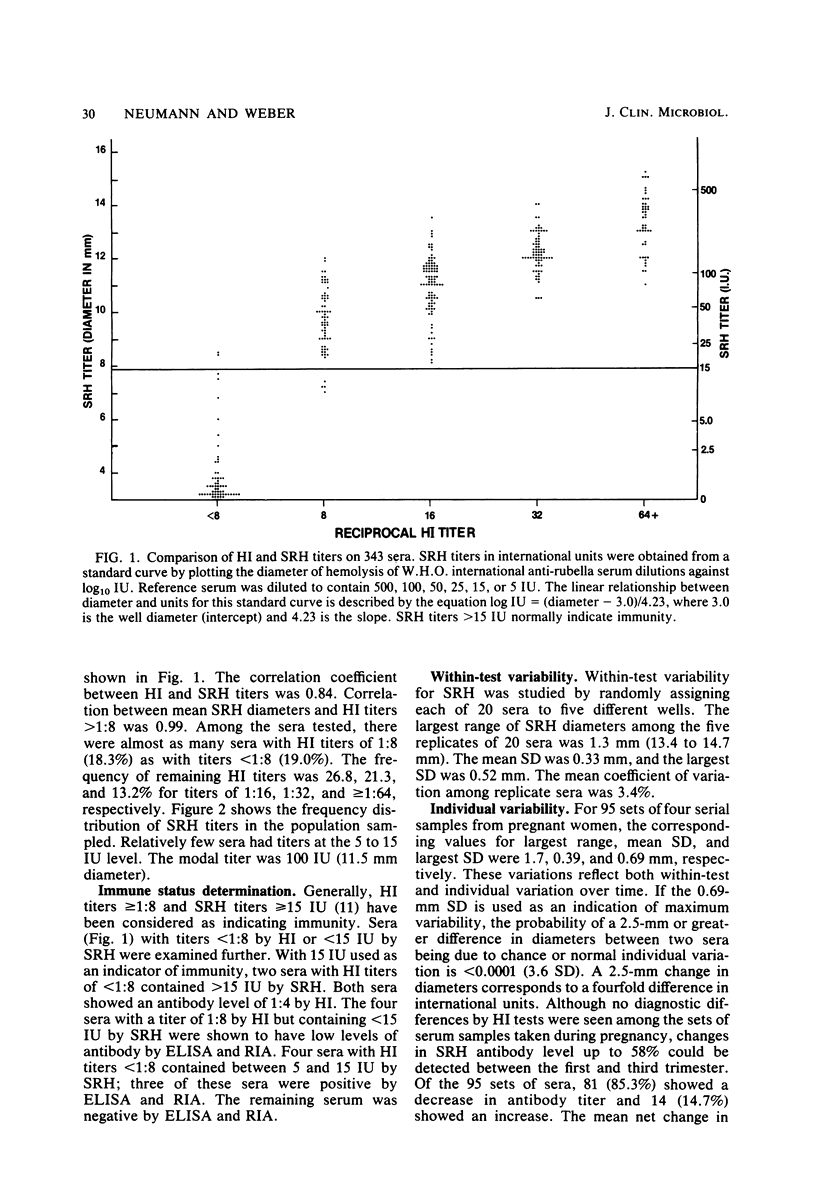
Abstract
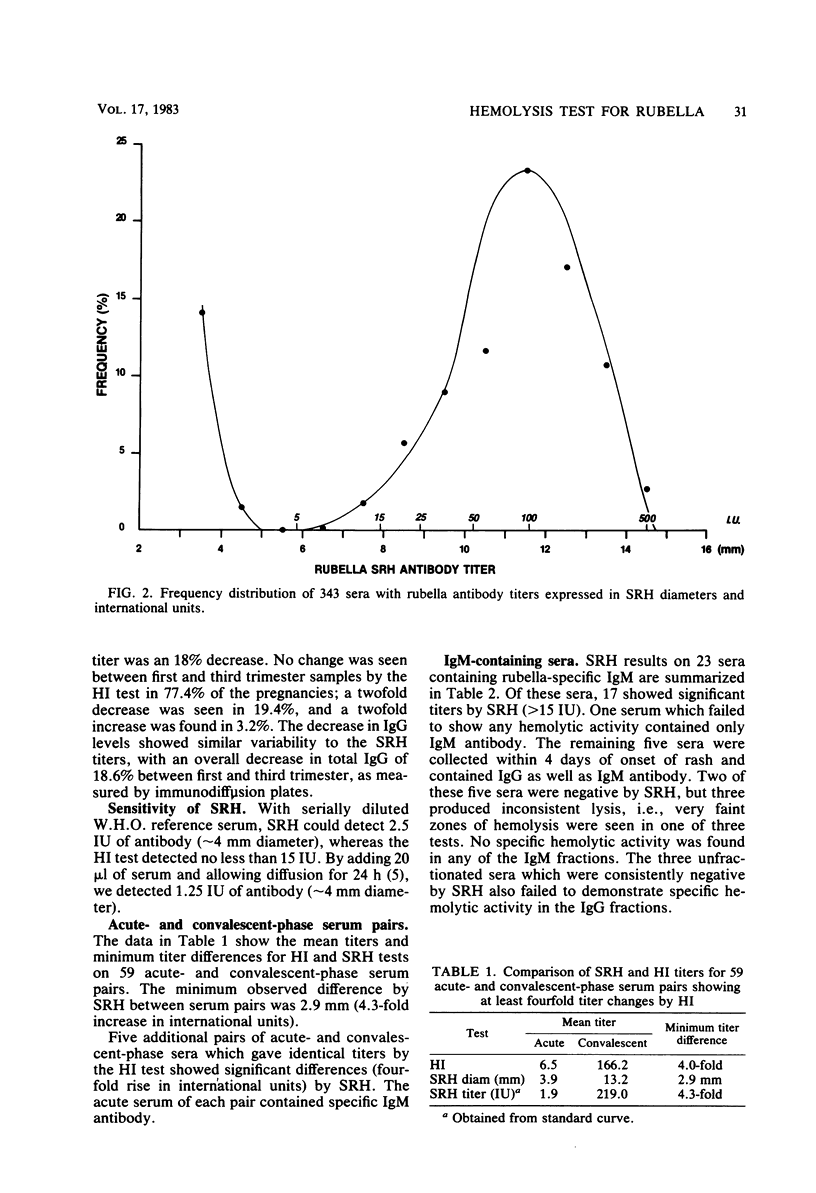
The single radial hemolysis (SRH) test was compared with the hemagglutination inhibition (HI) test for establishing rubella immune status and diagnosing recent infection. Correlation between mean SRH diameters and HI titers greater than or equal to 1:8 was high (R = 0.99). It is suggested that a level of greater than or equal to 5 IU represents low-level antibody and that greater than or equal to 15 IU is a conservative threshold for designation of immunity. Of 343 sera tested, only 1 false-positive was found by SRH with the 5 IU cutoff level. The SRH test could detect serum antibody levels as low as 2.5 IU, whereas 15 IU was generally the limit of resolution of the HI test. Data from sucrose density gradient fractionation of serum demonstrated that neither rubella-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) nor early postinfection HI-reactive IgG was detected by SRH. However, diagnostic changes in antibody titer measured by SRH were in general greater than those measured by HI. The SRH test showed diagnostic titer changes in some sera containing specific IgM for which no such changes were detected by the HI test. A 2.5-mm difference in hemolytic zone diameters (a fourfold rise in international units) between acute- and convalescent-phase serum pairs was chosen as being of diagnostic significance. This difference was less than the minimum observed difference of 2.9 mm from 59 serum pairs showing diagnostic changes by HI and far exceeded (greater than 3.6 standard deviations) the within-test and individual variability seen for 95 pregnant women from whom samples were obtained during each trimester.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Best J. M., Harcourt G. C., Druce A., Palmer S. J., O'Shea S., Banatvala J. E. Rubella immunity by four different techniques: results of challenge studies. J Med Virol. 1980;5(3):239–247. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzko D. B., Jelinek D. F., Wilcke B. W., Jr Nonspecific reactions in the hemagglutination inhibition test for detection of rubella antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):818–823. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.818-823.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellano G. A., Madden D. L., Hazzard G. T., Cleghorn C. S., Vails D. V., Ley A. C., Tzan N. R., Sever J. L. Evaluation of commercially available diagnostic test kits for rubella. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):578–584. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champsaur H., Dussaix E., Tournier P. Hemagglutination inhibition, single radial hemolysis, and ELISA tests for the detection of IgG and IgM to rubella virus. J Med Virol. 1980;5(4):273–286. doi: 10.1002/1096-9071(1980)5:4<273::aid-jmv1890050403>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forger J. M., 3rd, Gilfillan R. F. Single-radial hemolysis as a cost-effective determinant of Rubella antibody status. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):115–119. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.115-119.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee B., Jordan B. E., Mortimer P. R. An assessment of radial haemolysis in the detection of rubella antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jan;31(1):35–38. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P. E., Ryan J. M., Stewart J. A. Rubella hemagglutinin prepared with alkaline extraction of virus grown in suspension culture of BHK-21 cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 May;125(1):162–167. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett G. B., Palmer C. A., Mackay-Scollay E. M. Single-radial-hemolysis test for the assay of rubella antibody in antenatal, vaccinated, and rubella virus-infected patients. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):937–944. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe G., Drescher J. Description of a technique for the determination of the concentration and quality of rubella virus antibody molecules and experience with testing sera from humans with recent and past rubella infection. Arch Virol. 1980;65(2):109–121. doi: 10.1007/BF01317322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz J. B., Mortimer P. P., Mortimer P. R., Morgan-Capner P., Shafi M. S., White G. B. Rubella antibody measured by radial haemolysis. Characteristics and performance of a simple screening method for use in diagnostic laboratories. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Apr;84(2):213–222. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menser M. A. Rubella immunity in pregnancy. Med J Aust. 1981 May 16;1(10):538–538. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1981.tb135789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer P. P., Edwards J. M., Porter A. D., Tedder R. S., Mace J. E., Hutchinson A. Are many women immunized against rubella unnecessarily? J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Aug;87(1):131–138. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirofsky B., Rosner E. R. DTT test: a new method to differentiate IgM and IgG erythrocyte antibodies. Vox Sang. 1974;27(5):480–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1974.tb02446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., Benjamin S. R., Briggs M., Jenkins M., Mortimer P. P., Payne S. B. Evaluation of the single radial haemolysis (SRH) technique for rubella antibody measurement. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;31(6):521–526. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.6.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaug K., Orstavik I., Ulstrup J. C. Application of the passive haemolysis test for the determination of rubella virus antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Aug;83(4):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaug K., Ulstrup J. C., Stray-Pedersen B. A rubella epidemic in an unvaccinated pregnant population. I. Screening methods and serological results. Scand J Infect Dis. 1981;13(1):11–15. doi: 10.1080/00365548.1981.11690360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skendzel L. P. Current status of rubella testing: a report based on data from the College of American Pathologists' surveys, 1978-1980. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Oct;76(4 Suppl):547–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strannegård O., Grillner L., Lindberg I. M. Hemolysis-in-gel test for the demonstration of antibodies to rubella virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jun;1(6):491–494. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.6.491-494.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. N., Fulford K. M., Przybyszewski V. A., Pope V. Center for Disease Control Diagnostic Immunology Proficiency Testing Program results for 1977. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):388–395. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.388-395.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


