Abstract
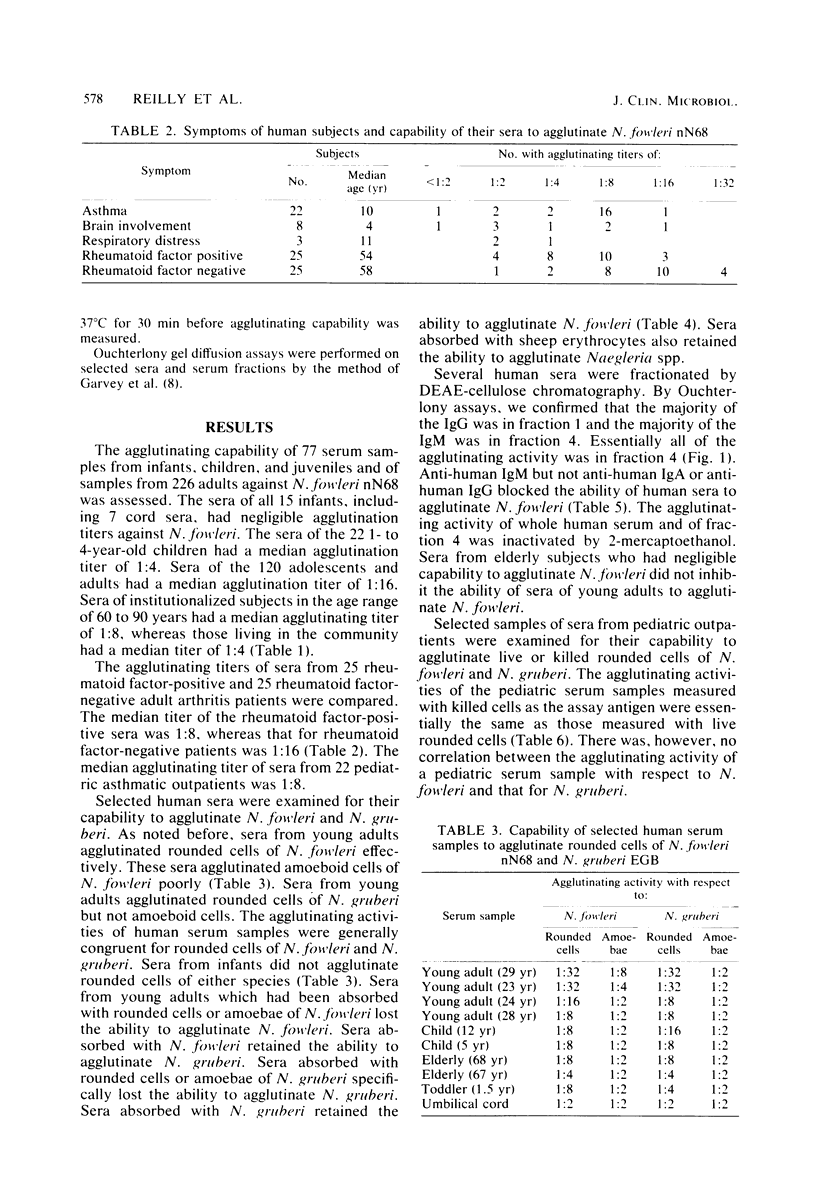
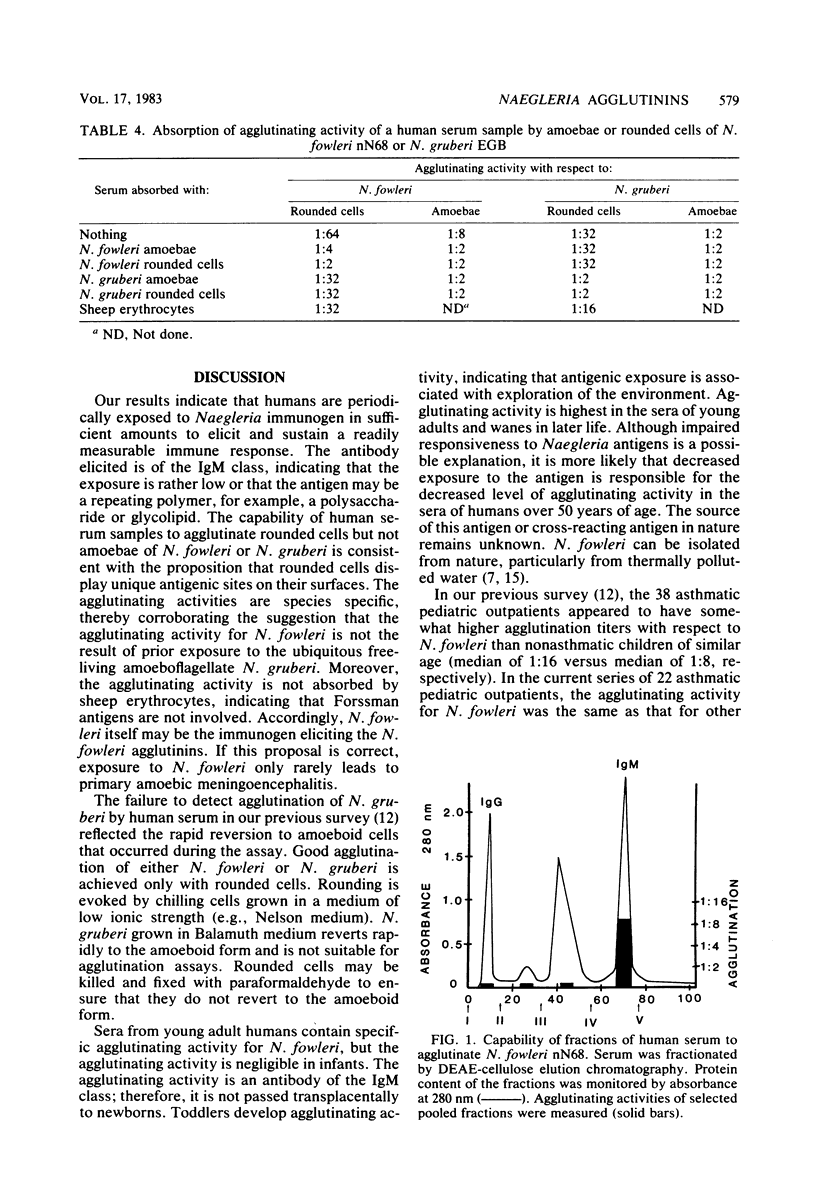
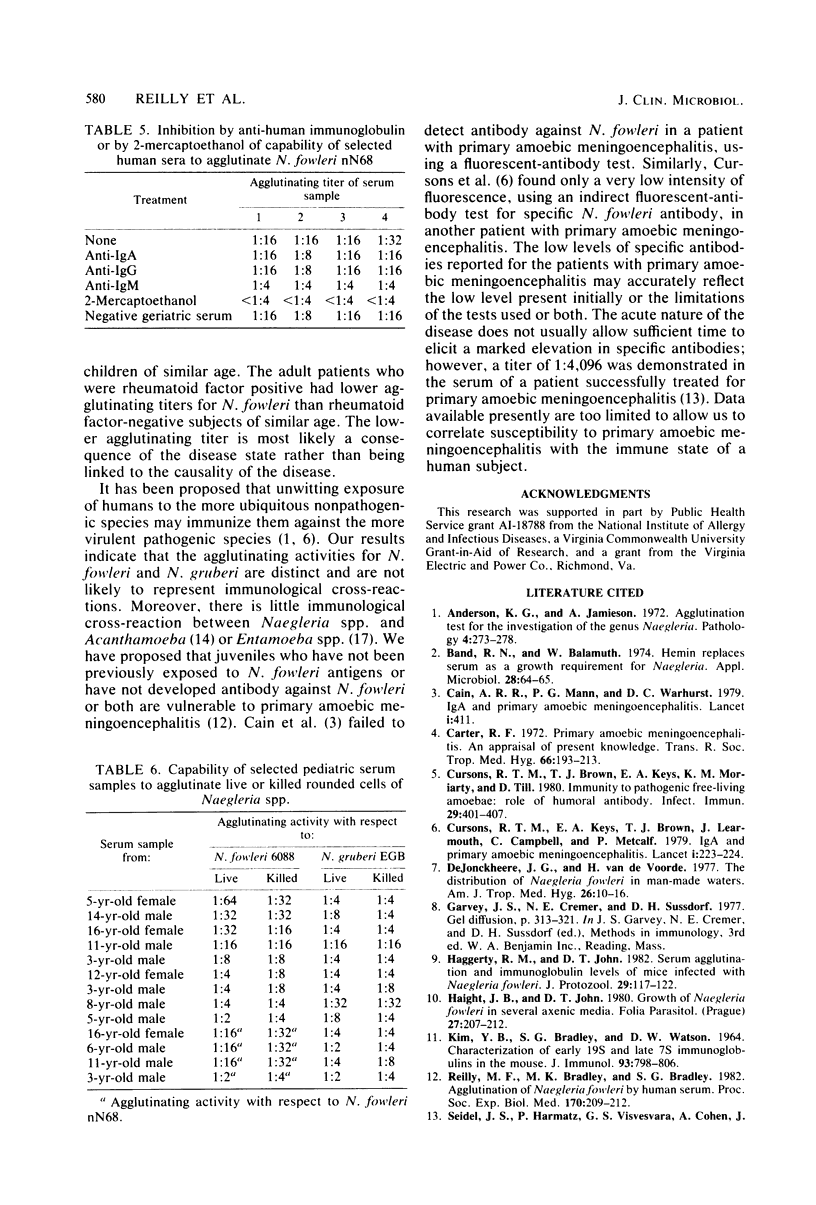
The capability of serum samples from 423 human subjects to agglutinate rounded cells of Naegleria fowleri nN68 was assessed. Sera from the umbilical cords of seven infants failed to agglutinate N. fowleri cells. The median agglutination titer was 1:4 for sera from children through age 4 years, 1:8 for sera from juveniles 5 to 15 years of age, and 1:16 for sera from subjects 15 to 30 years old. The agglutination titers of sera from older adults decreased to a median of 1:8 for the 40- to 60-year-old age group and to 1:4 for the 60- to 90-year-old subjects. Serum samples from young adults agglutinated rounded cells of both N. fowleri and N. gruberi. The agglutination activity for N. fowleri was removed by absorption with N. fowleri but not with N. gruberi. Conversely, agglutination activity for N. gruberi was removed by absorption with N. gruberi but not with N. fowleri. The agglutinating activity for N. fowleri was immunoglobulin M. Serum samples from children displayed markedly disparate capabilities to agglutinate N. fowleri and N. gruberi. Only rounded cells of N. fowleri or N. gruberi were reliably agglutinated by human serum samples. Live or paraformaldehyde-killed cells could be used in the assay, but live N. gruberi cells returned to the amoeboid form, and these agglutinated poorly.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K., Jamieson A. Agglutination test for the investigation of the genus Naegleria. Pathology. 1972 Oct;4(4):273–278. doi: 10.3109/00313027209068953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Band R. N., Balamuth W. Hemin replaces serum as a growth requirement for Naegleria. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jul;28(1):64–65. doi: 10.1128/am.28.1.64-65.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. F. Primary amoebic meningo-encephalitis. An appraisal of present knowledge. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1972;66(2):193–213. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(72)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Brown T. J., Keys E. A., Moriarty K. M., Till D. Immunity to pathogenic free-living amoebae: role of humoral antibody. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):401–407. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.401-407.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Keys E. A., Brown T. J., Learmonth J., Campbell C., Metcalf P. IgA and primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):223–224. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90635-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty R. M., John D. T. Serum agglutination and immunoglobulin levels of mice infected with Naegleria fowleri. J Protozool. 1982 Feb;29(1):117–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1982.tb02892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haight J. B., John D. T. Growth of Naegleria fowleri in several axenic media. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 1980;27(3):207–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIM Y. B., BRADLEY S. G., WATSON D. W. CHARACTERIZATION OF EARLY 19 S AND LATE 7 S IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN THE MOUSE. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:798–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly M. F., Bradley M. K., Bradley S. G. Agglutination of Naegleria fowleri by human serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1982 Jun;170(2):209–212. doi: 10.3181/00379727-170-41420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel J. S., Harmatz P., Visvesvara G. S., Cohen A., Edwards J., Turner J. Successful treatment of primary amebic meningoencephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 11;306(6):346–348. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202113060607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. R., Kilpatrick T., Willaert E., Capron A. Serologic analyses of cell-surface antigens of Acanthamoeba spp. with plasma membrane antisera. J Protozool. 1977 May;24(2):316–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb00986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. R., Tyndall R. L., Coutant C. C., Willaert E. Isolation of the etiological agent of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis from artifically heated waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):701–705. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.701-705.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tew J. G., Burmeister J., Greene E. J., Pflaumer S. K., Goldstein J. A radioimmunoassay for human antibody specific for microbial antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Healy G. R. Comparative antigenic analysis of pathogenic and free-living Naegleria species by the gel diffusion and immunoelectrophoresis techniques. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):95–108. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.95-108.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonckheere J., Voorde H. The distribution of Naegleria fowleri in man-made thermal waters. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Jan;26(1):10–15. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


