Abstract
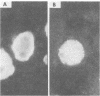
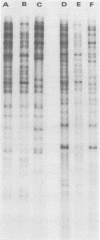
A total of 122 clinical isolates of herpes simplex virus (HSV) from 107 patients were typed by using an indirect immunoperoxidase technique with commercially available type-specific rabbit antisera, recently developed mouse monoclonal antibodies to HSV types 1 and 2, and restriction endonuclease analysis of viral DNA. With the commercially available type-specific rabbit antisera, 34% of clinical HSV isolates were of indeterminate type; 63% of them were typed as HSV type 1 and 37% as HSV type 2 by using monoclonal antibody and restriction enzyme typing systems. Typing by immunofluorescence assay with the monoclonal antibodies gave identical results to those obtained by restriction enzyme analysis. Simultaneous infection with both HSV types was demonstrated by monoclonal antibody typing in five isolates from three patients. These findings were subsequently confirmed by plaque purification and restriction endonuclease analysis of viral DNA. Monoclonal antibodies were as sensitive as restriction enzyme analysis for the typing of clinical HSV isolates. Because of their simplicity, they are more amenable to use in clinical laboratories than is restriction endonuclease analysis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balachandran N., Frame B., Chernesky M., Kraiselburd E., Kouri Y., Garcia D., Lavery C., Rawls W. E. Identification and typing of herpes simplex viruses with monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):205–208. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.205-208.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin D. R. Rapid typing of herpes simplex virus strains using the indirect immunoperoxidase method. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):568–571. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.568-571.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigam A. R., Richman D. D., Oxman M. N. Rapid typing of herpes simplex virus isolates by deoxyribonucleic acid:deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):226–234. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.226-234.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman T. G., Roizman B., Adams G., Stover B. H. Restriction endonuclease fingerprinting of herpes simplex virus DNA: a novel epidemiological tool applied to a nosocomial outbreak. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):488–498. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumpacker C. S., Schnipper L. E., Zaia J. A., Levin M. J. Growth inhibition by acycloguanosine of herpesviruses isolated from human infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):642–645. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawana T., Kawaguchi T., Sakamoto S. Clinical and virological studies on genital herpes. Lancet. 1976 Oct 30;2(7992):964–964. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90928-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonsdale D. M. A rapid technique for distinguishing herpes-simplex virus type 1 from type 2 by restriction-enzyme technology. Lancet. 1979 Apr 21;1(8121):849–852. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Dowdle W. R., Naib Z. M., Highsmith A., Harwell R. W., Josey W. E. Relation of pock size on chorioallantoic membrane to antigenic type of herpesvirus hominis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):1022–1028. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B. Immunochemistry of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1980;90:67–106. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67717-5_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Lostrom M. E., Tam M. R., Stone M. R., Burnette W. N. The isolation of hybrid cell lines producing monoclonal antibodies against the p15(E) protein of ecotropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D. V., Gallo D., Devlin V., Woodie J. D. Serological analysis of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):363–367. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.363-367.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D., Norrild B., Roizman B. Differential immunologic reactivity and processing of glycoproteins gA and gB of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 made in Vero and HEp-2 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5202–5206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. C., Corey L., Adams H. G., Vontver L. A., Holmes K. K. Risk of recurrence after first episodes of genital herpes. Relation to HSV type and antibody response. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 6;305(6):315–319. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108063050604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. W., Peutherer J. F., Robertson D. H. Virological studies in genital herpes. Lancet. 1976 Nov 13;2(7994):1089–1090. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., Bonin P., Holmes K. K., Gutman L., Wiesner P., Alexander E. R. Isolation of viruses, bacteria and other organisms from venereal disease clinic patients: methodology and problems associated with multiple isolations. Health Lab Sci. 1973 Apr;10(2):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]