Abstract
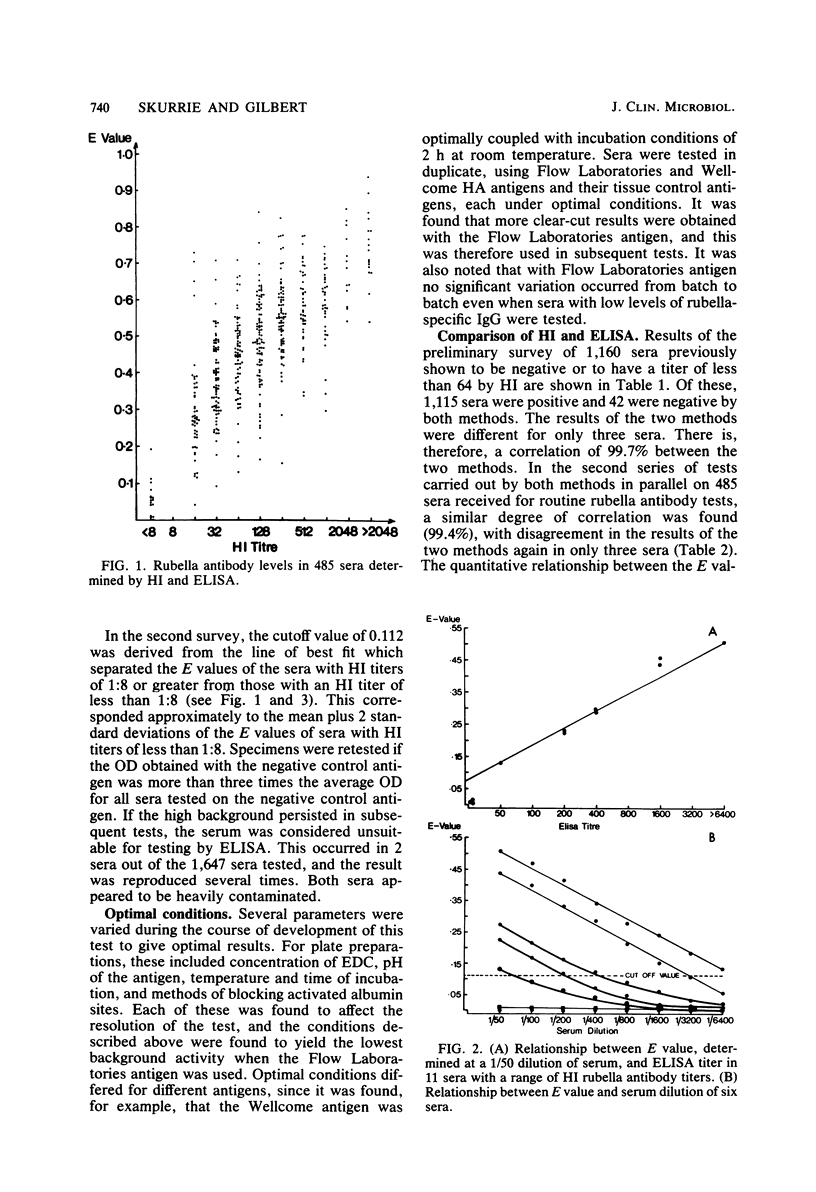
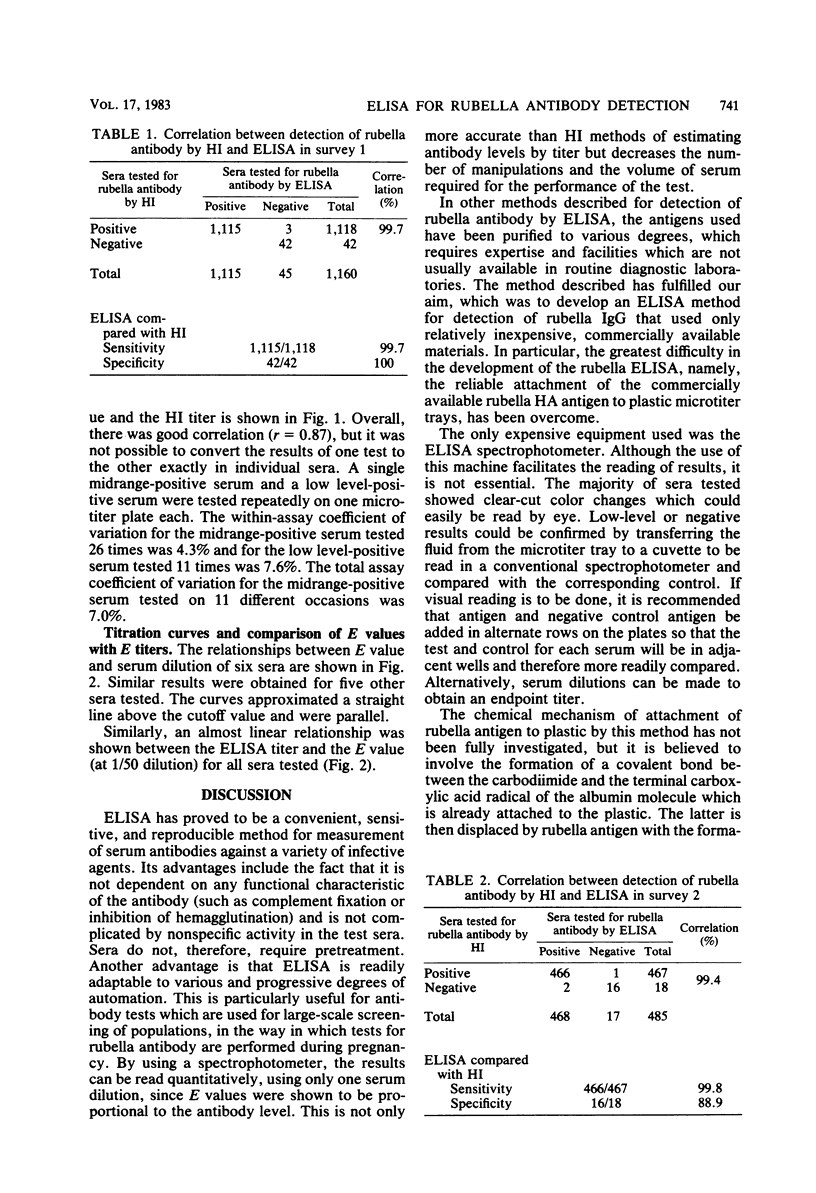
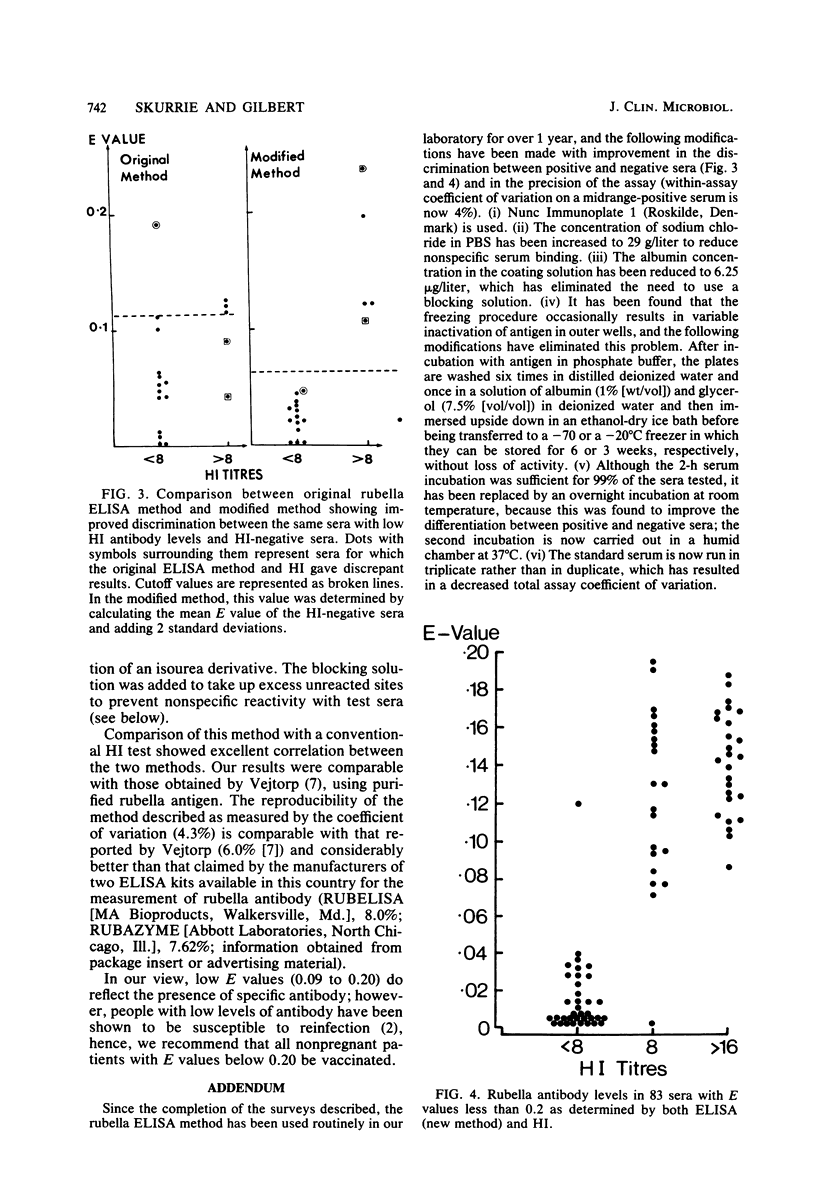
Many of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) techniques previously described for detection of rubella-specific antibodies employ complex technology not available in routine diagnostic laboratories. The method described allows the use of commercially available rubella hemagglutination inhibition (HI) antigen. Passive adsorption of these antigens to plastic is variable, but with the use of albumin as a bridge, it is possible to attach the antigen reliably to the plastic wells. Over 1,500 sera were tested by both HI and ELISA techniques to detect the presence of rubella antibodies. These sera were selected with a bias towards those with low levels of rubella-specific antibody, since it has been demonstrated that it is in this range that discrepancies are more likely to occur between HI and ELISA techniques. In 99% of the sera tested, the results of both techniques were in agreement. On the basis of these results, the technique offers a useful alternative to the routine rubella HI test and other ELISA techniques which need sophisticated antigen preparations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gravell M., Dorsett P. H., Gutenson O., Ley A. C. Detection of antibody to rubella virus by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136 (Suppl):S300–S303. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_2.s300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann D. M., Liebhaber H., Le Bouvier G. L., Rosenberg D. A., Halstead S. B. Rubella: reinfection of vaccinated and naturally immune persons exposed in an epidemic. N Engl J Med. 1970 Oct 8;283(15):771–778. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197010082831501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean B., Sonza S., Holmes I. H. Measurement of immunoglobulin A, G, and M class rotavirus antibodies in serum and mucosal secretions. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):314–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.314-319.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiattini F., Prencipe L., Bardelli F., Giannini G., Tarli P. The 4-hydroxybenzoate/4-aminophenazone chromogenic system used in the enzymic determination of serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1978 Dec;24(12):2161–2165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Dennis J. Modified hemagglutination-inhibition test for rubella employing human group O erythrocytes. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):471–475. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.471-475.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vejtorp M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for determination of rubella IgG antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1978 Dec;86B(6):387–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E. A simple method for detecting antibodies to rubella. Br J Exp Pathol. 1975 Aug;56(4):338–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


