Abstract
In correlating results obtained from a new latex-Rickettsia rickettsii test with results obtained from a reference microimmunofluorescence test for Rocky Mountain spotted fever, we found that for seropositive patients each microimmunofluorescence titer (up to 4,096) was usually double the median titer obtained from the latex-R. rickettsii test. The pattern of immunoserological response indicated that latex-R. rickettsii is reactive with sera containing either anti-R. rickettsii immunoglobulin M (IgM) or IgG or both. The agglutination efficiency of the new test was greater when the anti-rickettsial IgM/IgG ratio was greater than or equal to 1. Sera from late-convalescent patients were generally minimally reactive or nonreactive in the latex-R. rickettsii test unless anti-R. rickettsii IgM was present.
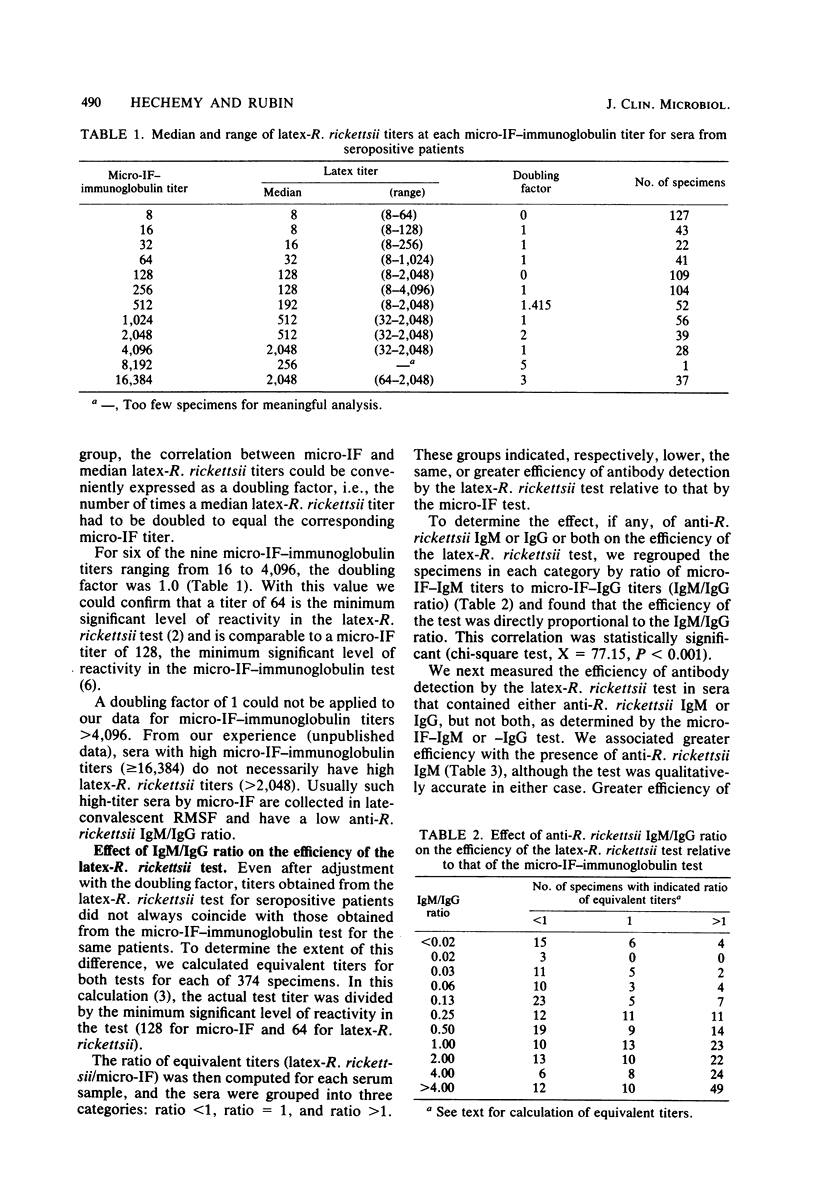
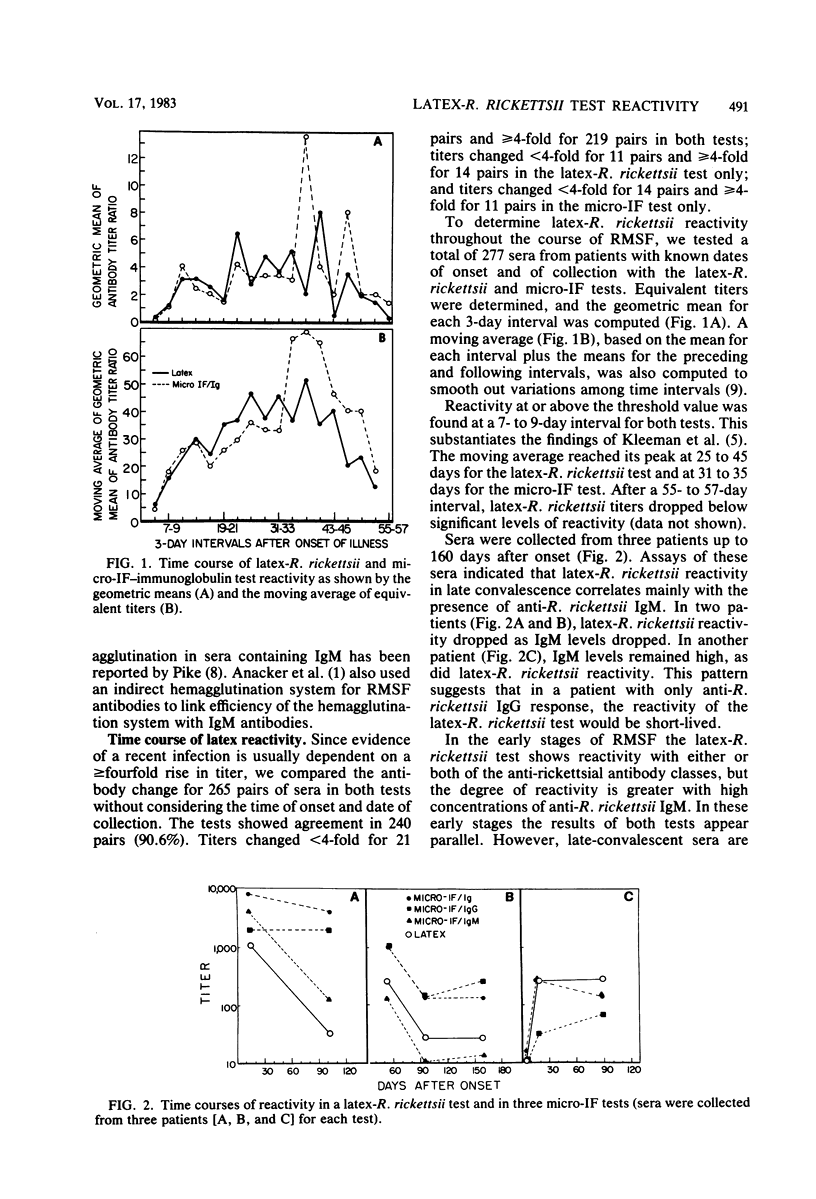
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., Philip R. N., Thomas L. A., Casper E. A. Indirect hemagglutination test for detection of antibody to Rickettsia rickettsii in sera from humans and common laboratory animals. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):677–684. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.677-684.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechemy K. E., Anacker R. L., Philip R. N., Kleeman K. T., MacCormack J. N., Sasowski S. J., Michaelson E. E. Detection of Rocky Mountain spotted fever antibodies by a latex agglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):144–150. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.144-150.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechemy K. E., Osterman J. V., Eisemann C. S., Elliott L. B., Sasowski S. J. Detection of typhus antibodies by latex agglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):214–216. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.214-216.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., MacCormack J. N., Sexton D., Thomas L. A., Anacker R. L., Burgdorfer W., Vick S. A comparison of serologic methods for diagnosis of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Jan;105(1):56–67. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M. G., Burgdorfer W. Microimmunofluorescence test for the serological study of rocky mountain spotted fever and typhus. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jan;3(1):51–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.1.51-61.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike R. M. Antibody heterogeneity and serological reactions. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Jun;31(2):157–174. doi: 10.1128/br.31.2.157-174.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


