Abstract
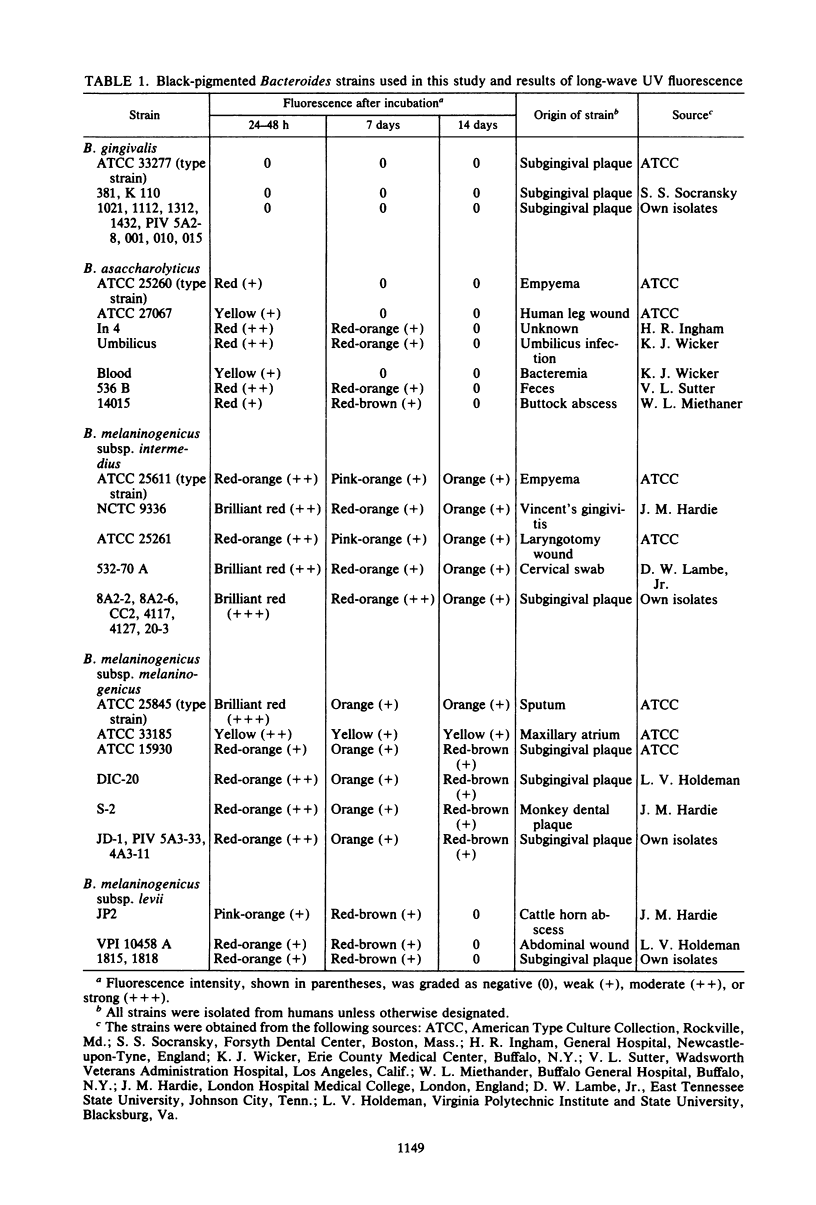
Black-pigmented Bacteroides strains were grown on blood agar, and the colonies were evaluated for fluorescence from long-wave UV light. Most test strains of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subsp. intermedius exhibited a brilliant red fluorescence. B. melaninogenicus subsp. melaninogenicus fluoresced mostly red-orange. Bacteroides asaccharolyticus showed a yellow or red fluorescence. The intensity of the Bacteroides fluorescence weakened when the black pigment of the colonies developed. In contrast, neither young nor old colonies of the oral species Bacteroides gingivalis displayed fluorescence. Since B. gingivalis can produce severe oral infections and also can seed to nonoral sites, awareness of the inability of this organism to fluoresce is important for microbiologists utilizing UV light fluorescence to screen for black-pigmented Bacteroides spp. The present data also indicate that UV light fluorescence may be a rapid method of distinguishing some black-pigmented Bacteroides spp.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chow A. W., Patten V., Guze L. B. Rapid screening of Veillonella by ultraviolet fluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Dec;2(6):546–548. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.6.546-548.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner P. D., Granato P. A., May C. B. Recovery and identification of anaerobes: a system suitable for the routine clinical laboratory. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Dec;26(6):904–913. doi: 10.1128/am.26.6.904-913.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding G. K., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M., Bricknell K. S. Characterization of bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Oct;4(4):354–359. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.4.354-359.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambe D. W., Jr, Ferguson K. P., Mayberry W. R. Characterization of Bacteroides gingivalis by direct fluorescent antibody staining and cellular fatty acid profiles. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Apr;28(4):367–374. doi: 10.1139/m82-056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Syed S. A., Loesche W. J. API ZYM system for identification of Bacteroides spp., Capnocytophaga spp., and spirochetes of oral origin. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):97–102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.97-102.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Hammond P. G., Slots J., Reed M. J., Genco R. J. Identification of Bacteroides gingivalis by fluorescent antibody staining. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 Jul-Aug;132B(1):69–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Hammond P., Slots J., Genco R. J. Evaluation of Fluoretec-M for detection of oral strains of Bacteroides asaccharolyticus and Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):682–686. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.682-686.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. B., Cherry G., Bornside B. B., Bornside G. H. Ultaviolet red fluorescence of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Appl Microbiol. 1969 May;17(5):760–762. doi: 10.1128/am.17.5.760-762.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J. S., Beeley J. A., MacFarlane T. W. A study of the pigment produced by Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Dent Res. 1976 Nov-Dec;55(6):1130–1130. doi: 10.1177/00220345760550062401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. Enzymatic characterization of some oral and nonoral gram-negative bacteria with the API ZYM system. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):288–294. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.288-294.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Genco R. J. Direct hemagglutination technique for differentiating Bacteroides asaccharolyticus oral strains from nonoral strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):371–373. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.371-373.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swindlehurst C. A., Shah H. N., Parr C. W., Williams R. A. Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of polypeptides from Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;43(2):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


