Abstract
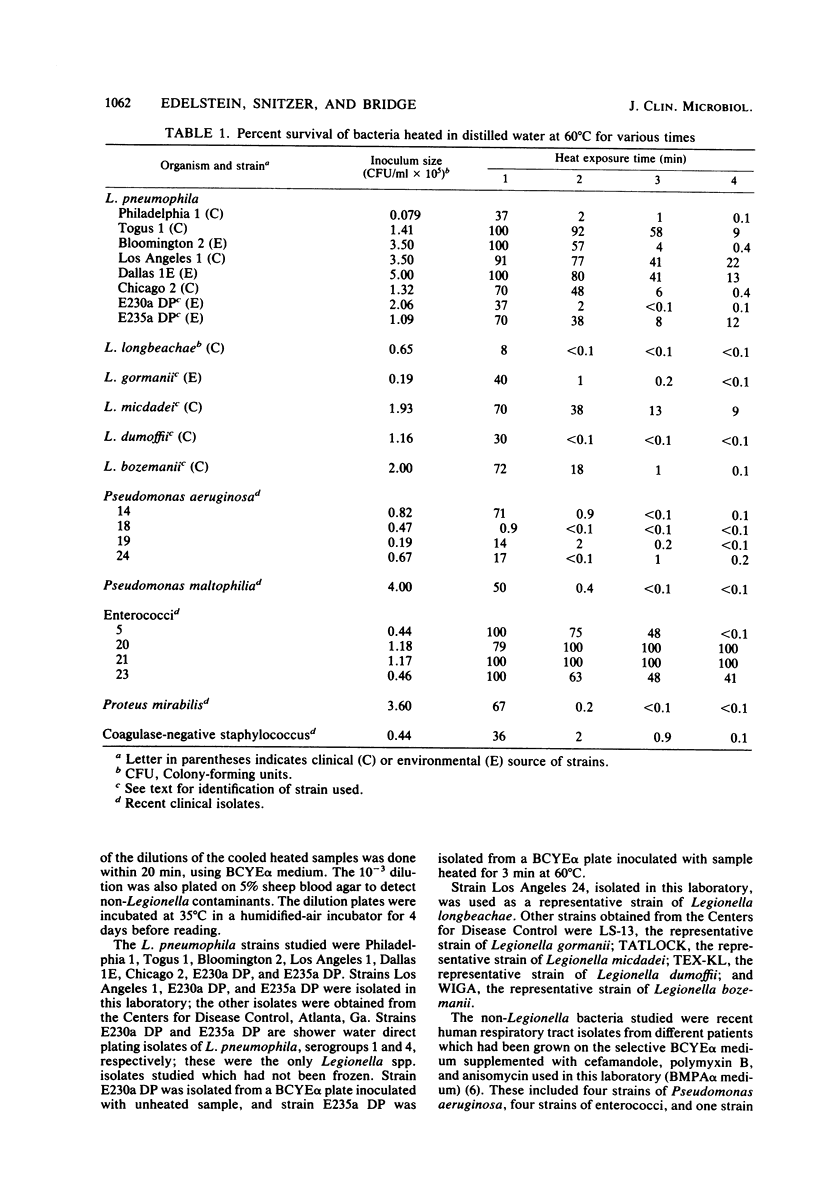
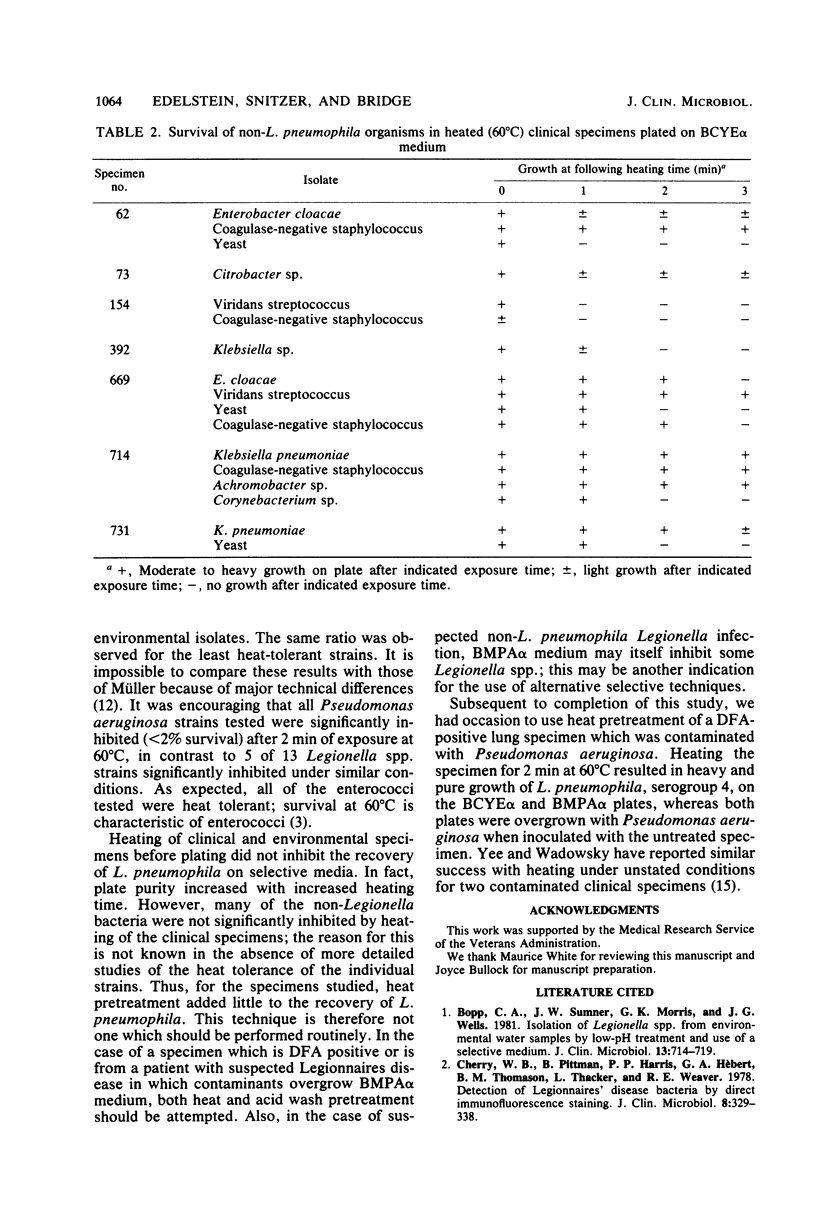
Heating of Legionella pneumophila and other Legionella spp. was studied to determine whether this technique could be used as a selective technique with contaminated clinical specimens. Studies of 13 different strains of Legionella spp. showed heterogeneous heat survival; heating at 60 degrees C for 1 to 2 min did not affect the survival of the majority of strains. Heating of four Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains at 60 degrees C for 2 min reduced bacterial counts by 98% or greater. Enterococci were heat tolerant, with virtually no inhibition under the same conditions. No inoculum effect was noted for any of the organisms tested. Heating of eight contaminated clinical specimens before plating on buffered charcoal-yeast extract medium reduced the numbers of contaminants on most plates but increased by only one the number of specimens yielding L. pneumophila. Plating the same specimens on selective media with or without heat pretreatment yielded L. pneumophila in every case. Heating of clinical specimens at 60 degrees C for 1 to 2 min before plating may occasionally increase the recovery of L. pneumophila from contaminated specimens, but this technique should not be generally used.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bopp C. A., Sumner J. W., Morris G. K., Wells J. G. Isolation of Legionella spp. from environmental water samples by low-pH treatment and use of a selective medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):714–719. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.714-719.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry W. B., Pittman B., Harris P. P., Hebert G. A., Thomason B. M., Thacker L., Weaver R. E. Detection of Legionnaires disease bacteria by direct immunofluorescent staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):329–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.329-338.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. J., Taylor J. A., Fitzgeorge R. B., Bartlett C. L., Barrow G. I. Legionella pneumophila in water plumbing systems. Lancet. 1982 Apr 24;1(8278):949–951. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91944-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Finegold S. M. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from a transtracheal aspirate. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):457–458. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.457-458.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Finegold S. M. Use of a semiselective medium to culture Legionella pneumophila from contaminated lung specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):141–143. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.141-143.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Laboratory diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):317–327. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Smith S. J., Tison D. L., Pope D. H. Ecological distribution of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.9-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Yee R. B., Mezmar L., Wing E. J., Dowling J. N. Hot water systems as sources of Legionella pneumophila in hospital and nonhospital plumbing fixtures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1104–1110. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1104-1110.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee R. B., Wadowsky R. M. Multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in unsterilized tap water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1330–1334. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1330-1334.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


