Abstract
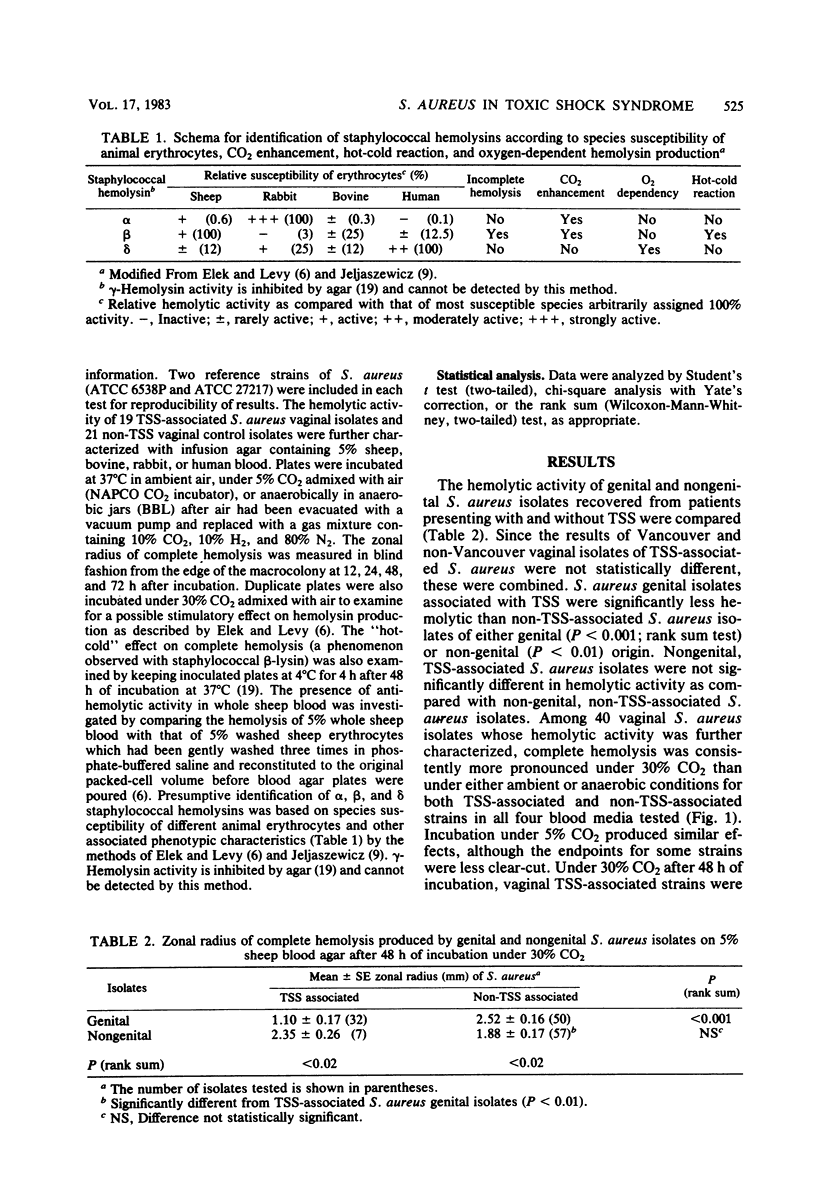
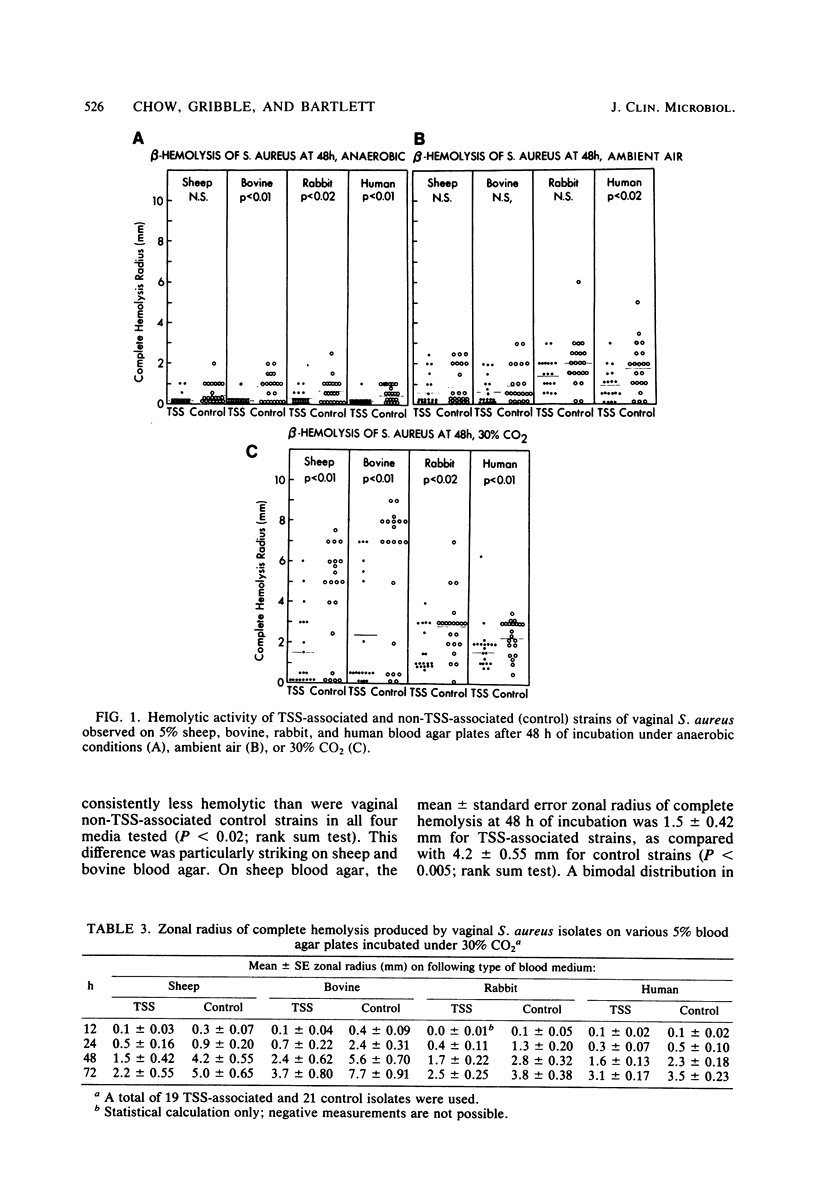
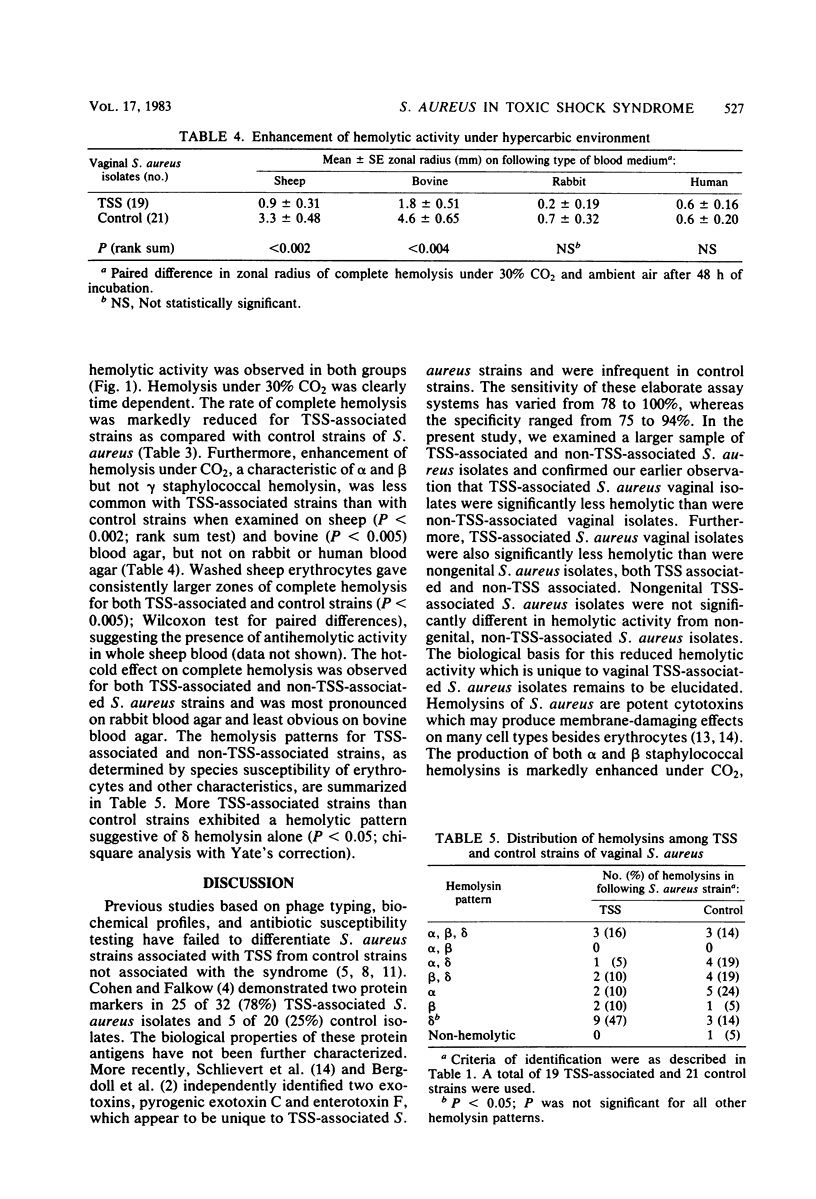
The hemolytic activity of 32 vaginal isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from patients with typical toxic shock syndrome (TSS) was contrasted with that of 50 vaginal isolates from patients without TSS, using a standardized inoculum (10(5) CFU) on 5% sheep blood agar after 48 h of incubation under 30% CO2. Additionally, 7 nongenital isolates from patients with nonmenstrual TSS and 57 strains of nongenital control isolates were included for comparison. Vaginal TSS strains were significantly less hemolytic than non-TSS S. aureus strains of either genital (P less than 0.001) or nongenital (P less than 0.01) origin. Vaginal TSS S. aureus strains were also less hemolytic than were nongenital TSS S. aureus strains (P less than 0.02). This reduced hemolytic activity of genital TSS S. aureus strains may provide a useful marker for screening and further delineation of toxigenic S. aureus associated with menstrually related TSS.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altemeier W. A., Lewis S. A., Schlievert P. M., Bergdoll M. S., Bjornson H. S., Staneck J. L., Crass B. A. Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome: phage typing and toxin capability testing. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):978–982. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Vaginal isolates of Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):442–449. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.442-449.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Falkow S. Protein antigens from Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic-shock syndrome. Science. 1981 Feb 20;211(4484):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.7466361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. P., Chesney P. J., Wand P. J., LaVenture M. Toxic-shock syndrome: epidemiologic features, recurrence, risk factors, and prevention. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1429–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D., LEVY E. Distribution of haemolysins in pathogenic and non-pathogenic staphylococci. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;62(4):541–554. doi: 10.1002/path.1700620405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Goodpasture H. C., Peterie J. D., Voth D. W. Toxic shock syndrome in menstruating women. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Feb;94(2):156–163. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-2-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Epidermal toxin production by Staphylococcus aureus strains from patients with toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):972–974. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna U. G., Meadows J. A., 3rd, Brewer N. S., Wilson W. R., Perrault J. Toxic shock syndrome, a newly recognized disease entity. Report of 11 cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980 Nov;55(11):663–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M. Nonenteric toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Sep;43(3):320–360. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.3.320-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands K. N., Schmid G. P., Dan B. B., Blum D., Guidotti R. J., Hargrett N. T., Anderson R. L., Hill D. L., Broome C. V., Band J. D. Toxic-shock syndrome in menstruating women: association with tampon use and Staphylococcus aureus and clinical features in 52 cases. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1436–1442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J., Fishaut M., Kapral F., Welch T. Toxic-shock syndrome associated with phage-group-I Staphylococci. Lancet. 1978 Nov 25;2(8100):1116–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tofte R. W., Williams D. N. Toxic shock syndrome: clinical and laboratory features in 15 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Feb;94(2):149–156. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-2-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M. The hemolysins of Staphylococcus aureus. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):317–344. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.317-344.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


