Abstract
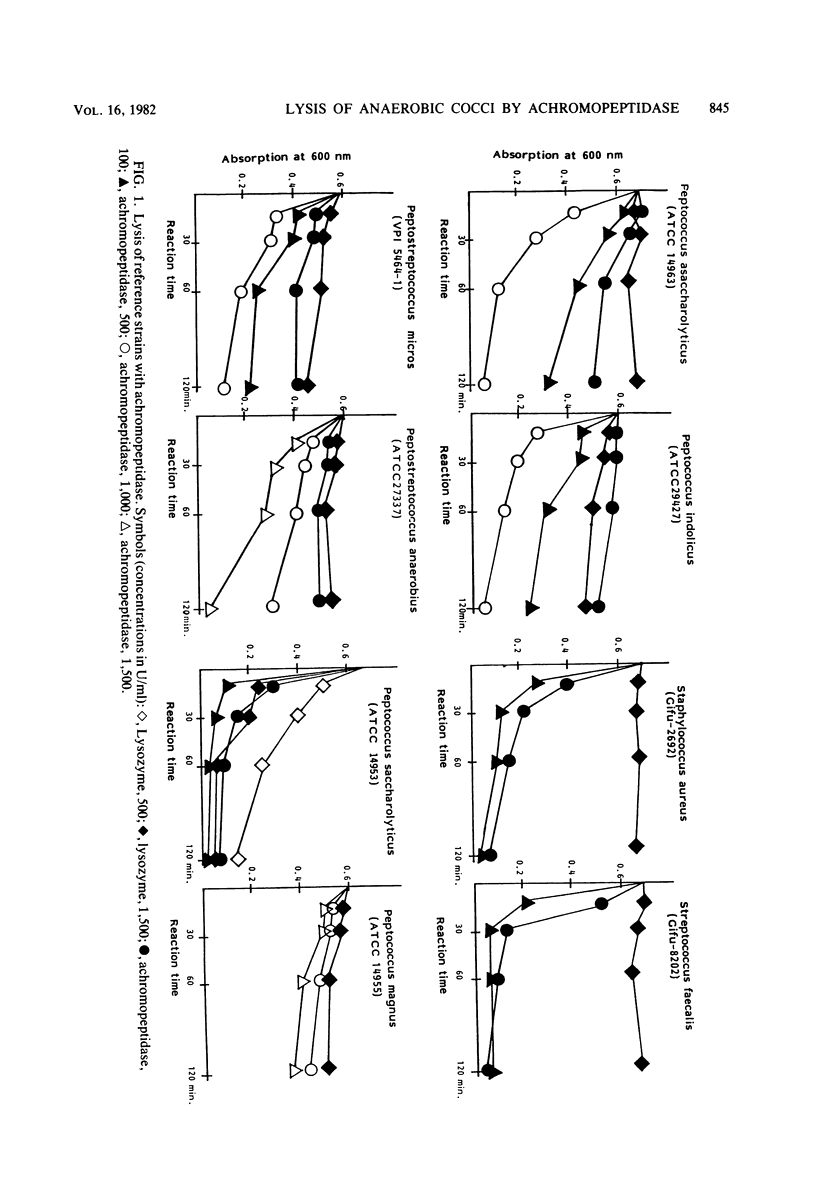
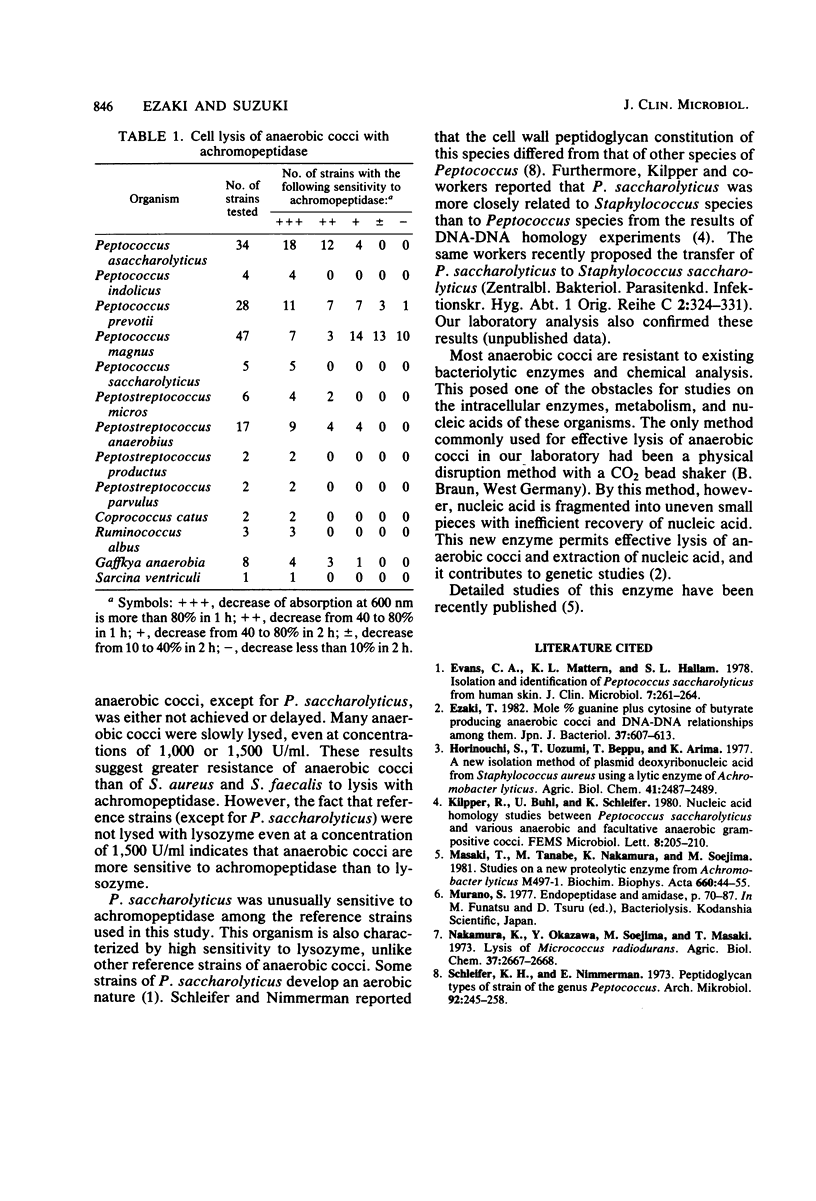
Achromopeptidase, which has potent bacteriolytic activity for most of the gram-positive aerobic bacteria, was for the first time used for the lysis of anaerobic cocci. Most of the lysozyme-resistant gram-positive anaerobic cocci were lysed with this new enzyme. Peptococcus magnus was the only organism tested resistant to achromopeptidase. P. saccharolyticus was quite unusual because it was very sensitive to both achromopeptidase and lysozyme.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Evans C. A., Mattern K. L., Hallam S. L. Isolation and identification of Peptococcus saccharolyticus from human skin. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Mar;7(3):261–264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.3.261-264.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki T. [Mole % guanine plus cytosine of butyrate-producing anaerobic cocci and DNA-DNA relationship among them]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1982 May;37(3):607–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T., Tanabe M., Nakamura K., Soejima M. Studies on a new proteolytic enzyme from A chromobacter lyticus M497-1. I. Purification and some enzymatic properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 24;660(1):44–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Nimmermann E. Peptidoglycan types of strains of the genus Peptococcus. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Nov 2;93(3):245–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00412024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


