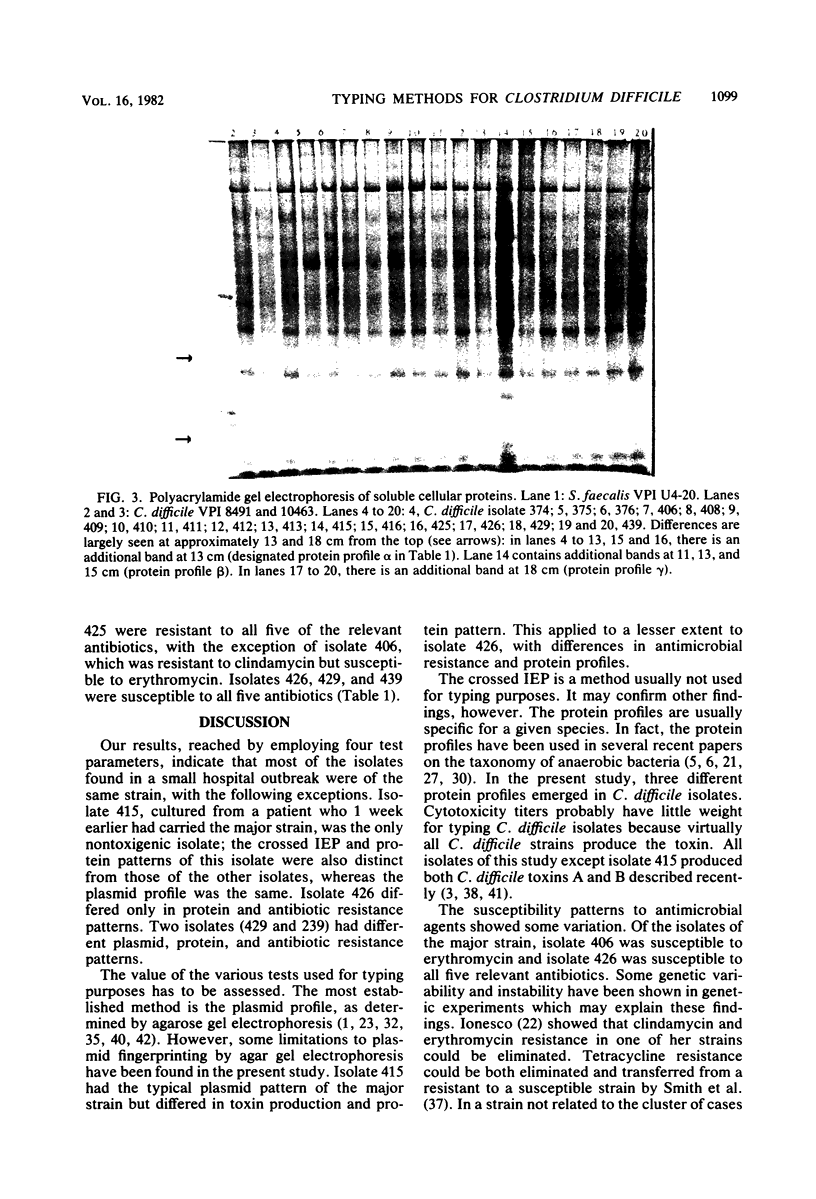
Abstract
During an outbreak of diarrheal disease due to Clostridium difficile in a surgical ward, 16 C. difficile isolates were cultured from fecal samples of 15 patients. Agarose gel electrophoresis for the detection of plasmid DNA, crossed immunoelectrophoresis for the detection of extracellular antigens and toxins, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for analyses of soluble proteins, assays for cytotoxicity, and a comparison of susceptibility to antimicrobial agents were employed. At least 12 of the 16 isolates were shown to be phenotypically the same strain. These findings suggest that in a hospital setting, diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis caused by C. difficile can be of nosocomial origin and that they can spread from patient to patient.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L., Vishniavsky N., Stiver H. G. Plasmid pattern analysis of Staphylococcal epidermidis isolates from patients with prosthetic valve endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):627–632. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.627-632.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Chang T. W., Gurwith M., Gorbach S. L., Onderdonk A. B. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis due to toxin-producing clostridia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 9;298(10):531–534. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803092981003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato E. P., Hash D. E., Holdeman L. V., Moore W. E. Electrophoretic study of Clostridium species. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):688–702. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.688-702.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L., Onderdonk A. B. Clindamycin-induced enterocolitis in hamsters as a model of pseudomembranous colitis in patients. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):526–529. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.526-529.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudmore M. A., Silva J., Jr, Fekety R., Liepman M. K., Kim K. H. Clostridium difficile colitis associated with cancer chemotherapy. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Feb;142(2):333–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzink J., Bartlett J. G. In vitro susceptibility of Clostridium difficile isolates from patients with antibiotic-associated diarrhea or colitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):695–698. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrich M., Van Tassell R. L., Libby J. M., Wilkins T. D. Production of Clostridium difficile antitoxin. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1041–1043. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1041-1043.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekety R., Kim K. H., Batts D. H., Browne R. A., Cudmore M. A., Silva J., Jr, Toshniwal R., Wilson K. H. Studies on the epidemiology of antibiotic-associated Clostridium difficile colitis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Nov;33(11 Suppl):2527–2532. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.11.2527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekety R., Kim K. H., Brown D., Batts D. H., Cudmore M., Silva J., Jr Epidemiology of antibiotic-associated colitis; isolation of Clostridium difficile from the hospital environment. Am J Med. 1981 Apr;70(4):906–908. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George R. H., Symonds J. M., Dimock F., Brown J. D., Arabi Y., Shinagawa N., Keighley M. R., Alexander-Williams J., Burdon D. W. Identification of Clostridium difficile as a cause of pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J. 1978 Mar 18;1(6114):695–695. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6114.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Sutter V. L., Citron D., Finegold S. M. Selective and differential medium for isolation of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.214-219.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Sutter V. L., Goldstein E. J., Ludwig S. L., Finegold S. M. Aetiology of antimicrobial-agent-associated colitis. Lancet. 1978 Apr 15;1(8068):802–803. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)93001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield C., Burroughs A., Szawathowski M., Bass N., Noone P., Pounder R. Is pseudomembranous colitis infectious? Lancet. 1981 Feb 14;1(8216):371–372. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91683-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haji T. C., Lewis P. S., Sanderson P. J. Pseudomembranous colitis-an infectious disease? Lancet. 1981 Jul 25;2(8239):208–209. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90397-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionesco H. Transfert de la résistance à la tétracycline chez Clostridium difficile. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1980 Mar-Apr;131A(2):171–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H. W., Sweeney H. M., Nathan C., Weinstein R. A., Kabins S. A., Cohen S. Identity and interspecific transfer of gentamicin-resistance plasmids in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):738–747. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. H., Fekety R., Batts D. H., Brown D., Cudmore M., Silva J., Jr, Waters D. Isolation of Clostridium difficile from the environment and contacts of patients with antibiotic-associated colitis. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):42–50. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Price A. B., Borriello S. P. Epidemiology of experimental enterocecitis due to Clostridium difficile. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):408–413. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Price A. B., Honour P., Borriello S. P. Clostridium difficile and the aetiology of pseudomembranous colitis. Lancet. 1978 May 20;1(8073):1063–1066. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90912-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan D. W., Kelly J. K. Pseudomembranous colitis in a leukaemia unit: a report of five fatal cases. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Dec;32(12):1237–1243. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.12.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills P. R., Main A. N., Gemmell C. G., Wright P. A., Lee F. D., Russell R. I. Pseudomembranous colitis as infectious disease. Lancet. 1981 Mar 7;1(8219):552–552. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92879-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Hash D. E., Holdeman L. V., Cato E. P. Polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis of soluble proteins for studies of bacterial floras. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):900–907. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.900-907.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi J. T., Hecht D. W. Plasmid profiles in epidemiologic studies of infections by Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):637–643. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce P. F., Jr, Wilson R., Silva J., Jr, Garagusi V. F., Rifkin G. D., Fekety R., Nunez-Montiel O., Dowell V. R., Jr, Hughes J. M. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis: an epidemiologic investigation of a cluster of cases. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):269–274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. R., Petrou M., Lucas C., Chung J. T., Barrett A. J., Borriello S. P., Honour P. Spread of Clostridium difficile among patients receiving non-absorbable antibiotics for gut decontamination. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Aug 8;283(6288):408–409. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6288.408-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaberg D. R., Tompkins L. S., Falkow S. Use of agarose gel electrophoresis of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid to fingerprint gram-negative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1105–1108. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1105-1108.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz J. F., Sahel J., Sarles H. Colite pseudomembraneuse d'allure épidémique. Nouv Presse Med. 1979 Dec 17;8(49):4048–4048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Markowitz S. M., Macrina F. L. Transferable tetracycline resistance in Clostridium difficile. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):997–1003. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan N. M., Pellett S., Wilkins T. D. Purification and characterization of toxins A and B of Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1032–1040. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1032-1040.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Barry A. L., Wilkins T. D., Zabransky R. J. Collaborative evaluation of a proposed reference dilution method of susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):495–502. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Wachsmuth I. K., Shangkuan Y. H., Schmidt E. V., Barrett T. J., Schrader J. S., Scherach C. S., McGee H. B., Feldman R. A., Brenner D. J. Salmonellosis associated with marijuana: a multistate outbreak traced by plasmid fingerprinting. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 27;306(21):1249–1253. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205273062101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor N. S., Thorne G. M., Bartlett J. G. Comparison of two toxins produced by Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):1036–1043. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.1036-1043.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Plorde J. J., Falkow S. Molecular analysis of R-factors from multiresistant nosocomial isolates. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):625–636. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toshniwal R., Silva J., Jr, Fekety R., Kim K. H. Studies on the epidemiology of colitis due to Clostridium difficile in hamsters. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):51–54. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytgat F. Fréquence d'isolement de Clostridium difficile dans les selles de malades hospitalisés: sensibilité aux antibiotiques des souches isolées. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1980 Jul-Aug;131B(1):11–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]