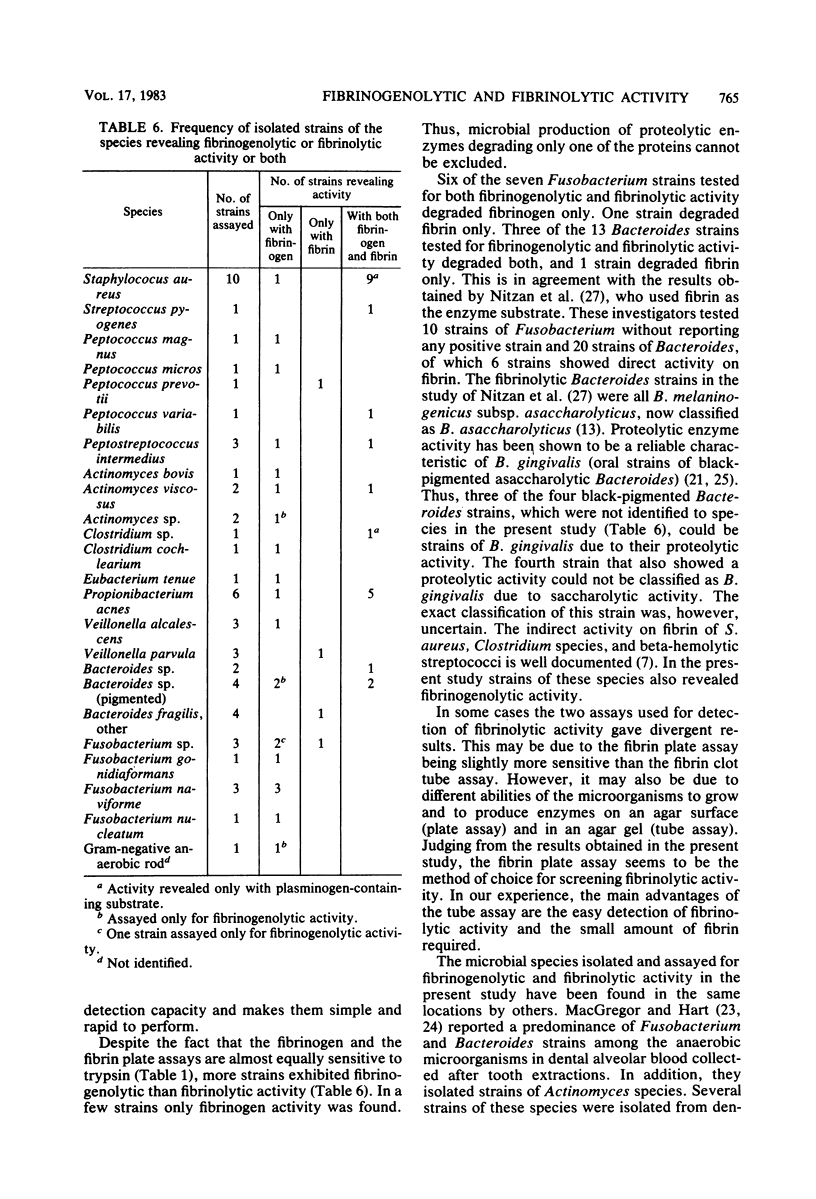
Abstract
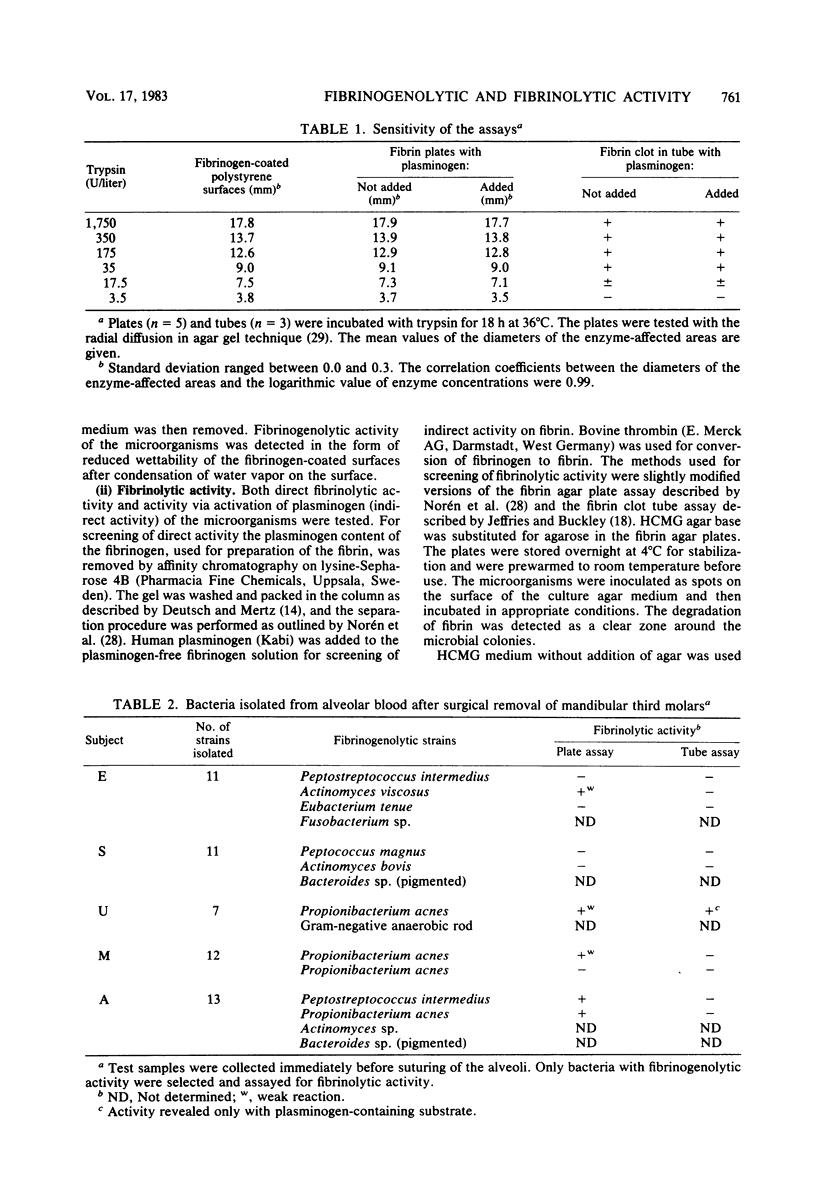
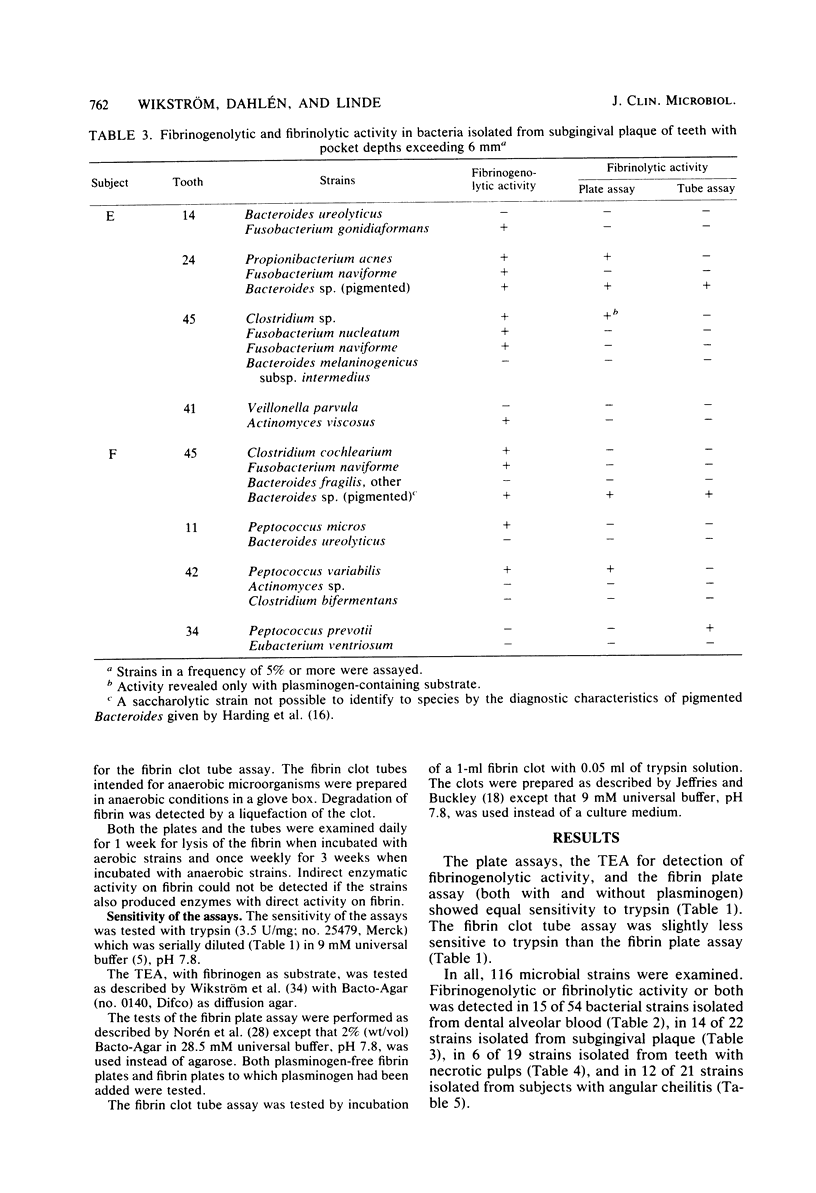
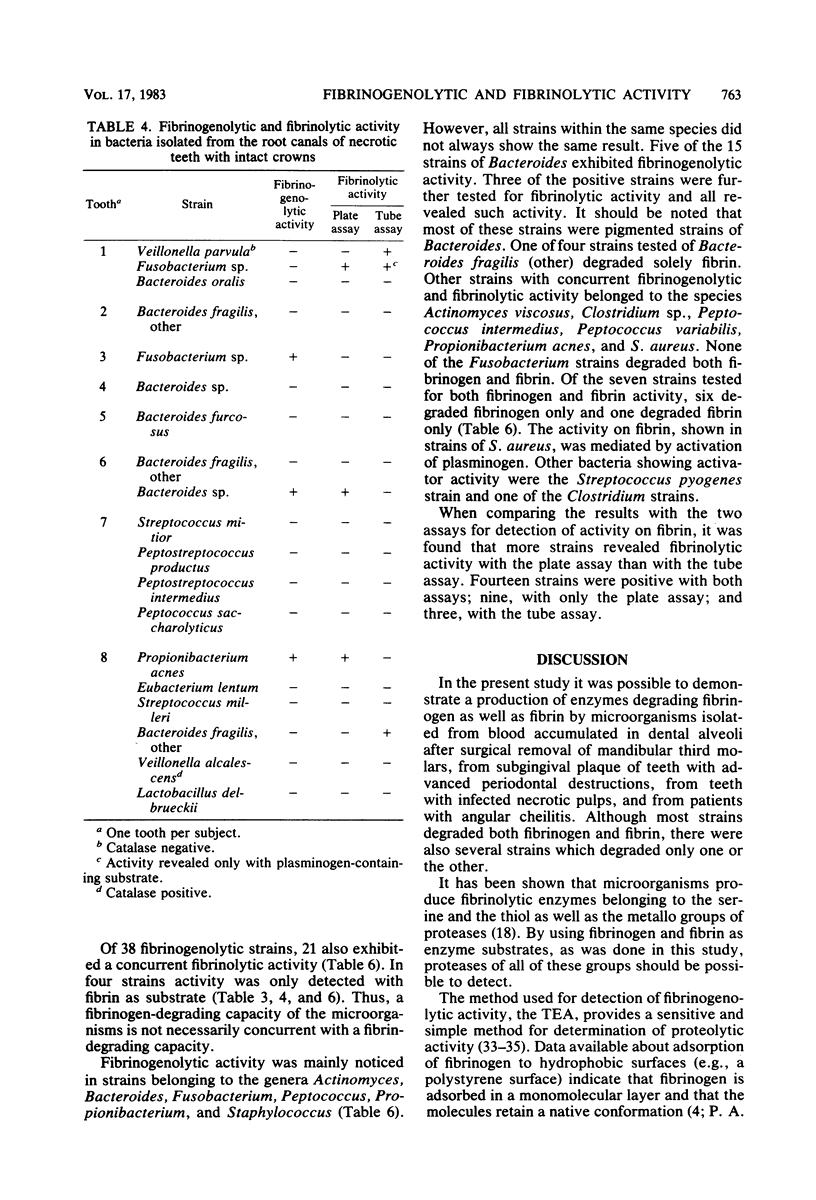
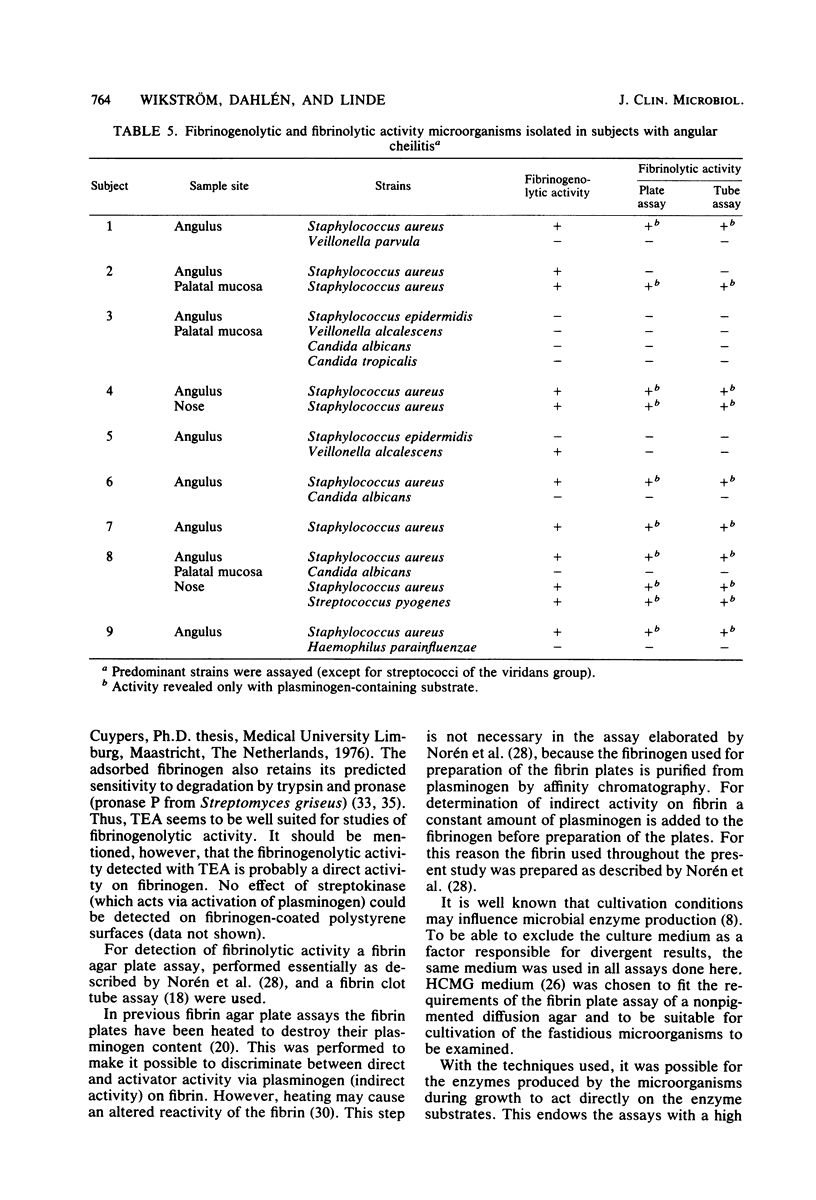
Samples were taken from blood accumulated in dental alveoli after surgical removal of mandibular third molars, from subgingival plaque of teeth with advanced periodontal destructions, from teeth with infected necrotic pulps, and from subjects suffering from angular cheilitis. Of the microorganisms subcultured from these samples, 116 strains were assayed for enzymes degrading fibrinogen and fibrin. Enzymes degrading fibrinogen were assayed with the thin-layer enzyme assay cultivation technique. This assay involves the cultivation of microorganisms on culture agars applied over fibrinogen-coated polystyrene surfaces. Enzymes degrading fibrin were assayed with both a plate assay and a tube assay, in which fibrin was mixed with a microbial culture medium. Microorganisms degrading fibrinogen or fibrin or both were isolated from all sampling sites. Activity was mainly detected in strains of Actinomyces, Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, Peptococcus, Propionibacterium, and Staphylococcus aureus. Most Fusobacterium strains degraded fibrinogen only. Enzymes degrading fibrinogen as well as enzymes degrading fibrin via activation of plasminogen were revealed in strains of Clostridium, S. aureus, and Streptococcus pyogenes. It was generally found that fibrinogen was degraded by more strains than was fibrin, which indicates that different proteases may be involved.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birn H. Bacteria and fibrinolytic activity in "dry socket". Acta Odontol Scand. 1970 Dec;28(6):773–783. doi: 10.3109/00016357009028246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlén G., Bergenholtz G. Endotoxic activity in teeth with necrotic pulps. J Dent Res. 1980 Jun;59(6):1033–1040. doi: 10.1177/00220345800590060501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlén G., Heijl L., Lindhe J., Möller A. Development of plaque and gingivitis following antibiotic therapy in dogs. J Clin Periodontol. 1982 May;9(3):223–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1982.tb02062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlén G., Linde A., Möller A. J., Ohman A. A retrospective study of microbiologic samples from oral mucosal lesions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1982 Mar;53(3):250–255. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(82)90299-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding G. K., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M., Bricknell K. S. Characterization of bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Oct;4(4):354–359. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.4.354-359.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries L., Buckley D. E. The detection and differentiation of fibrinolytic enzymes in bacteria. J Appl Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;49(3):479–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1980.tb04723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantz W. E., Henry C. A. Isolation and classification of anaerobic bacteria from intact pulp chambers of non-vital teeth in man. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Jan;19(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSEN M. Heat denaturation of plasminogen in the fibrin plate method. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953 Feb 28;27(4):371–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00951.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Syed S. A., Loesche W. J. Rapid identification of Bacteroides gingivalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):345–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.345-346.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg C., Nord C. E., Ramström G. Penicillin treatment in oral surgery in patients with coagulation disorders. Int J Oral Surg. 1975 Oct;4(5):198–204. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9785(75)80026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor A. J., Hart P. Bacteria of the extraction wound. J Oral Surg. 1970 Dec;28(12):885–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor A. J., Hart P. Effect of bacteria and other factors on pain and swelling after removal of ectopic mandibular third molars. J Oral Surg. 1969 Mar;27(3):174–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller A. J. Microbiological examination of root canals and periapical tissues of human teeth. Methodological studies. Odontol Tidskr. 1966 Dec 20;74(5 Suppl):1–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitzan D., Sperry J. F., Wilkins T. D. Fibrinolytic activity of oral anaerobic bacteria. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(6):465–470. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norén I., Ramström G., Wallén P. Fibrin plate method with reagents purified by affinity chromatography and its use for determination of fibrinolytic and other proteolytic activity in saliva, bile and plasma. Haemostasis. 1975;4(2):110–124. doi: 10.1159/000214094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petruson B. Epistaxis. A clinical study with special reference to fibrinolysis. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1974;317:1–73. doi: 10.3109/00016487409129566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. The predominant cultivable microflora of advanced periodontitis. Scand J Dent Res. 1977 Jan-Feb;85(2):114–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1977.tb00541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Haffer C., Bratthall G. T., Visconti R. A., Socransky S. S. A study of the bacteria associated with advancing periodontitis in man. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):278–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M. B. Detection of microbial proteolytic activity by a cultivation plate assay in which different proteins adsorbed to a hydrophobic surface are used as substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):393–400. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.393-400.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M., Elwing H., Linde A. Determination of proteolytic activity: a sensitive and simple assay utilizing substrate adsorbed to a plastic surface and radial diffusion in gel. Anal Biochem. 1981 Dec;118(2):240–246. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittgow W. C., Jr, Sabiston C. B., Jr Microorganisms from pulpal chambers of intact teeth with necrotic pulps. J Endod. 1975 May;1(5):168–171. doi: 10.1016/S0099-2399(75)80115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


