milstien S., Spiegel S. 2007. Autocrine and paracrine roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 18: 300–307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pettus B. J., Bielawska A., Subramanian P., Wijesinghe D. S., Maceyka M., Leslie C. C., Evans J. H., Freiberg J., Roddy P., Hannun Y. A., et al. 2004. Ceramide 1-phosphate is a direct activator of cytosolic phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 11320–11326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pettus B. J., Chalfant C. E., Hannun Y. A. 2004. Sphingolipids in inflammation: roles and implications. Curr. Mol. Med. 4: 405–418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hannun Y. A., Obeid L. M. 2008. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9: 139–150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ruvolo P. P. 2003. Intracellular signal transduction pathways activated by ceramide and its metabolites. Pharmacol. Res. 47: 383–392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chavez J. A., Holland W. L., Bar J., Sandhoff K., Summers S. A. 2005. Acid ceramidase overexpression prevents the inhibitory effects of saturated fatty acids on insulin signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 280: 20148–20153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chavez J. A., Knotts T. A., Wang L. P., Li G., Dobrowsky R. T., Florant G. L., Summers S. A. 2003. A role for ceramide, but not diacylglycerol, in the antagonism of insulin signal transduction by saturated fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 10297–10303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Merrill A. H., Jr., Wang E., Mullins R. E. 1988. Kinetics of long-chain (sphingoid) base biosynthesis in intact LM cells: effects of varying the extracellular concentrations of serine and fatty acid precursors of this pathway. Biochemistry. 27: 340–345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Williams R. D., Wang E., Merrill A. H., Jr 1984. Enzymology of long-chain base synthesis by liver: characterization of serine palmitoyltransferase in rat liver microsomes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 228: 282–291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cowart L. A., Hannun Y. A. 2007. Selective substrate supply in the regulation of yeast de novo sphingolipid synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 282: 12330–12340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Alvarez-Vasquez F., Sims K. J., Okamoto Y., Cowart L. A., Voit E. O., Hannun Y. 2005. Simulation and evaluation of sphingolipid metabolism in S. cerevisiae. Nature. 433: 425–429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Seumois G., Fillet M., Gillet L., Faccinetto C., Desmet C., Francois C., Dewals B., Oury C., Vanderplasschen A., Lekeux P., et al. 2007. De novo C16- and C24-ceramide generation contributes to spontaneous neutrophil apoptosis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 81: 1477–1486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Spiegel S., Milstien S. 2002. Sphingosine 1-phosphate, a key cell signaling molecule. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 25851–25854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lamour N. F., Chalfant C. E. 2005. Ceramide-1-phosphate: the “missing” link in eicosanoid biosynthesis and inflammation. Mol. Interv. 5: 358–367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Straczkowski M., Kowalska I., Nikolajuk A., Dzienis-Straczkowska S., Kinalska I., Baranowski M., Zendzian-Piotrowska M., Brzezinska Z., Gorski J. 2004. Relationship between insulin sensitivity and sphingomyelin signaling pathway in human skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 53: 1215–1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Boomkamp S. D., Butters T. D. 2008. Glycosphingolipid disorders of the brain. Subcell. Biochem. 49: 441–467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chavez J. A., Summers S. A. 2003. Characterizing the effects of saturated fatty acids on insulin signaling and ceramide and diacylglycerol accumulation in 3T3–L1 adipocytes and C2C12 myotubes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 419: 101–109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Van Heek M., Compton D. S., France C. F., Tedesco R. P., Fawzi A. B., Graziano M. P., Sybertz E. J., Strader C. D., Davis H. R., Jr 1997. Diet-induced obese mice develop peripheral, but not central, resistance to leptin. J. Clin. Invest. 99: 385–390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bielawski J., Szulc Z. M., Hannun Y. A., Bielawska A. 2006. Simultaneous quantitative analysis of bioactive sphingolipids by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Methods. 39: 82–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Merrill A. H., Jr., Sullards M. C., Allegood J. C., Kelly S., Wang E. 2005. Sphingolipidomics: high-throughput, structure-specific, and quantitative analysis of sphingolipids by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Methods. 36: 207–224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Olivera A., Rosenthal J., Spiegel S. 1996. Effect of acidic phospholipids on sphingosine kinase. J. Cell. Biochem. 60: 529–537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mao C., Obeid L. M. 2008. Ceramidases: regulators of cellular responses mediated by ceramide, sphingosine, and sphingosine-1-phosphate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1781: 424–434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Miyake Y., Kozutsumi Y., Nakamura S., Fujita T., Kawasaki T. 1995. Serine palmitoyltransferase is the primary target of a sphingosine-like immunosuppressant, ISP-1/myriocin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 211: 396–403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kitatani K., Idkowiak-Baldys J., Bielawski J., Taha T. A., Jenkins R. W., Senkal C. E., Ogretmen B., Obeid L. M., Hannun Y. A. 2006. Protein kinase C-induced activation of a ceramide/protein phosphatase 1 pathway leading to dephosphorylation of p38 MAPK. J. Biol. Chem. 281: 36793–36802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Karahatay S., Thomas K., Koybasi S., Senkal C. E., Elojeimy S., Liu X., Bielawski J., Day T. A., Gillespie M. B., Sinha D., et al. 2007. Clinical relevance of ceramide metabolism in the pathogenesis of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): attenuation of C(18)-ceramide in HNSCC tumors correlates with lymphovascular invasion and nodal metastasis. Cancer Lett. 256: 101–111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sugiura M., Kono K., Liu H., Shimizugawa T., Minekura H., Spiegel S., Kohama T. 2002. Ceramide kinase, a novel lipid kinase. Molecular cloning and functional characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 23294–23300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lamour N. F., Chalfant C. E. 2008. Ceramide kinase and the ceramide-1-phosphate/cPLA2alpha interaction as a therapeutic target. Curr. Drug Targets. 9: 674–682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Graf C., Zemann B., Rovina P., Urtz N., Schanzer A., Reuschel R., Mechtcheriakova D., Muller M., Fischer E., Reichel C., et al. 2008. Neutropenia with impaired immune response to Streptococcus pneumoniae in ceramide kinase-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 180: 3457–3466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lamour N. F., Stahelin R. V., Wijesinghe D. S., Maceyka M., Wang E., Allegood J. C., Merrill A. H., Jr., Cho W., Chalfant C. E. 2007. Ceramide kinase uses ceramide provided by ceramide transport protein: localization to organelles of eicosanoid synthesis. J. Lipid Res. 48: 1293–1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hirabayashi Y., Igarashi Y., Merrill A. H., Jr 2006. Sphingolipid Biology. 1st ed. Springer-Verlag, Tokyo: pp. 25–47. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kitatani K., Idkowiak-Baldys J., Hannun Y. A. 2008. The sphingolipid salvage pathway in ceramide metabolism and signaling. Cell. Signal. 20: 1010–1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bruni P., Donati C. 2008. Pleiotropic effects of sphingolipids in skeletal muscle. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65: 3725–3736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Donati C., Meacci E., Nuti F., Becciolini L., Farnararo M., Bruni P. 2005. Sphingosine 1-phosphate regulates myogenic differentiation: a major role for S1P2 receptor. FASEB J. 19: 449–451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Pickersgill L., Litherland G. J., Greenberg A. S., Walker M., Yeaman S. J. 2007. Key role for ceramides in mediating insulin resistance in human muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 282: 12583–12589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Coll T., Eyre E., Rodriguez-Calvo R., Palomer X., Sanchez R. M., Merlos M., Laguna J. C., Vazquez-Carrera M. 2008. Oleate reverses palmitate-induced insulin resistance and inflammation in skeletal muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 283: 11107–11116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Katan M. B., Zock P. L., Mensink R. P. 1994. Effects of fats and fatty acids on blood lipids in humans: an overview. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 60 (Suppl. 6): 1017S–1022S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gaster M., Rustan A. C., Beck-Nielsen H. 2005. Differential utilization of saturated palmitate and unsaturated oleate: evidence from cultured myotubes. Diabetes. 54: 648–656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Thakker G. D., Frangogiannis N. G., Bujak M., Zymek P., Gaubatz J. W., Reddy A. K., Taffet G., Michael L. H., Entman M. L., Ballantyne C. M. 2006. Effects of diet-induced obesity on inflammation and remodeling after myocardial infarction. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 291: H2504–H2514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Shah C., Yang G., Lee I., Bielawski J., Hannun Y. A., Samad F. 2008. Protection from high fat diet-induced increase in ceramide in mice lacking plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 283: 13538–13548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Boden G. 2006. Fatty acid-induced inflammation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle and liver. Curr. Diab. Rep. 6: 177–181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.de Ferranti S., Mozaffarian D. 2008. The perfect storm: obesity, adipocyte dysfunction, and metabolic consequences. Clin. Chem. 54: 945–955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Bergman R. N., Kim S. P., Hsu I. R., Catalano K. J., Chiu J. D., Kabir M., Richey J. M., Ader M. 2007. Abdominal obesity: role in the pathophysiology of metabolic disease and cardiovascular risk. Am. J. Med. 120: S3–S8. (discussion S29–S32). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Unger R. H. 2003. Minireview: weapons of lean body mass destruction: the role of ectopic lipids in the metabolic syndrome. Endocrinology. 144: 5159–5165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Unger R. H., Orci L. 2000. Lipotoxic diseases of nonadipose tissues in obesity. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 24(Suppl 4): S28–S32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Taha T. A., Hannun Y. A., Obeid L. M. 2006. Sphingosine kinase: biochemical and cellular regulation and role in disease. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 39: 113–131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Donati C., Bruni P. 2006. Sphingosine 1-phosphate regulates cytoskeleton dynamics: implications in its biological response. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1758: 2037–2048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Stratford S., Hoehn K. L., Liu F., Summers S. A. 2004. Regulation of insulin action by ceramide: dual mechanisms linking ceramide accumulation to the inhibition of Akt/protein kinase B. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 36608–36615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Snook C. F., Jones J. A., Hannun Y. A. 2006. Sphingolipid-binding proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1761: 927–946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Senkal C. E., Ponnusamy S., Rossi M. J., Bialewski J., Sinha D., Jiang J. C., Jazwinski S. M., Hannun Y. A., Ogretmen B. 2007. Role of human longevity assurance gene 1 and C18-ceramide in chemotherapy-induced cell death in human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Mol. Cancer Ther. 6: 712–722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Miller T. A., LeBrasseur N. K., Cote G. M., Trucillo M. P., Pimentel D. R., Ido Y., Ruderman N. B., Sawyer D. B. 2005. Oleate prevents palmitate-induced cytotoxic stress in cardiac myocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336: 309–315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.