Abstract
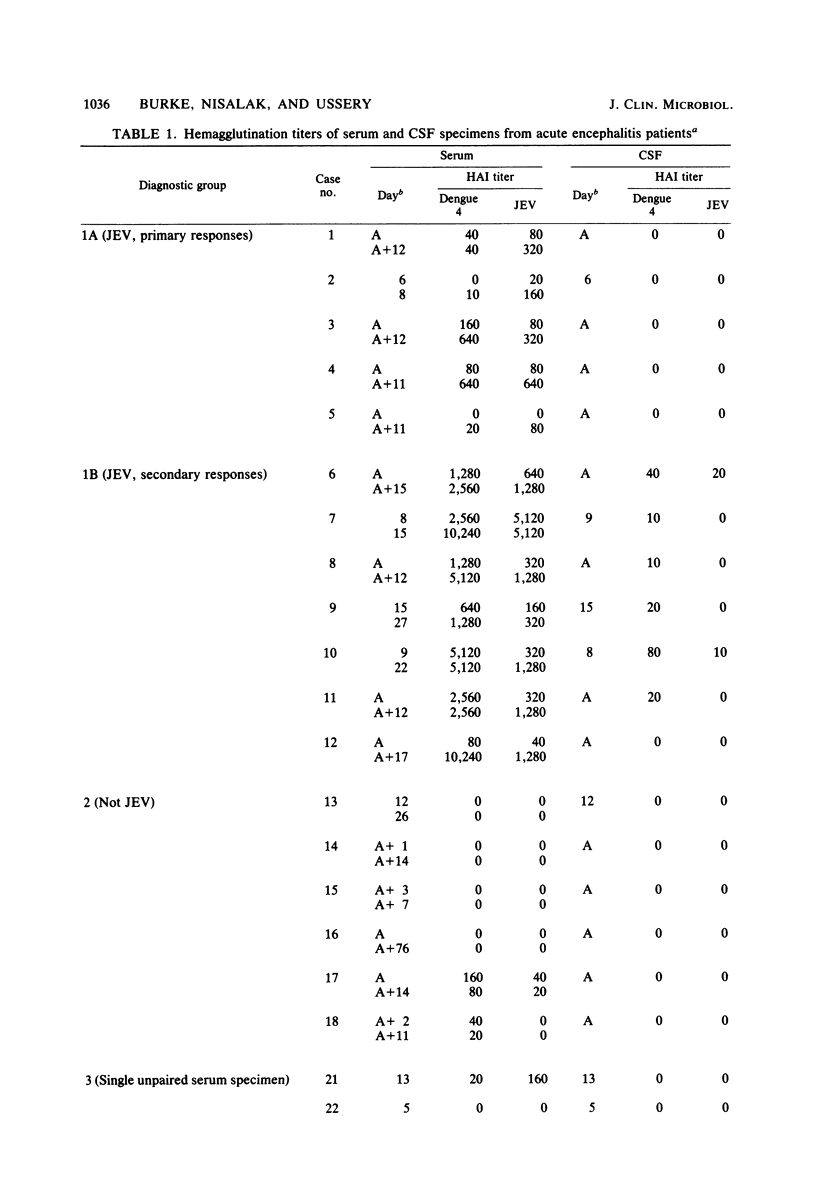
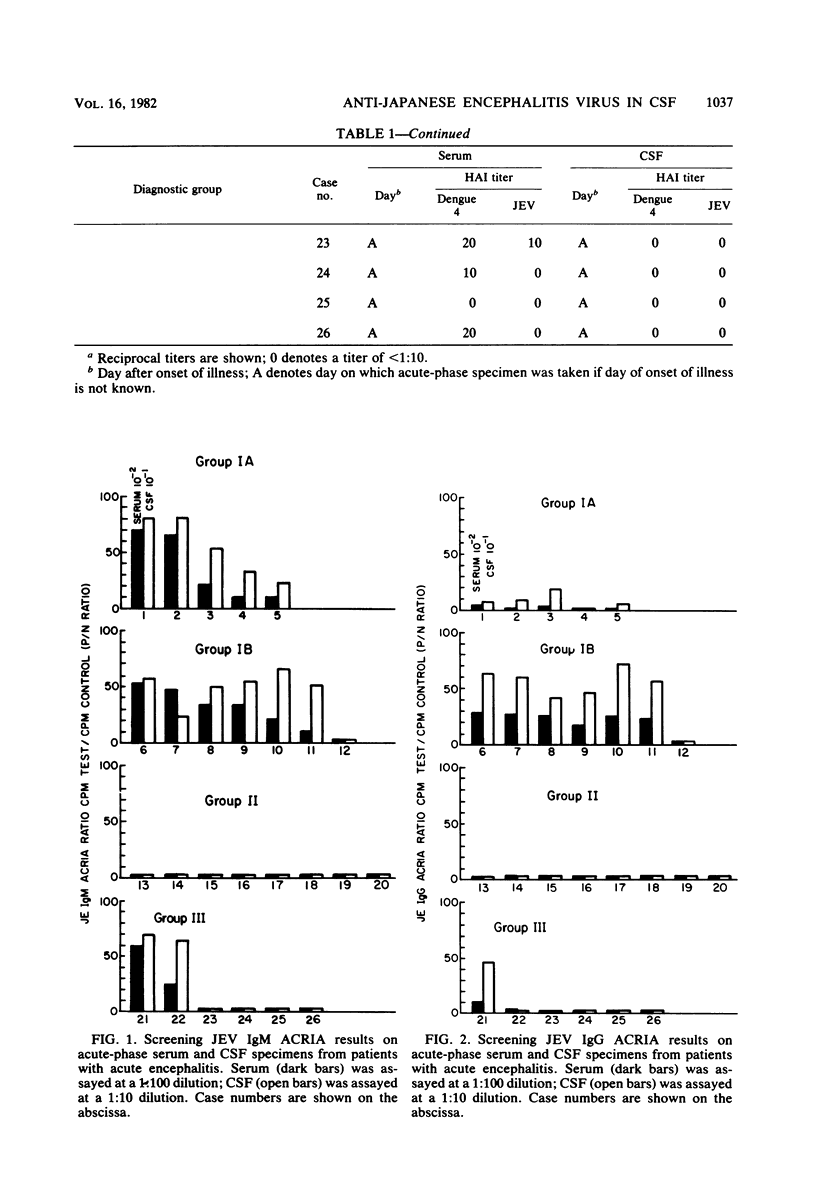
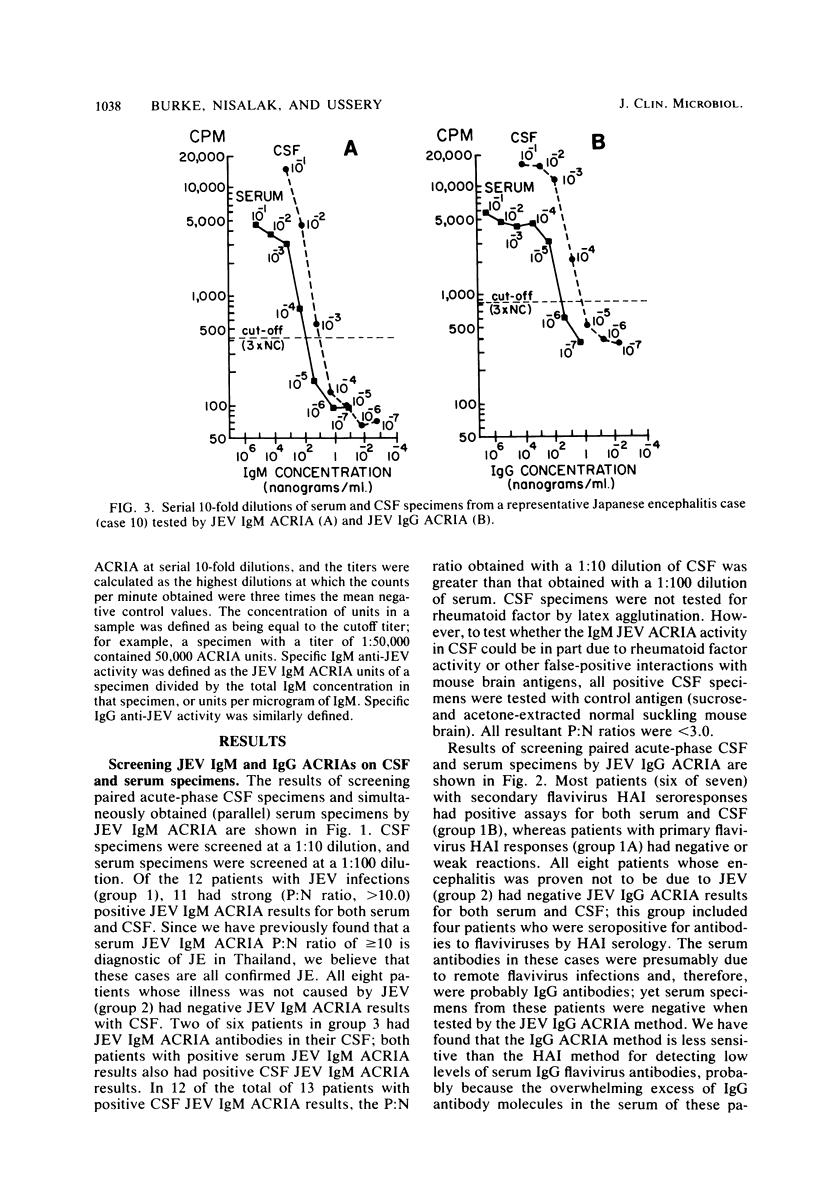
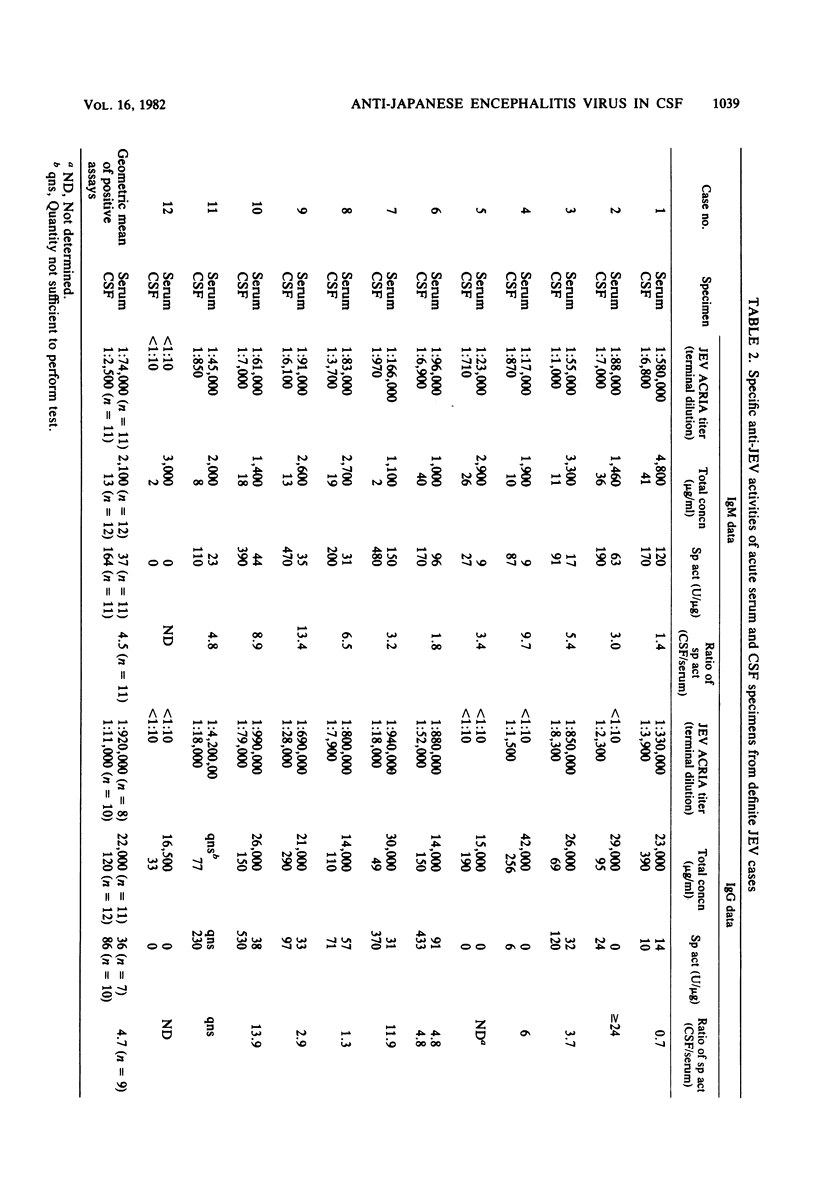
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG antibodies to Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) were detected in acute-phase cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) specimens from patients with acute encephalitis by using a solid-phase radioimmunoassay of the antibody capture type. Of 12 patients with JEV infections subsequently proven by hemagglutination inhibition serology, 11 had JEV IgM antibodies, as measured by antibody capture radioimmunoassay, in the first CSF specimen (geometric mean titer, 1:2,500) compared with 0 of 8 patients with acute encephalitis proven not to be due to JEV. Specific IgM anti-JEV activity (units per microgram) was greater in CSF than in parallel serum specimens in all 11 positive cases by more than fourfold on the average (range, 1.4 to 13). Among seven patients with broadly reactive hemagglutination inhibition seroresponses typical of persons previously exposed to other flaviviruses, six had high levels of JEV IgG antibodies (as measured by antibody capture radioimmunoassay) in their acute-phase CSF (geometric mean titer, 1:26,000), whereas in five patients experiencing their first flavivirus infection, JEV IgG antibodies measured by antibody capture radio-immunoassay were either absent (one patient) or weakly reactive (four patients; geometric mean titer, 1:3,200). Specific IgG anti-JEV activity was greater in CSF than in parallel serum specimens in eight of the nine positive cases measured (range, 1.3- to 24-fold). The antibody capture solid-phase immunoassay approach is well suited for detecting specific antibody activity in CSF.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke D. S., Nisalak A. Detection of Japanese encephalitis virus immunoglobulin M antibodies in serum by antibody capture radioimmunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):353–361. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.353-361.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diment J. A., Chantler S. M. Enzyme immunoassay for detection of rubella specific IgM antibody. Lancet. 1981 Feb 14;1(8216):394–395. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91723-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., Wielaard F., van der Veen J. A new principle for the detection of specific IgM antibodies applied in an ELISA for hepatitis A. J Med Virol. 1979;4(1):25–32. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Hagrassy M. M., Banatvala J. E., Coltart D. J. Coxsackie-B-virus-specific IgM responses in patients with cardiac and other diseases. Lancet. 1980 Nov 29;2(8205):1160–1162. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92595-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryden A., Link H., Norrby E. Cerebrospinal fluid and serum immunoglobulins and antibody titers in mumps meningitis and aseptic meningitis of other etiology. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):852–861. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.852-861.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydén A., Link H. Predominance of oligoclonal IgG type lambda in CSF in aseptic meningitis. Arch Neurol. 1979 Aug;36(8):478–480. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500440048008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W. H., Lüer W. Selective detection of IgM-antibody against core antigen of the hepatitis B virus by a modified enzyme immune assay. J Med Virol. 1979;4(3):227–238. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon A., Steinberg S., Greenberg S., Taber L. Varicella-zoster-associated encephalitis: detection of specific antibody in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):764–767. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.764-767.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman R. A., Edelman R., Willhight M., Pantuwatana S., Udomsakdi S. Study of Japanese encephalitis virus in Chiangmai Valley, Thailand. 3. Human seroepidemiology and inapparent infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1973 Aug;98(2):133–149. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann H., Frisch-Niggemeyer W., Heinz F., Kunz C. Immunoglobulins to tick-borne encephalitis in the cerebrospinal fluid of man. J Med Virol. 1979;4(3):241–245. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. P., Lauter C. B., Lerner A. M. Simultaneous serum and CSF antibodies in herpes simplex virus encephalitis. JAMA. 1978 Jul 28;240(4):356–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Müller R. Immunoglobulins in multiple sclerosis and infections of the nervous system. Arch Neurol. 1971 Oct;25(4):326–344. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00490040052007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Panelius M., Salmi A. A. Immunoglobulins and measles antibodies in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jan;28(1):23–30. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490190041004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Tibbling G. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. III. Evaluation of IgG synthesis within the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):397–401. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii: use for diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):757–766. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porras C., Barboza J. J., Fuenzalida E., Adaros H. L., Oviedo A. M., Furst J. Recovery from rabies in man. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Jul;85(1):44–48. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-1-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


