INTRODUCTION
There is unexplained variability in the extent to which patients recover after stroke, particularly from the reference point of the first few days after onset. Among studies tracking motor impairment and recovery, only 30–50% of the variance of recovery is explained by the most commonly reported predictors --lesion volume and initial stroke severity 1, 2. We hypothesized that functional imaging early after stroke could provide information over and above initial severity and lesion volume about the degree of subsequent recovery. Several prior functional imaging studies have reported altered brain activation patterns in patients at various stages of motor recovery after stroke3–6. These studies describe brain activation related to concurrent recovered performance at the time of scanning that differs to varying degrees from what is seen in age-matched controls. In this study we used functional imaging to ask a specific and unique question about motor recovery after stroke: can functional imaging in the early period after stroke detect brain activation related to subsequent recovered performance? Should such activation be identified then it could serve as a physiological target for intervention (e.g. non-invasive brain stimulation) in this early time period.
To investigate whether brain activation early after stroke can be correlated with subsequent recovery, we scanned patients approximately 48 hours after stroke using fMRI, and defined recovery as the change in motor impairment from the time of scanning to a follow up point 3 months later. We used 3 different statistical tests: 1) a multivariate test, which is most sensitive to spatially diffuse activation, 2) voxel-wise statistical parametric mapping (SPM), which is most sensitive to focal activation, and 3) primary motor cortex (M1) region of interest (ROI) analysis, which is most sensitive to average activation within this region. The ROI analysis was chosen to test existing hypotheses implicating M1 and the corticospinal tract in recovery.7–9 All tests controlled for lesion volume and initial stroke severity, as well as other established clinical variables.
METHODS
Subjects
We recruited stroke patients from a large screening data base of all patients with the diagnosis of ischemic stroke admitted to Columbia University Medical Center between December, 2004 and April, 2007 (n=993), part of Columbia’s Specialized Program of Translational Research in Acute Stroke (SPOTRIAS), an NINDS-funded national network to investigate new pathophysiologic, diagnostic and clinical approaches in acute stroke. Thirty-three consecutive patients with first ever ischemic stroke and hemiparesis able to undergo fMRI within 48 hours of stroke onset were recruited. Five patients were eligible but refused the fMRI scan. Three underwent the fMRI, but did not complete the 3-month clinical follow up (1 developed dementia, 1 left the country, 1 was incarcerated). Two patients had recurrent stroke prior to the 3-month follow-up and were excluded from analysis. The final sample size of 23 was considered adequate for a functional imaging study of this type. Patients with aphasia or hemineglect alone were not included in this analysis. See Table 1 for more demographic and clinical details.
Table 1.
Demographic, imaging and clinical data. C=cortical, S=subcortical lesion location, WM=white matter, FM=Fugl-Meyer, Dyn=hand dynamometry, OT=occupational therapy, PT=physical therapy, U=unknown.
| Pt | Age/Gend | Lesio n Side | Cort/Subcort | Location | Lesion Vol (cc) | Cort vol | Subcort vol | FM initial | FM 3mo | Delta FM | Dyn initial | Diabetes Mellitus | OT/PT Hrs/wk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56/F | R | S | Int capsule, basal ganglia | 1.588 | 0 | 1.588 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | No | 10 |
| 2 | 51/F | L | S | Corona radiata/Basal ganglia | 4.678 | 0 | 4.678 | 61 | 66 | 5 | 19 | No | 2 |
| 3 | 59/F | R | S | Pons | 0.422 | 0 | 0.422 | 63 | 66 | 3 | 11 | No | 0 |
| 4 | 70/M | R | S | Pons | 1.155 | 0 | 1.155 | 57 | 63 | 6 | 33 | No | 0 |
| 5 | 48/M | R | S | Corona radiate/Basal ganglia | 13.49 | 0 | 13.49 | 63 | 66 | 3 | 27 | No | 0 |
| 6 | 47/M | L | S | Pons | 0.668 | 0 | 0.668 | 24 | 63 | 39 | 1 | No | 0 |
| 7 | 65/M | R | C | Occipital/Frontal | 8.807 | 0 | 8.807 | 25 | 63 | 38 | 0 | Yes | 3 |
| 8 | 63/M | L | S | Internal capsule | 1.550 | 0 | 1.550 | 31 | 57 | 26 | 0 | No | 0 |
| 9 | 59/F | L | C/S | Insula/Corona | 5.541 | 0.251 | 5.290 | 5 | 11 | 6 | 0 | Yes | 0 |
| 10 | 65/F | R | S | Corona | 1.431 | 0 | 1.431 | 46 | 61 | 15 | 5 | Yes | 0 |
| 11 | 77/M | R | C | Insula/precentral | 4.992 | 4.992 | 0 | 21 | 55 | 34 | 0 | No | 0 |
| 12 | 67/F | R | S | Internal Capsule | 0.7756 | 0 | 0.7756 | 14 | 40 | 26 | 1 | No | 9 |
| 13 | 56/M | R | S | Corona radiata/External capsule | 11.326 | 0 | 11.326 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | Yes | 6 |
| 14 | 59/M | L | S | Pons | 1.311 | 0 | 1.311 | 6 | 46 | 40 | 0 | Yes | 15 |
| 15 | 42/F | L | C/S | Insula/Corona radiate | 2.248 | 1.400 | 0.848 | 59 | 66 | 7 | 26 | No | 4 |
| 16 | 69/M | L | C/S | Occipital/Pons/R Insula Inf frontal/Corona radiate | 0.3552 | 0.0392 | 0.316 | 37 | 64 | 27 | 0 | No | 4 |
| 17 | 78/M | R/L | C/S | Radiata, L Occcipital | 3.736 | 1.610 | 2.126 | 18 | 53 | 35 | 0 | Yes | U |
| 18 | 43/M | R | S | Pos | 0.580 | 0 | 0.580 | 49 | 62 | 13 | 30 | Yes | 0 |
| 19 | 48/M | L | S | Internal capsule | 0.679 | 0 | 0.679 | 62 | 65 | 3 | 21 | No | 3.5 |
| 20 | 72/M | L | C | Inferior frontal/Insula | 47.579 | 47.579 | 0 | 64 | 66 | 2 | 16 | No | 0 |
| 21 | 60/M | L | S | Pons/temp/par WM | 0.695 | 0 | 0.695 | 49 | 64 | 15 | 27 | Yes | 0 |
| 22 | 45/M | R | S | Corona radiate | 4.416 | 0 | 4.416 | 62 | 66 | 4 | 40 | No | 0 |
| 23 | 59/M | L | S | Pons | 0.412 | 0 | 0.412 | 8 | 40 | 32 | 1 | No | 14 |
All patients except for 4 underwent a single session of fMRI scanning at our target of 24–48 hours after stroke onset (the remaining 4 patients had their scans between 49 and 96 hours due to scheduling delays; mean time to scan=47.8±21.6h, median=46h). Exclusion criteria also included seizure at stroke onset, moderate to severe aphasia or other cognitive impairment that precluded training on the fMRI task, or any contraindication to MRI. None of the patients had neglect or apraxia on examination. Patients did not smoke on the day of scanning (they were inpatients); caffeine intake was not recorded. The strict eligibility criteria permitted us to control for unwanted variables while preserving the wide spectrum of initial motor severity that would contribute to the correlation analysis. Total lesion volumes were estimated by summing the volumes of the DWI lesion in each slice (length by width by slice thickness measured with the measurement tool in the PACS system software) in which the DWI was positive.
Recovery measure
Motor impairment was measured with the upper limb Fugl-Meyer assessment (FM)11, which has a maximum score of 66, and is valid and highly reliable over a wide spectrum of severities.12–16 FM was assessed on the day of scanning (FMinitial) and again at 3 months (FM3 months). Recovery (ΔFM) was defined as ΔFM = FM3 months − FMinitial. Our decision to use a change score as our measure of recovery was based on the idea that the degree of change, rather than the final level achieved, would better reflect a biological recovery process 17.
In addition to the FM we also measured hand dynamometry at baseline on the day of scanning (DYNinitial). The reason for doing so was that hand dynamometry score should presumably correlate with the degree of difficulty subjects would have to perform the fMRI hand closure task. DYNinitial was taken as an average of 3 measurements of maximal grip force.
fMRI data acquisition
Patients underwent gradient echo-echoplanar fMRI (GE 1.5 T, 64 × 64 matrix, FOV = 19 cm, 21 slices, slice thickness/skip = 4.5 mm/0 mm, TR = 4000 ms, TE = 52 ms, flip angle = 60°) while performing the repetitive hand closure task described below. One session (40 volumes) was performed per hand. The order in which the hands (affected/unaffected) were tested was counterbalanced across patients except for those with complete plegia (see below).
Motor task used during fMRI
The task was a simple repetitive hand closure in synchrony with a 1 Hz metronome click, following a block design: 20-second rest epochs alternating with 20-second task epochs (4 cycles total per hand). The instruction was: ”Close your hand gently in rhythm with the click you hear. Start and stop when you hear the instructions through the headphones.” The metronome click was played continuously via MRI-compatible headphones in the scanner. No other instructions were given with respect to a particular level of grip force. Auditory “Start” and “Stop” commands were given via the headphones at the beginning and end of each 20-second task block. Separate runs were performed for the affected hand and unaffected hand. For patients with plegia, defined as maximum grip force of <1 kg on dynamometry, the unaffected had was tested first in order to demonstrate correct understanding of the task in the scanner. For these patients instructions were given to "do exactly what you did with your good hand.” Differences in in-scanner performance were controlled for by including FMinitial and DYNinitial in the regression model (see statistical analysis method below). Although in-scanner performance clearly could differ across patients, this approach allowed us to include in our analysis patients with a wide spectrum of initial severity. Patients were pre-trained on the task outside of the scanner, lying supine with the metronome tone until they could perform the task without difficulty. Qualitative, direct visual assessment of mirror movements was made by an investigator during scanning (only rare, intermittent movements of the opposite hand or foot were seen). No other quantitative behavioral data were acquired during pre-training or the scanning itself.
fMRI pre-processing
All image pre-processing was implemented using the SPM5 program (Wellcome Department of Imaging Neuroscience). The following steps were performed per patient: All functional images were realigned to the first volume of the first session. The first functional image was then used to determine parameters (7 × 8 × 7 non-linear basis functions) for transformation into a Talairach standard space18 defined by the Montreal Neurologic Institute gradient echo-echoplanar template brain supplied with SPM5. This transformation was then applied to all the functional volumes, which were re-sliced using sinc-interpolation to 2 mm × 2 mm × 2 mm. Using knowledge of the infarct location, all images were oriented such that the right side of the brain corresponded to the ipsilesional hemisphere.
Image processing and statistical analysis
The general statistical approach applied to the fMRI data comprised in turn: 1) a within-subject, voxel-wise regression of the fMRI time series to estimate task-related brain activation (i.e., standard SPM first-level19), 2) an across-subject, voxel-wise regression of the first-level regression coefficients on a set of predictors including ΔFM, yielding second-level regression coefficient at each voxel (i.e., standard SPM second-level19), and 3) the application of 3 different statistical tests applied to the relationship between the second-level regression coefficients and ΔFM: (i) a multivariate test, which assesses effects of interest in all voxels in the brain with a single, global test statistic, (ii) an SPM test of cluster-wise significance (height thresholded at p < 0.001 uncorrected and with cluster size threshold = 163 voxels; this cluster size threshold was chosen as it provided a map-wise corrected cluster-wise false positive rate of 0.05 given the chosen height threshold), and (iii) a t-test on the spatially averaged signal within the ROI. The purpose of using three different tests for the same relationship was that they have different relative sensitivities for different types of spatial signals: the multivariate test is relatively more sensitive to low amplitude, spatially diffuse signals; the SPM cluster-wise test is relatively more sensitive to intense, spatially focal signals (though there is also some dependence on spatial extent); the ROI test has the best sensitivity for the average effect in a given ROI.
For the first-level analysis, fMRI time series from each subject were regressed voxel-wise on a square wave convolved with the default hemodynamic response function in SPM5 (high-pass filter cut-off = .01875 Hz). The resulting regression coefficient at each voxel (for each subject) was divided by the corresponding time series mean to yield values proportional to percent fMRI signal change. These images were then spatially smoothed (isotropic Gaussian kernel, full width-at-half-maximum = 8 mm). The resulting images were then entered into a second-level, across subject, random effects regression model that included ΔFM as a covariate. Additional covariates included variables that were significant in a previous regression analysis to predict ΔFM (initial stroke severity (FMinitial), sub-cortical lesion volume, and age), as well as others that were not significant but included because of a plausible biological relationship to ΔFM: baseline grip force (DYNinitial), cortical lesion volume, and cortical and subcortical lesion location. The point of including all these variables besides ΔFM was to ensure that any correlation detected between task-related brain activation and ΔFM reflects a linear relationship over and above that between these other variables and ΔFM.
Tests for statistical significance were then applied. It should be noted that the null hypothesis for both the multivariate test and the SPM cluster-wise test was the same, namely that there are no second-level effects of interest (i.e. correlations between task-related fMRI activation and ΔFM) at any voxel. The tests differ in their results, however. Rejecting the null hypothesis with the cluster-wise test allows formal localization of effects in suprathreshold clusters, whereas rejecting the null hypothesis with the multivariate test only provides evidence for the existence of effects somewhere in the brain without the ability to infer effects at the individual voxel level. This is because the multivariate statistical test involves assessing the significance of all the voxels in the search volume in ensemble, not separately. The process can be heuristically understood as an averaging across voxels of the F-statistics associated with the effects of interest, and then comparing this single value to an appropriate null hypothesis F distribution. More details are provided in a Supplementary Section. For full details, see Worsley et al. (1997).20
The spatial distribution of the multivariate correlation, which can be referred to as the “recovery pattern,” is simply the standard statistical parametric map (SPM(t)) of the second-level regression. Once the recovery pattern (correlation) was identified by applying the multivariate test, we could then compute for each subject a “pattern expression” (degree of expression of the recovery pattern) by taking the inner product of the recovery pattern with each second level dependent image after having adjusted the latter for effects of the additional predictors. This would allow us to represent graphically the value of the fMRI signal correlation for each individual plotted against their ΔFM.
The M1 ROI was defined as the BA4 ROI from WFU Pickatlas (version 2.4).21 The same second-level regression model described above was applied to the spatially averaged first-level regression coefficient within this ROI, and a t-test was performed on the resulting second-level coefficient corresponding to ΔFM.
RESULTS
Patient data
Of the 23 who were analyzed in the study, average age was 59.0±10.5, 16 were male, 22 were right handed. All lesions involved some part of the corticospinal tract. Twelve had strokes in the right hemisphere, 16 were subcortical only (7 brainstem, 9 striatocapsular/corona radiata), 3 were cortical only (2 frontal/insula, 1 frontal/occipital), and 4 were combined (2 insula/coronal radiata, 1 occipital/frontal/insula/corona radiata, 1 occipital/pons). A single patient had bilateral strokes (pt 17) -- although the left hemisphere lesion was a small cortical occipital infarct (see Table 1). Eleven of the patients received physiotherapy after stroke (total number of hours per week of therapy listed in Table 1).
Behavioral results
Each subject’s FMinitial, ΔFM, and hand dynamometry at time of scanning are shown in Table 1. FMinitial ranged from 6 to 63 (mean = 36.3 ± 22.9). Dynamometry scores at the time of scanning ranged from 0 to 40 kg. ΔFM ranged from 0 to 40 (mean = 16.5 ± 14.5). All patients performed the in-scanner hand closure task without difficulty with the unaffected hand.
Main effect of task
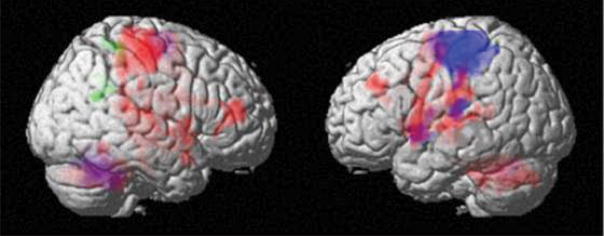
We first tested for brain activation associated with the main effect of the motor task (i.e. the across-subject average of the motor task-versus-rest regression coefficient) in order to establish that fMRI as implemented in this study would yield patterns of task-related activity consistent with previous reports. Although theoretical concerns existed whether altered vasoreactivity early after stroke22 could have precluded our finding a common pattern across patients, this was not the case. Using SPM cluster-wise testing (p<.05, corrected), we found that with use of the unaffected hand there were significant clusters in contralateral M1 and S1, supplementary motor area, and ipsilateral cerebellum, consistent with previous studies in healthy subjects23–25 (see Figure 1, blue color). With use of the affected hand there were activations not only in areas homologous to those just mentioned but also extra activations in ipsilateral M1, ipsilateral premotor cortex, bilateral prefrontal cortex, and contralateral cerebellum, as has been described previously26–28 (see Figure 1, red color). Table 2 lists coordinates of the maxima of the significant clusters.
Figure 1.
Table 2.
| corrected, cluster p-value | cluster size (voxels) | t(30) | z* | x (mm) | y (mm) | z (mm) | Brodmann Area | Anatomical Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔFM, AFF hand | ||||||||
| 0.028 | 191 | 4.31 | 3.77 | 24 | −38 | 52 | Brodmann area 3 | Right Cerebrum, Parietal Lobe, Postcentral Gyrus |
| 25 | −35 | 48 | ||||||
| 0.038 | 176 | 4.31 | 3.77 | 24 | −50 | 34 | Brodmann area 31 | Right Cerebrum, Limbic Lobe, Cingulate Gyrus |
| 24 | −47 | 32 | ||||||
| ΔFM, UNAFF hand | ||||||||
| no significant clusters | ||||||||
| mean activation, AFF hand | ||||||||
| < 0.001 | 1537 | 9.13 | 6.27 | −4 | −8 | 58 | Brodmann area 6 | Left Cerebrum, Frontal Lobe, Medial Frontal Gyrus |
| < 0.001 | 4287 | 8.61 | 6.07 | −18 | −50 | −30 | n/a | Left Cerebellum, Anterior Lobe |
| < 0.001 | 8794 | 8.5 | 6.02 | 40 | −24 | 62 | Brodmann area 3 | Right Cerebrum, Parietal Lobe, Postcentral Gyrus |
| 0.003 | 307 | 5.06 | 4.27 | −36 | 38 | 34 | Brodmann area 9 | Left Cerebrum, Frontal Lobe, Superior Frontal Gyrus |
| 0.001 | 376 | 5.00 | 4.23 | 46 | 46 | 12 | Brodmann area 10 | Right Cerebrum, Frontal Lobe, Middle Frontal Gyrus |
| 0.045 | 168 | 4.60 | 3.97 | 36 | −50 | −16 | Brodmann area 37 | Right Cerebrum, Temporal Lobe, Fusiform Gyrus |
| < 0.001 | 863 | 4.48 | 3.89 | −56 | −22 | 12 | Brodmann area 41 | Left Cerebrum, Temporal Lobe, Transverse Temporal Gyrus |
| mean activation, UNAFF hand | ||||||||
| < 0.001 | 2898 | 13.13 | 7.51 | −38 | −22 | 54 | Brodmann area 3 | Left Cerebrum, Parietal Lobe, Postcentral Gyrus, |
| < 0.001 | 1459 | 10.02 | 6.59 | 18 | −50 | −26 | n/a | Right Cerebellum, Anterior Lobe, Dentate |
| < 0.001 | 515 | 7.60 | 5.63 | −4 | −10 | 58 | Brodmann area 6 | Left Cerebrum, Frontal Lobe, Medial Frontal Gyrus |
| 0.018 | 212 | 5.75 | 4.68 | −54 | −22 | 12 | Brodmann area 40 | Left Cerebrum, Parietal Lobe, Postcentral Gyrus |
| 0.010 | 239 | 4.73 | 4.06 | −44 | −4 | 14 | Brodmann area 13 | Left Cerebrum, Sub-lobar, Insula |
this is the standard normal random variable corresponding to the t-value via probability transform
Recovery-related fMRI results
We next tested for correlations between brain activation early after stroke and ΔFM while controlling for the clinical variables described in the methods section. The multivariate test was significant for use of the affected [F(595,4934) = 1.93, p < 0.001], but not the unaffected [F(595,4934) = 0.91, p = 0.99] hand. Because the multivariate test cannot be used to infer anatomical information at the voxel level the recovery-related activation pattern identified with this test is not illustrated in a figure. Applying the SPM cluster-wise test to the correlation between fMRI signal and ΔFM (p<.05, corrected), we found significant clusters in the right (ipsilesional) post-central gyrus and posterior cingulate gyrus for affected hand activity (see Figure 1, green color, table 2 for maxima coordinates), and none for the unaffected hand. It is important to understand that areas other than those identified in the cluster-wise analysis could have activation truly correlated with ΔFM, as sensitivity of the SPM test is poor for sufficiently low voxel-wise statistical effect sizes. However, such weak voxel-wise effects, taken in ensemble over the entire brain could lead to an appreciable multivariate statistical effect size, which was the reasoning behind our use of the multivariate test. As it turned out, both multivariate and SPM test results were positive, but we are careful not to conclude that the suprathreshold SPM clusters were the sole contributors to the multivariate test result. We also note the distinction between the clusters of activation associated with ΔFM and those atypical clusters of “extra” activation associated with the main effect of task when using the affected hand. The fact that these extra activations did not show significant correlation with ΔFM suggests that they are not predominantly related to subsequent recovery.
Testing specifically for fMRI- ΔFM correlations in primary motor cortex with the ROI test, we found no statistically significant result in either contralateral [t(15) = 1.58, two-tailed p = 0.14] or ipsilateral [t(15) = 1.40, two-tailed p = 0.18] M1 ROIs. The correlations were also not significant in either the contralateral [t(15) = −0.31, two-tailed p = 0.76] or ipsilateral [t(15) = 0.59, two-tailed p = 0.56] M1 ROIs when using the unaffected hand.
Figure 2 shows a scatter plot of ΔFM for each of the 23 patients plotted against their recovery pattern expression derived from the multivariate test: those with lower expression of the recovery pattern had lower ΔFM s; those with higher expressions had higher ΔFM s. Of note is the wide distribution of locations on the plot among patients with severe paresis (FMinitial<20) at onset (data points in black). Even though these patients all were severely affected at onset, those with little subsequent recovery had a very low expression of the pattern in the early period after stroke and those with greater subsequent recovery expressed the pattern to a much greater extent. This dissociation could be expected because we controlled for severity at onset in the regression model, and supports the finding that there may be subpopulations of patients -- perhaps most striking among those with severe motor deficits -- who recover either proportionally to their initial deficits, or very poorly,17 and that their relative expression of the recovery pattern may be reflecting a biological difference between them.
Figure 2.
DISCUSSION
We identified a correlation between task-related fMRI activity in the first few days after stroke and subsequent motor recovery. This study is the first to demonstrate an association between fMRI activation early after stroke and a later measure of recovery. Previous studies, including our own, have shown atypical task-related activations days to weeks after stroke prior to or while recovery is ongoing27–31. The functional significance of any such activity, however, cannot be determined in the absence of a quantitative relationship between the fMRI signal and a later behavioral measure of recovery, and without simultaneously controlling for stroke severity at the time of scanning, lesion volume, and other clinical variables. The fMRI task used to determine the correlation with ΔFM was a distal hand movement task whereas the behavioral measure (FM) assesses both distal and proximal movements. This meant that information about overall motor recovery can be derived by engaging the motor system in a simple motor task in the scanner. Our findings provide evidence for a functional relevance of early brain activity over and above clinical predictors.
There were several variables that were not in our model, including gender, lesion location, stroke etiology and cognition. Whereas these variables have been shown to affect recovery when disability scales and functional scores are used as outcome measures,32–34 some, such as gender, do not appear to predict recovery when motor impairment is used as an outcome as we did in this study.17, 35, 36 Stroke etiology (cardioembolic, atherothrombotic, lacunar) was not included because this variable’s salient physiological effects were subsumed under existing variables -- lesion volume, cortical vs. subcortical lesion location and stroke severity. Most of our patients had relatively small strokes. Although controlling for lesion volume in the model allows us to generalize our results, future work with a larger cohort could assess the correlations specifically in patients with larger strokes.
Potential concerns with respect to our result include those related to the effects of rehabilitation, medical co-morbidities, and mirror movements. Specifically, these could affect the relationship between brain activation and ΔFM. For example, differences in rehabilitation dosage could attenuate correlations with early brain activation. However, this concern is moot as we found a significant correlation between ΔFM and brain activation. Another potential rehabilitation-related concern is that the recovery pattern was simply a surrogate for a relationship between rehabilitation dose and ΔFM; this would mean that brain activation, which was measured before any therapy was delivered or any decisions about therapy were made, would need to correlate with the amount of therapy subsequently delivered, which would seem implausible. The same problem with temporal causality would apply to medical co-morbidity or the use of sedative medications. Finally, although subtle mirror movements could not be ruled out, in order for this variable to alter our main finding, one would have to postulate that mirror movements correlated positively with recovery, when in fact, the opposite has been reported.37
The fMRI recovery pattern was identified using a multivariate statistical method. Because multivariate tests assess effects across all voxels simultaneously, correction for multiple comparisons is not required. For the same reason, however, the method cannot be used to infer regional anatomical information at the individual voxel level.38 To assess focal effects we used SPM cluster-wise testing. The SPM results were negative except for two clusters (right post-central gyrus, cingulate cortex). To make sense of the paucity of suprathreshold clusters in the face of a statistically significant multivariate result, it is necessary to recognize that statistical significance in a multivariate test does not require that that the effects at any single voxel exceed the SPM threshold. Rather, a spatially diffuse pattern of activity with many regions contributing to the overall effect may produce this type of result. We consider it most likely that a widely distributed pattern of brain activity (of which the post-central gyrus and cingulate are only a small part) is the true correlate of motor recovery in our study.
The correlations between ΔFM and brain activation averaged within contralateral and ipsilateral M1 ROIs were not significant. This result suggests that early recovery processes per se do not involve activation in M1. However, this is not to say that residual CST integrity is not important to allow subsequent behavioral expression of these recovery processes.39 Indeed this dissociation between activation related to future recovery versus activation related to performance at the time of scanning at any time point over the course of recovery is the central idea of this paper. The former reflects processes required to achieve subsequent recovery; the latter reflects the outcome of these processes. We would suggest that a major contributor to inter-individual differences in motor recovery is the degree to which other brain regions, whose existence is implied by our multivariate result, can recruit and facilitate the ipsilesional residual CST and other descending pathways.
We have established the presence of a correlation between an acute brain imaging pattern and degree of subsequent motor recovery, which we hypothesize represents capacity to monitor and evaluate motor performance and drive adaptive changes that lead to recovery, similar to changes that have been reported to occur with motor learning in healthy subjects40–42. In such studies, several areas that are not directly connected to the corticospinal tract contribute to the acquisition of motor skills, which are then expressed through corticospinal tract output. Animal studies also support the idea that cortical reorganization remote from the site of the injury mediates recovery. For example, it has recently been shown that a lesion in the primary motor cortex of squirrel monkeys leads to major anatomical reorganization in cortical areas distant from the injury43. In humans, a longitudinal study that used transcranial magnetic stimulation to assess corticospinal tract integrity and cortico-cortical excitability in a group of patients with stroke-related hemiparesis showed that motor performance at 3 months correlated only weakly with a measure of corticospinal tract integrity but strongly with a measure of the degree of cortico-cortical excitability7, suggesting that variables other than how well the corticospinal tract is working at a given time determine how well it is able to work later. Indeed, the fact that we included measures of impairment at the time of scanning (FMinitial and DYNinitial) as predictors in the regression model means that the detected multivariate correlation between task-related fMRI activation and ΔFM is not explainable simply as a relationship between FMinitial or DYNinitial and ΔFM.
Our findings suggest that there are determinants of the recovery process that are present early after stroke. The presence of significant recovery-related activation in this time period justifies the investigation of interventions designed to enhance the recovery process. Further study will be needed to assess the ability of early brain activation to prospectively predict recovery, to elucidate the anatomical basis of the recovery pattern, and to investigate whether analogous recovery patterns exist in patients with other stroke deficits such as aphasia or hemineglect.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Catherine Handy and Katherine O’Brien, and Lauren Engel for their assistance in data collection and Steven Dashnaw for technical support. Funded by NIH grants NINDS P50NS049060 (RSM) and K02 048099 (JWK)
Footnotes
The authors have no financial relationships or other conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
- 1.Duncan PW, Goldstein LB, Matchar D, et al. Measurement of motor recovery after stroke. Outcome assessment and sample size requirements. Stroke. 1992;23:1084–1089. doi: 10.1161/01.str.23.8.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Feys H, De Weerdt W, Nuyens G, et al. Predicting motor recovery of the upper limb after stroke rehabilitation: value of a clinical examination. Physiother Res Int. 2000;5:1–18. doi: 10.1002/pri.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ward NS, Brown MM, Thompson AJ, Frackowiak RS. Neural correlates of outcome after stroke: a cross-sectional fMRI study. Brain. 2003;126:1430–1448. doi: 10.1093/brain/awg145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chollet F, DiPiero V, Wise RJ, et al. The functional anatomy of motor recovery after stroke in humans: a study with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol. 1991;29:63–71. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Weiller C, Chollet F, Friston KJ, et al. Functional reorganization of the brain in recovery from striatocapsular infarction in man. Ann Neurol. 1992;31:463–472. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cramer SC, Nelles G, Benson RR, et al. A functional MRI study of subjects recovered from hemiparetic stroke. Stroke. 1997;28:2518–2527. doi: 10.1161/01.str.28.12.2518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Swayne OB, Rothwell JC, Ward NS, Greenwood RJ. Stages of Motor Output Reorganization after Hemispheric Stroke Suggested by Longitudinal Studies of Cortical Physiology. Cereb Cortex. 2008 doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhm218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fisher CM. Concerning the mechanism of recovery in stroke hemiplegia. Can J Neurol Sci. 1992;19:57–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tombari D, Loubinoux I, Pariente J, et al. A longitudinal fMRI study: in recovering and then in clinically stable sub-cortical stroke patients. Neuroimage. 2004;23:827–839. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Thirion B, Pinel P, Meriaux S, et al. Analysis of a large fMRI cohort: Statistical and methodological issues for group analyses. Neuroimage. 2007;35:105–120. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.11.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fugl-Meyer AR. Post-stroke hemiplegia assessment of physical properties. Scand J Rehabil Med Suppl. 1980;7:85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Duncan PW, Propst M, Nelson SG. Reliability of the Fugl-Meyer assessment of sensorimotor recovery following cerebrovascular accident. Phys Ther. 1983;63:1606–1610. doi: 10.1093/ptj/63.10.1606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gladstone DJ, Danells CJ, Black SE. The fugl-meyer assessment of motor recovery after stroke: a critical review of its measurement properties. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2002;16:232–240. doi: 10.1177/154596802401105171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Platz T, Pinkowski C, van Wijck F, et al. Reliability and validity of arm function assessment with standardized guidelines for the Fugl-Meyer Test, Action Research Arm Test and Box and Block Test: a multicentre study. Clin Rehabil. 2005;19:404–411. doi: 10.1191/0269215505cr832oa. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Woodbury ML, Velozo CA, Richards LG, et al. Longitudinal stability of the Fugl-Meyer Assessment of the upper extremity. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89:1563–1569. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2007.12.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sanford J, Moreland J, Swanson LR, et al. Reliability of the Fugl-Meyer assessment for testing motor performance in patients following stroke. Phys Ther. 1993;73:447–454. doi: 10.1093/ptj/73.7.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Prabhakaran S, Zarahn E, Riley C, et al. Inter-individual Variability in the Capacity for Motor Recovery After Ischemic Stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2008;22:64–71. doi: 10.1177/1545968307305302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Talairach J, Tournoux P. Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain. Thieme; New York: 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Holmes AaFK. Generalisability, random effects and population inference. NeuroImage. 1998;7:S754. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Worsley KJ, Poline JB, Friston KJ, Evans AC. Characterizing the response of PET and fMRI data using multivariate linear models. Neuroimage. 1997;6:305–319. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1997.0294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Maldjian JA, Laurienti PJ, Kraft RA, Burdette JH. An automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of fMRI data sets. Neuroimage. 2003;19:1233–1239. doi: 10.1016/s1053-8119(03)00169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dettmers C, Young A, Rommel T, et al. CO2 reactivity in the ischaemic core, penumbra, and normal tissue 6 hours after acute MCA-occlusion in primates. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1993;125:150–155. doi: 10.1007/BF01401843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wexler BE, Fulbright RK, Lacadie CM, et al. An fMRI study of the human cortical motor system response to increasing functional demands. Magn Reson Imaging. 1997;15:385–396. doi: 10.1016/s0730-725x(96)00232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ehrsson HH, Fagergren A, Jonsson T, et al. Cortical activity in precision-versus power-grip tasks: an fMRI study. J Neurophysiol. 2000;83:528–536. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.83.1.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rao SM, Binder JR, Bandettini PA, et al. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of complex human movements. Neurology. 1993;43:2311–2318. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.11.2311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cao Y, D’Olhaberriague L, Vikingstad EM, et al. Pilot study of functional MRI to assess cerebral activation of motor function after poststroke hemiparesis. Stroke. 1998;29:112–122. doi: 10.1161/01.str.29.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Marshall RS, Perera GM, Lazar RM, et al. Evolution of cortical activation during recovery from corticospinal tract infarction. Stroke. 2000;31:656–661. doi: 10.1161/01.str.31.3.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Foltys H, Krings T, Meister IG, et al. Motor representation in patients rapidly recovering after stroke: a functional magnetic resonance imaging and transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003;114:2404–2415. doi: 10.1016/s1388-2457(03)00263-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Calautti C, Leroy F, Guincestre JY, et al. Sequential activation brain mapping after subcortical stroke: changes in hemispheric balance and recovery. Neuroreport. 2001;12:3883–3886. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200112210-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gerloff C, Bushara K, Sailer A, et al. Multimodal imaging of brain reorganization in motor areas of the contralesional hemisphere of well recovered patients after capsular stroke. Brain. 2006;129:791–808. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ward NS, Brown MM, Thompson AJ, Frackowiak RS. Neural correlates of motor recovery after stroke: a longitudinal fMRI study. Brain. 2003;126:2476–2496. doi: 10.1093/brain/awg245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Man DW, Tam SF, Hui-Chan C. Prediction of functional rehabilitation outcomes in clients with stroke. Brain Inj. 2006;20:205–211. doi: 10.1080/02699050500454621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Saxena SK, Ng TP, Koh G, et al. Is improvement in impaired cognition and depressive symptoms in post-stroke patients associated with recovery in activities of daily living? Acta Neurol Scand. 2007;115:339–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2006.00751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Paolucci S, Bragoni M, Coiro P, et al. Quantification of the probability of reaching mobility independence at discharge from a rehabilitation hospital in nonwalking early ischemic stroke patients: a multivariate study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008;26:16–22. doi: 10.1159/000135648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Oken O, Yavuzer G. Spatio-temporal and kinematic asymmetry ratio in subgroups of patients with stroke. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2008;44:127–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wolf SL, Newton H, Maddy D, et al. The Excite Trial: relationship of intensity of constraint induced movement therapy to improvement in the wolf motor function test. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2007;25:549–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nelles G, Cramer SC, Schaechter JD, et al. Quantitative assessment of mirror movements after stroke. Stroke. 1998;29:1182–1187. doi: 10.1161/01.str.29.6.1182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Petersson KM, Nichols TE, Poline JB, Holmes AP. Statistical limitations in functional neuroimaging. I. Non-inferential methods and statistical models. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999;354:1239–1260. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1999.0477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Stinear CM, Barber PA, Smale PR, et al. Functional potential in chronic stroke patients depends on corticospinal tract integrity. Brain. 2006 doi: 10.1093/brain/awl333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tamas Kincses Z, Johansen-Berg H, Tomassini V, et al. Model-free characterization of brain functional networks for motor sequence learning using fMRI. Neuroimage. 2008;39:1950–1958. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.09.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Grafton ST, Schmitt P, Van Horn J, Diedrichsen J. Neural substrates of visuomotor learning based on improved feedback control and prediction. Neuroimage. 2008;39:1383–1395. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.09.062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Krakauer JW, Ghilardi M-F, Mentis M, Barnes A, Veytsman M, Eidelberg D, Ghez C. Differential cortical and subcortical activations in learning rotations and gains for reaching: A PET study. J Neurophysiol. 2003 doi: 10.1152/jn.00675.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dancause N, Barbay S, Frost SB, et al. Extensive cortical rewiring after brain injury. J Neurosci. 2005;25:10167–10179. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3256-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]