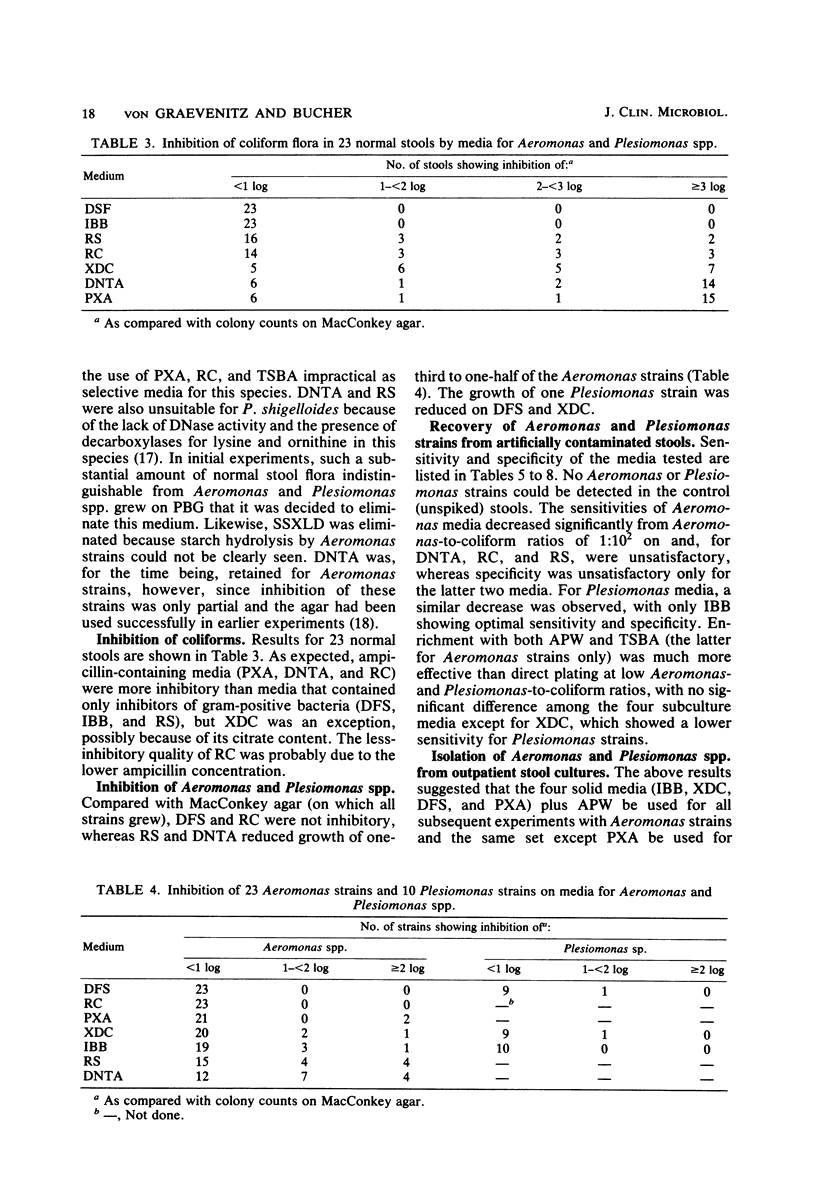
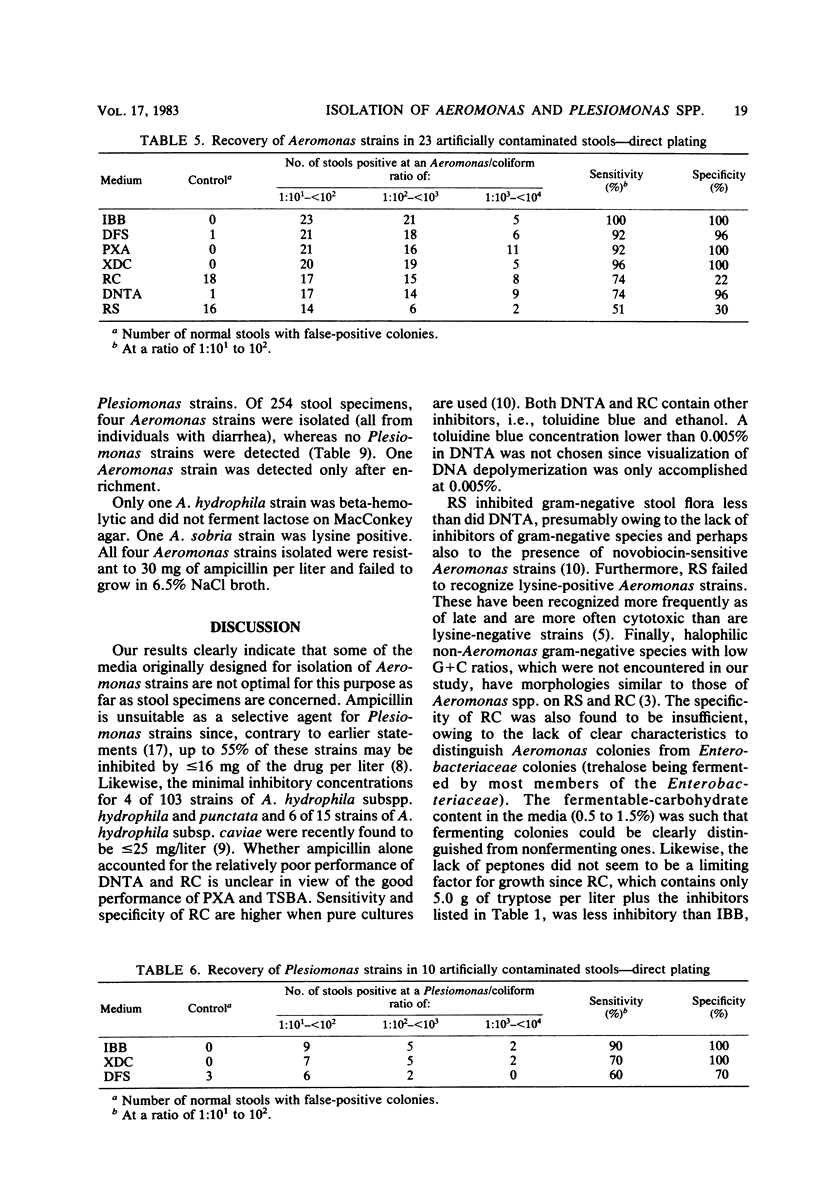
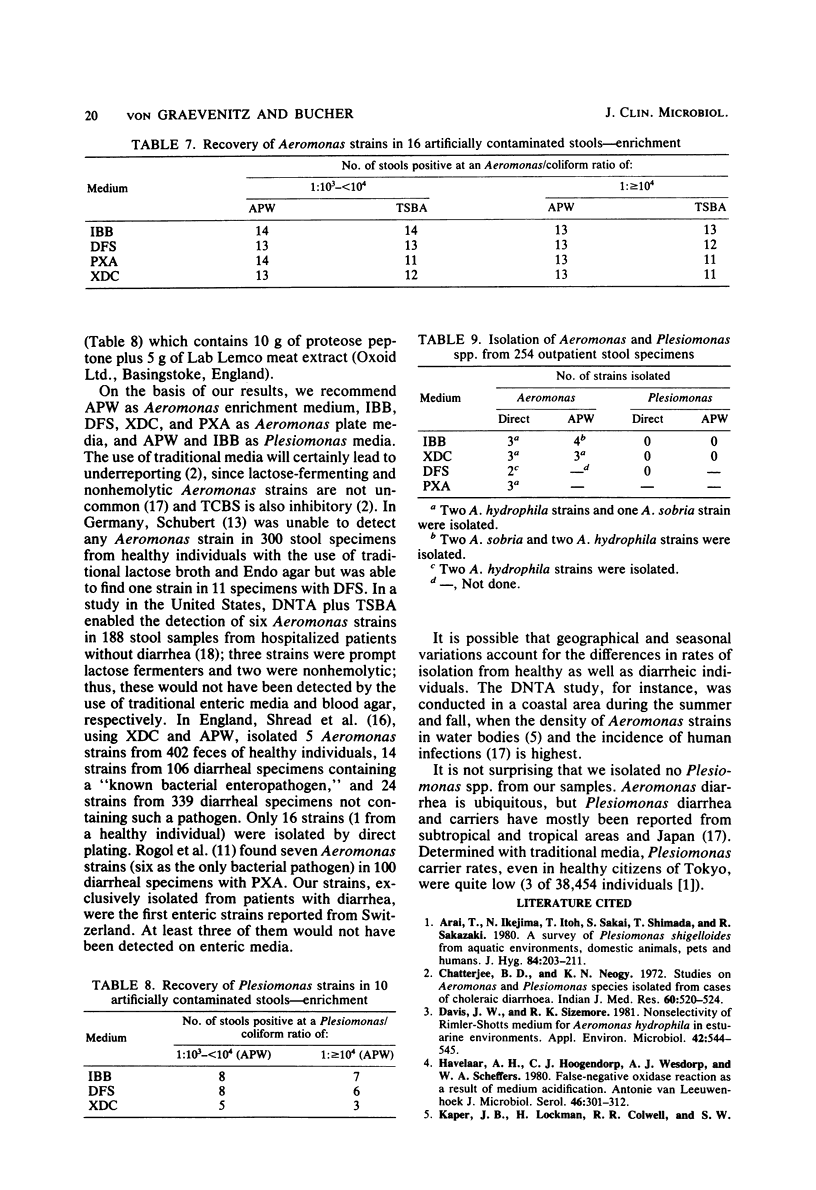
Abstract
We studied nine solid and two liquid media for their suitability to select Aeromonas and Plesiomonas spp. from human stools, using artificially contaminated samples as well as 254 samples from outpatients with and without diarrhea. Media with optimal sensitivity and specificity for Aeromonas spp. were alkaline peptone-water, Trypticase soy broth with ampicillin, inositol-brilliant green-bile salts agar, dextrin-fuchsin-sulfite agar, xylose-sodium desoxycholate-citrate agar, and Pril-xylose-ampicillin agar. For Plesiomonas sp., alkaline peptone-water and inositol-brilliant green-bile salts agar were optimal. Four strains of Aeromonas spp. were detected in patient samples with these media.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai T., Ikejima N., Itoh T., Sakai S., Shimada T., Sakazaki R. A survey of Plesiomonas shigelloides from aquatic environments, domestic animals, pets and humans. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Apr;84(2):203–211. doi: 10.1017/s002217240002670x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee B. D., Neogy K. N. Studies on Aeromonas and Plesiomonas species isolated from cases of choleraic diarrhoea. Indian J Med Res. 1972 Apr;60(4):520–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. W., Sizemore R. K. Nonselectivity of Rimler-Shotts Medium for Aeromonas hydrophila in Estuarine Environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Sep;42(3):544–545. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.3.544-545.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havelaar A. H., Hoogendorp C. J., Wesdorp A. J., Scheffers W. A. False-negative oxidase reaction as a result of medium acidification. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1980;46(4):301–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00421977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Aeromonas hydrophila: ecology and toxigenicity of isolates from an estuary. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;50(2):359–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M., Véron M. A taxonomic study of the Aeromonas hydrophila-Aeromonas punctata group. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):11–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. J., Robinson J. O., Wagener L. B., Burke V. In-vitro susceptibility of Aeromonas app. to antimicrobial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Apr;9(4):267–274. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.4.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippey S. R., Cabelli V. J. Membrane filter procedure for enumeration of Aeromonas hydrophila in fresh waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):108–113. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.108-113.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogol M., Sechter I., Grinberg L., Gerichter C. B. Pril-xylose-ampicillin agar, a new selective medium for the isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Med Microbiol. 1979 May;12(2):229–231. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-2-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland F. P. Salt-starch xylose lysine deoxycholate agar. A single medium for the isolation of sodium and non-sodium dependent enteric gram-negative bacilli. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1977 Dec 27;163(4):241–249. doi: 10.1007/BF02125508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotts E. B., Jr, Rimler R. Medium for the isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):550–553. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.550-553.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Graevenitz A., Zinterhofer L. The detection of Aeromonas hydrophila in stool specimens. Health Lab Sci. 1970 Jul;7(3):124–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


