Abstract
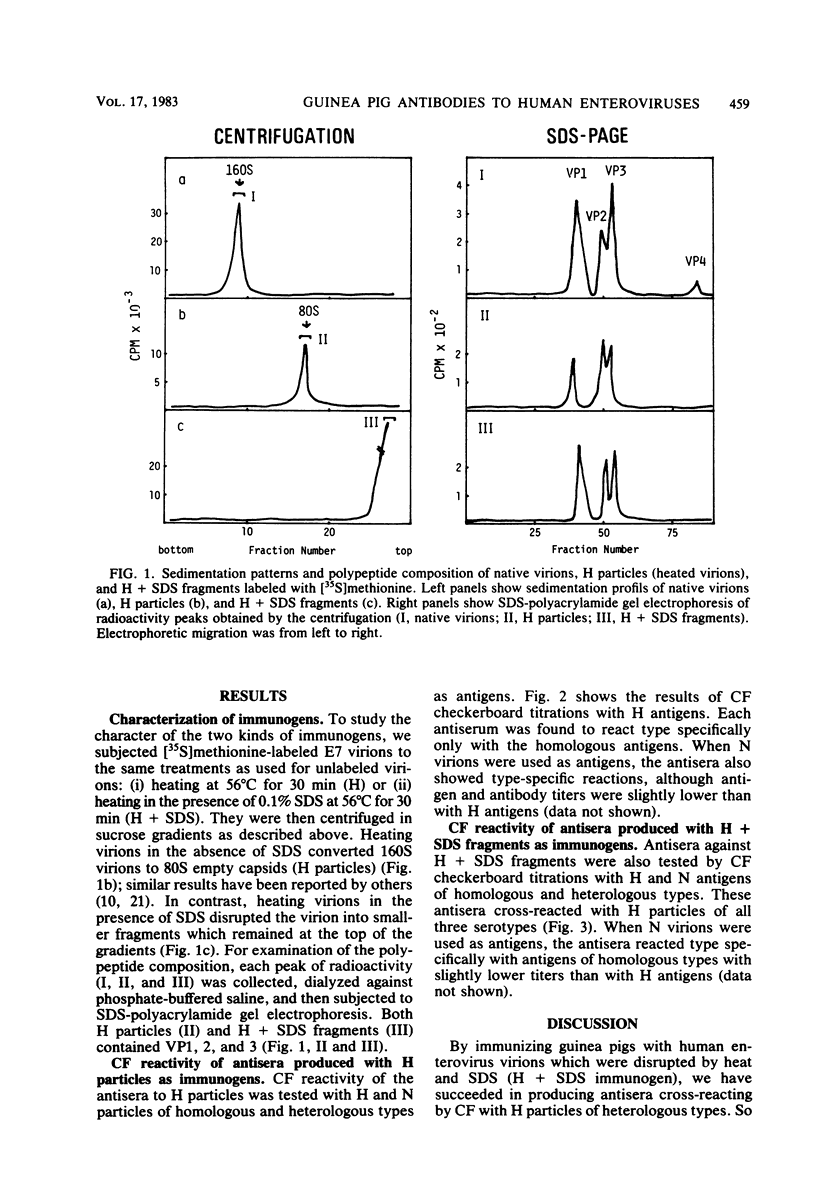
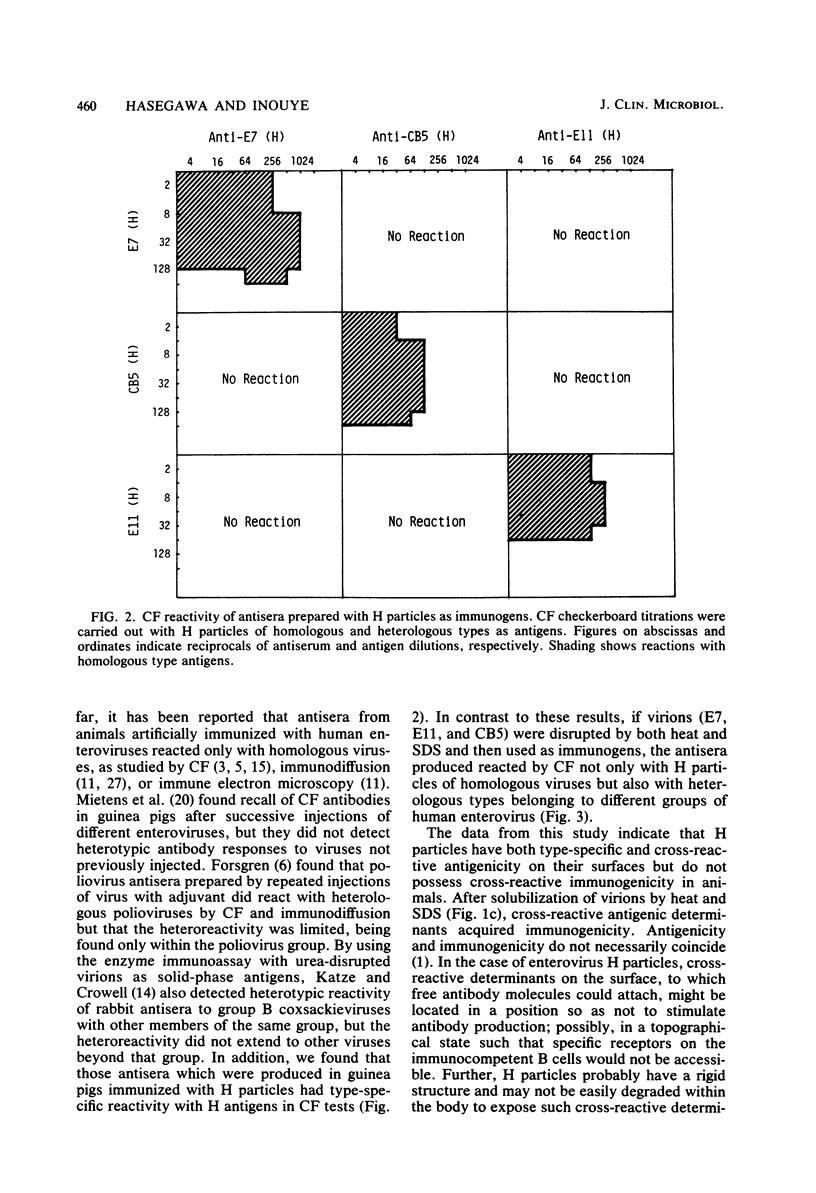
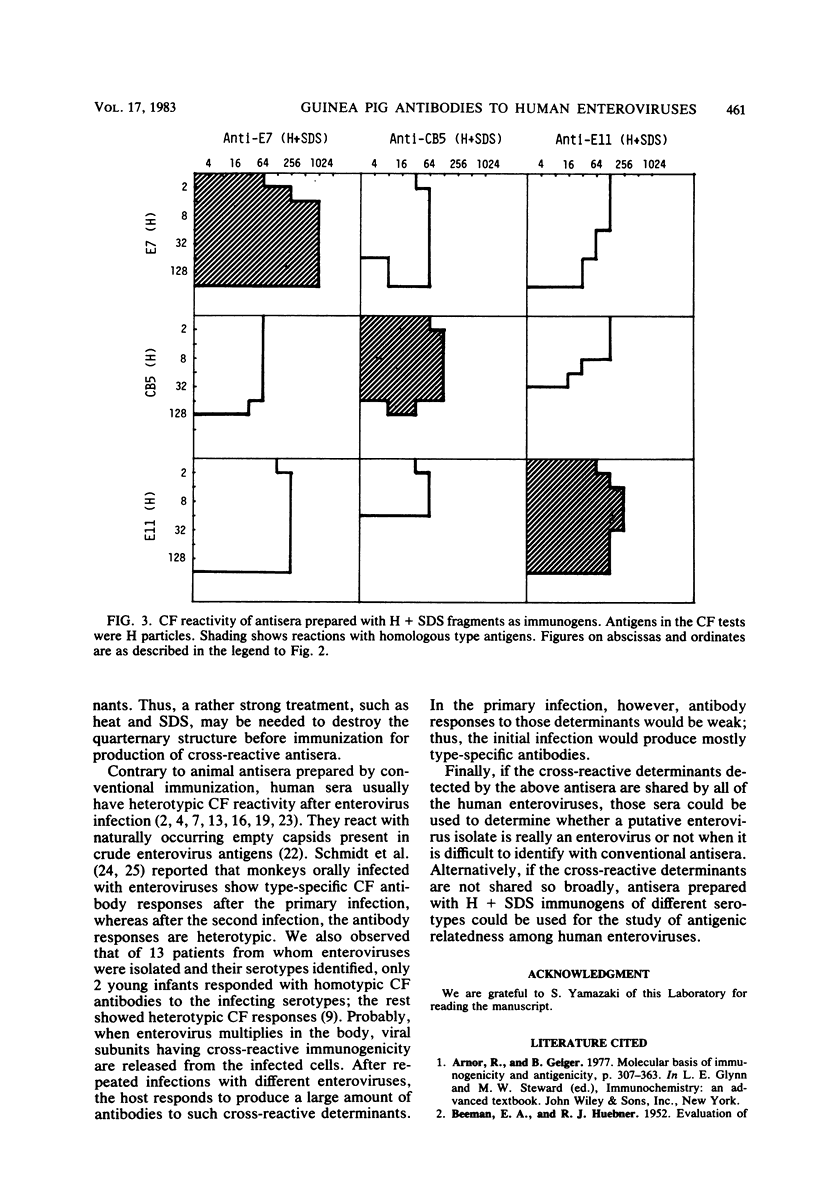
We studied the type specificity of the antisera which were produced in guinea pigs by immunization with heat-disrupted virions of human enteroviruses (echovirus types 7 and 11 and coxsackievirus type B5). When guinea pigs were immunized with heated virions (H particles), the antibodies produced reacted type specifically by complement fixation with the homologous H particles. By contrast, when guinea pigs were immunized with disrupted virions prepared by heating in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate, antibodies were produced which reacted broadly. Heterotypic complement-fixing antibody responses of humans to enterovirus infections are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEEMAN E. A., HUEBNER R. J., COLE R. M. Studies of Coxsackie viruses; laboratory aspects of Group A viruses. Am J Hyg. 1952 Jan;55(1):83–107. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSSELL R. H., KARZON D. T., BARRON A. L., HALL F. T. Hemagglutination-inhibiting, complement-fixing and neutralizing antibody responses in ECHO 6 infection, including studies on heterotypic responses. J Immunol. 1962 Jan;88:47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASALS J., OLITSKY R. K., MURPHY L. C. Hemagglutination and complement fixation with type I and II Albany strains of Coxsackie virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1949 Dec;72(3):636–638. doi: 10.3181/00379727-72-17524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren M. Relationship between poliovirus and echovirus 6 antigens. I. Immunization experiments in guinea pigs. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;39(1):108–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01241534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALONEN P., ROSEN L., HUEBNER R. J. Homologous and heterologous complement fixing antibody in persons infected with ECHO; Coxsackie and poliomyelitis viruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jun;101(2):236–241. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-24896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMELER K., HAMPARIAN V. V. Studies on the complement fixing antigens of poliomyelitis. I. Demonstration of type and group specific antigens in native and heated viral preparations. J Immunol. 1958 Dec;81(6):499–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa A., Inouye S. Antigenicity and polypeptide composition of native and heated echovirus type 7 procapsids. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jan;42(1):119–125. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa A., Inouye S. [Diagnostic value of CF antibody titration in human enterovirus infections (author's transl)]. Rinsho Byori. 1982 Mar;30(3):266–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Katagiri S., Fukuda M., Fukushi K., Watanabe Y. Kinetic studies on the thermal degradation of purified poliovirus. Biken J. 1965 Sep;8(3):143–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. H., Gnau J. M., Hilty M. D., Chema S., Ottolenghi A. C., Hamparian V. V. Picornaviruses: rapid differentiation and identification by immune electronmicroscopy and immunodiffusion. J Med Microbiol. 1977 May;10(2):203–212. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-2-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSSON T., BOTTIGER M., LOFDAHL A. An outbreak of aseptic meningitis with a rubella-like rash probably caused by ECHO virus type 4. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1958;8(3):306–317. doi: 10.1007/BF01243745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAFT L. M., MELNICK J. L. Immunological reactions of the Coxsackie viruses. II. The complement fixation test. J Exp Med. 1950 Nov 1;92(5):483–497. doi: 10.1084/jem.92.5.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Crowell R. L. Immunological studies of the group B coxsackieviruses by the sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunoprecipitation. J Gen Virol. 1980 Oct;50(2):357–367. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-2-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNETTE E. H., SCHMIDT N. J., MAGOFFIN R. L., HAGENS S. J., DUKELLIS E. J. A COMPARISON OF THE REACTIVITY OF POLIOVIRUS COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGENS (NATIVE, HEATED AND SUCROSE DENSITY GRADIENT C AND D) WITH HUMAN SERA. J Immunol. 1964 Feb;92:261–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. The synthesis of Sendai virus polypeptides in infected cells. II. Intracellular distribution of polypeptides. Virology. 1977 Sep;81(2):371–381. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIETENS C., HUMMELER K., HENLE W. RECALL OF COMPLEMENT FIXING ANTIBODIES TO ENTEROVIRUSES IN GUINEA PIGS. J Immunol. 1964 Jan;92:17–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J., Sangar D. V., Brown F. A comparative chemical and serological study of the full and empty particles of foot-and mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1975 Mar;26(3):227–238. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-3-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT N. J., DENNIS J., FROMMHAGEN L. H., LENNETTE E. H. SEROLOGIC REACTIVITY OF CERTAIN ANTIGENS OBTAINED BY FRACTIONATION OF COXSACKIE VIRUSES IN CESIUM CHLORIDE DENSITY GRADIENTS. J Immunol. 1963 Apr;90:654–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT N. J., DENNIS J., LENNETTE E. H. Complement-fixing antibody responses to ECHO virus types 12 and 19 of patients with enterovirus infections. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Feb;109:364–369. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT N. J., DENNIS J., LENNETTE E. H., HO H. H., SHINOMOTO T. T. ANTIBODY RESPONSES OF RHESUS (MACACA MULATTA) MONKEYS EXPERIMENTALLY INFECTED WITH COXSACKIEVIRUSES OF GROUP B AND GROUP A, TYPE 9. I. ANTIBODY RESPONSES WITH THE COXSACKIEVIRUS GROUP. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:54–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT N. J., LENNETTE E. H. Gel double diffusion studies with group B and group A, type 9 Coxsackie viruses. I. The technique and reactions obtained with hyperimmune animal sera and human sera. J Immunol. 1962 Jul;89:85–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT N. J., LENNETTE E. H. Modification of the homotypic specificity of poliomyelitis complement-fixing antigens by heat. J Exp Med. 1956 Jul 1;104(1):99–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Dennis J., Lennette E. H. Antibody responses of rhesus (Macaca mulatta) monkeys experimentally infected with coxsackieviruses of group B and group A, type 9. II. Heterotypic antibody responses to echoviruses, polioviruses and reovirus type 1. J Immunol. 1967 May;98(5):1060–1066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


