Abstract
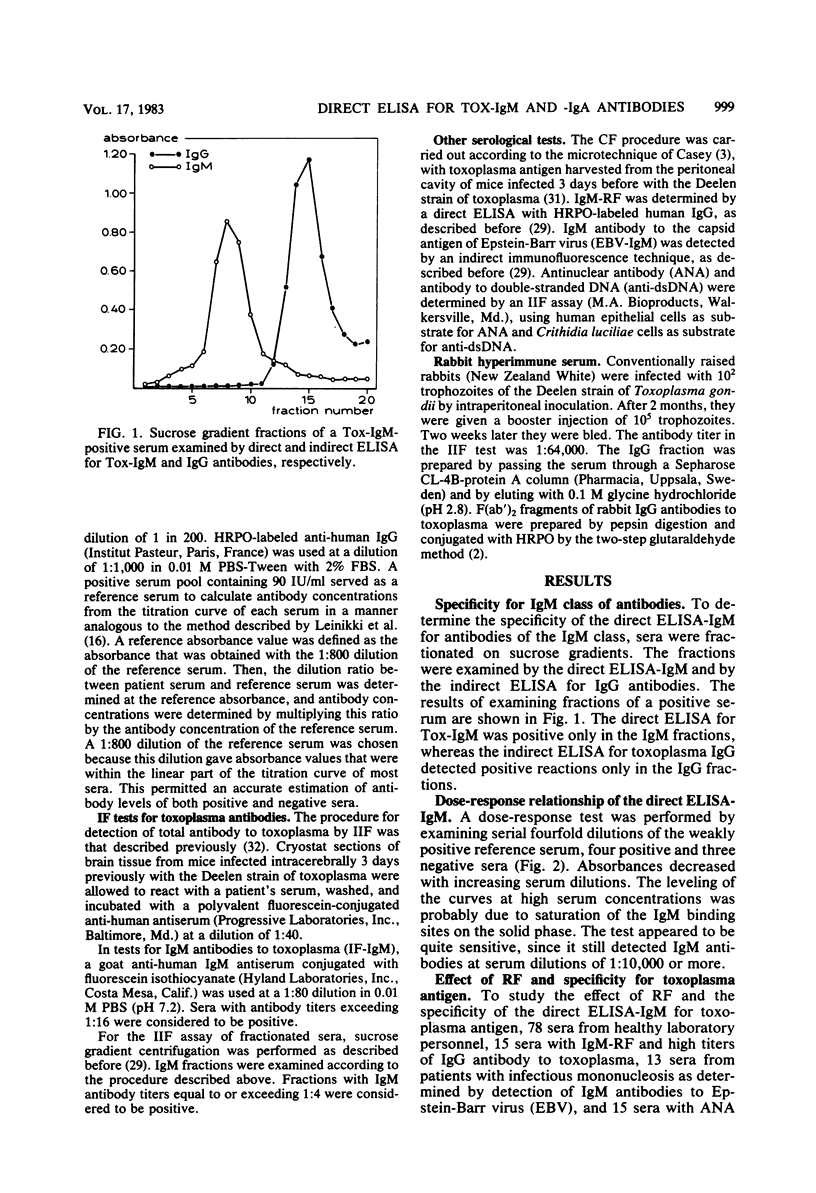
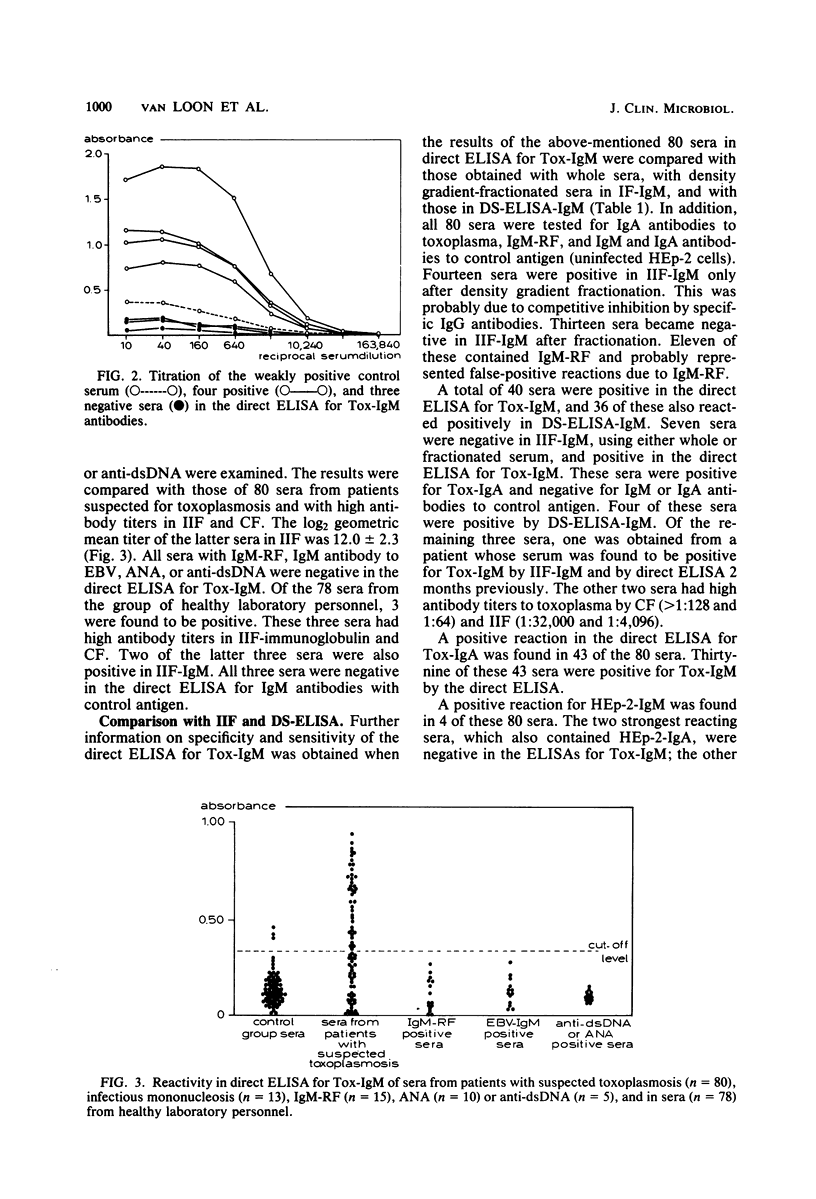
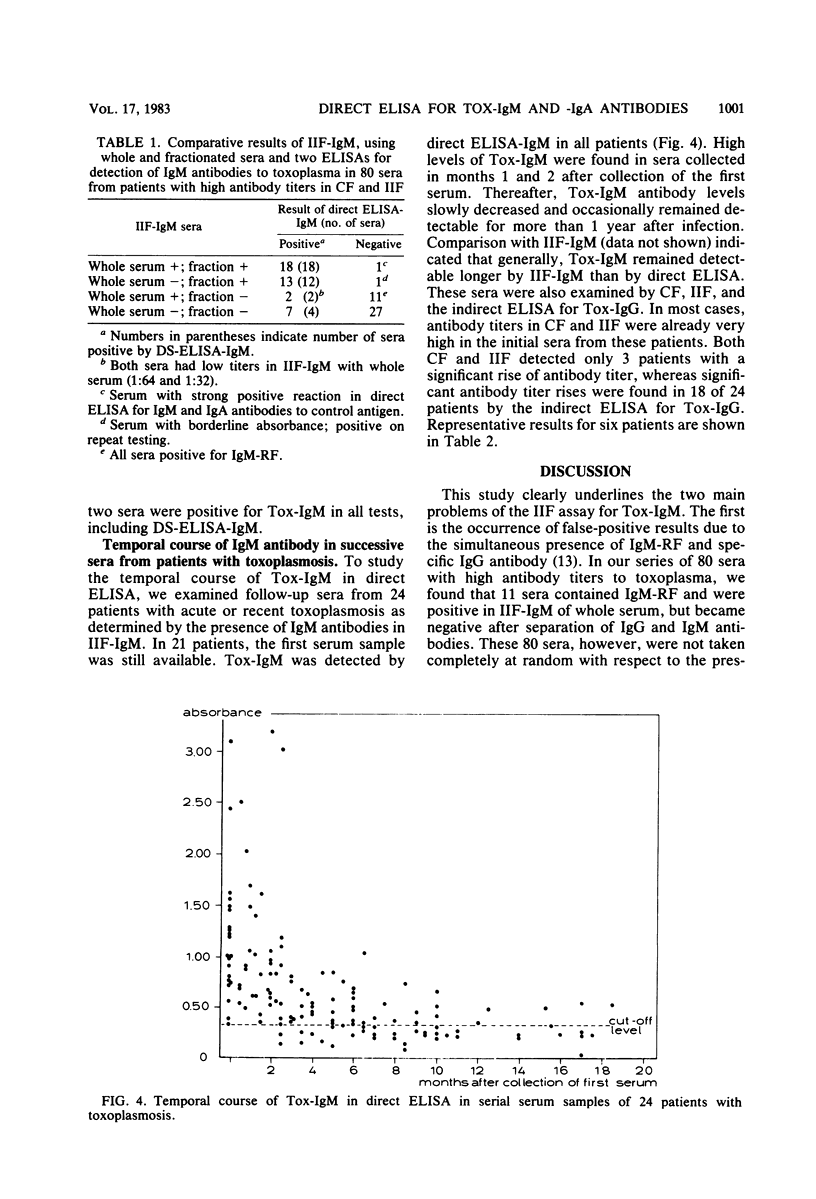
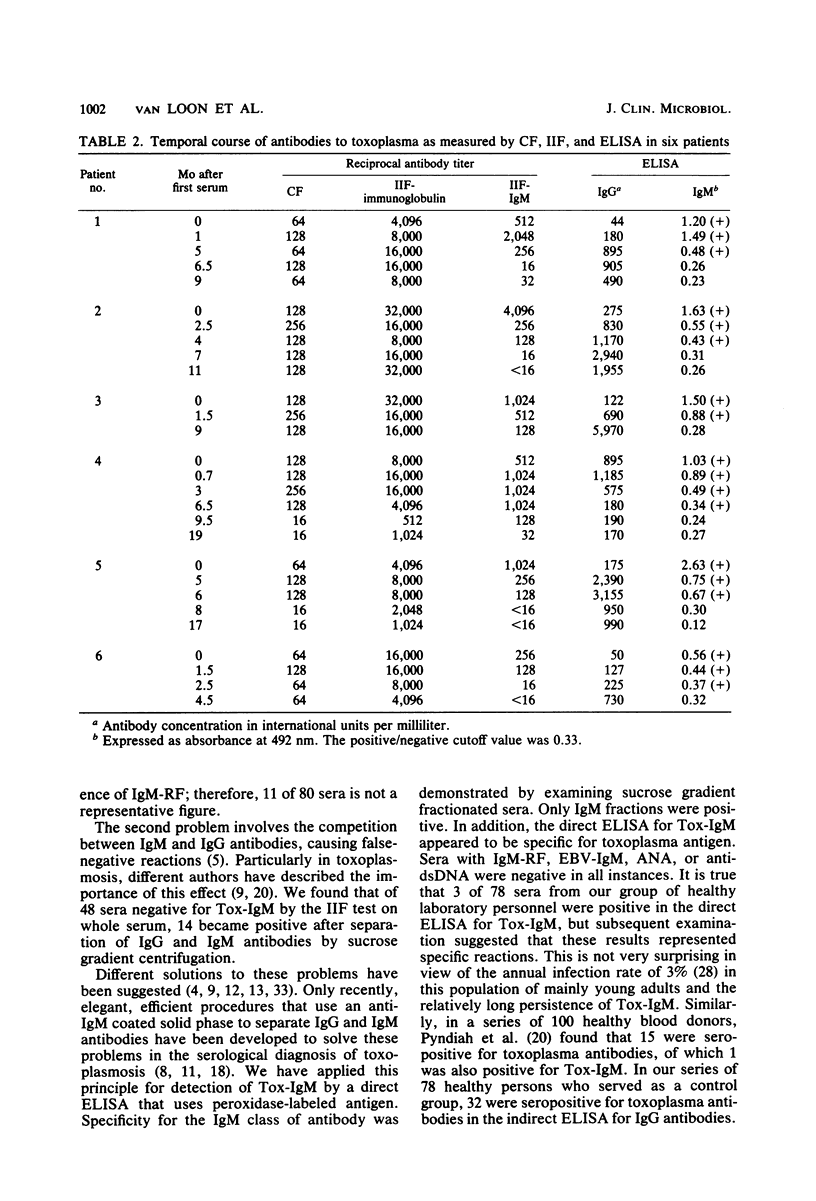
A direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is described that uses horseradish peroxidase-labeled antigen for detection of immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgA antibodies to toxoplasma. In this assay, polystyrene microtiter plates were sensitized with anti-human IgM or IgA antibody to separate IgM or IgA from other classes of antibody. The presence of IgM or IgA antibodies to toxoplasma (Tox-IgM, Tox-IgA) was then detected by sequential addition of soluble horseradish peroxidase-labeled toxoplasma antigen and substrate. As judged by examining sucrose gradient-fractionated sera, the assay was specific for IgM or IgA classes of antibody. In contrast to the indirect immunofluorescence for IgM antibodies to toxoplasma, no inhibition of IgM reactivity by specific IgG antibodies could be detected. Furthermore, rheumatoid factor did not cause false-positive results. Of 80 single sera with high antibody titer to toxoplasma in indirect immunofluorescence and complement fixation, 40 were positive in the direct ELISA for Tox-IgM, 36 were positive in the double-sandwich ELISA, and only 21 were positive in the indirect immunofluorescence for Tox-IgM when whole serum was used. In the indirect immunofluorescence, another 13 sera became positive after sucrose gradient fractionation. The direct ELISA for IgA antibodies to toxoplasma was positive in 43 sera, of which 39 were positive in the direct ELISA for Tox-IgM. High levels of IgM antibodies were found within 3 months after the onset of symptoms, slowly decreasing thereafter. Tox-IgM may persist for more than 1 year after infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo F. G., Barnett E. V., Gentry L. O., Remington J. S. False-positive anti-Toxoplasma fluorescent-antibody tests in patients with antinuclear antibodies. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):270–275. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.270-275.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boorsma D. M., Streefkerk J. G. Periodate or glutaraldehyde for preparing peroxidase conjugates? J Immunol Methods. 1979;30(3):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler S., Devries E., Allen P. R., Hurn B. A. A rapid immunofluorescent procedure for the detection of specific IgG and IgM antibody in sera using Staphylococcus aureus and latex-IgG as absorbents. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):367–380. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Julian A. J. Competition between, and effectiveness of, IgG and IgM antibodies in indirect fluorescent antibody and other tests. J Immunol. 1967 Jan;98(1):143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., Wielaard F., van Gruijthuijsen H., Swinkels J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):805–806. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.805-806.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., van der Veen J. Specific detection of IgM-antibodies by ELISA, applied in hepatitis-A. Lancet. 1978 Sep 23;2(8091):684–685. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filice G. A., Yeager A. S., Remington J. S. Diagnostic significance of immunoglobulin M antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii detected after separation of immunoglobulin M from immunoglobulin G antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):336–342. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.336-342.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flehmig B., Ranke M., Berthold H., Gerth H. J. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of IgM antibodies to hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Aug;140(2):169–175. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco E. L., Walls K. W., Sulzer A. J. Reverse enzyme immunoassay for detection of specific anti-Toxoplasma immunoglobulin M antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):859–864. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.859-864.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekker A. C., Brand-Saathof B., Vis J., Meijers R. C. Indirect immunofluorescence test for detection of IgM antibodies to cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):596–600. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde B., Barnett E. V., Remington J. S. Method for differentiation of nonspecific from specfic toxoplasma IgM fluorescent antibodies in patients with rheumatoid factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Apr;148(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozin F., Fowler M., Koethe S. M. A comparison of the sensitivities and specificities of different substrates for the fluorescent antinuclear antibody test. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;74(6):785–790. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/74.6.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krech U., Wilhelm J. A. A solid-phase immunosorbent technique for the rapid detection of rubella IgM by haemagglutination inhibition. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):281–286. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinikki P. O., Shekarchi I., Dorsett P., Sever J. L. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay determination of specific rubella antibody levels in micrograms of immunoglobulin G per milliliter of serum in clinical samples. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):419–423. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.419-423.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Barnett E. V., Remington J. S. Method for avoiding false-positive results occurring in immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays due to presence of both rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):73–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.73-78.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii: use for diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):757–766. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersen E. K. Recency of Toxoplasma gondii infections correlated with results obtained in dye test and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Dec;89(6):407–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyndiah N., Krech U., Price P., Wilhelm J. Simplified chromatographic separation of immunoglobulin M from G and its application to toxoplasma indirect immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):170–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.170-174.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Miller M. J., Brownlee I. IgM antibodies in acute toxoplasmosis. I. Diagnostic significance in congenital cases and a method for their rapid demonstration. Pediatrics. 1968 Jun;41(6):1082–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Miller M. J., Brownlee I. IgM antibodies in acute toxoplasmosis. II. Prevalence and significance in acquired cases. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 May;71(5):855–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Siqueira-Linhares M., Chardonnet Y., Levy E., Aymard M., Bosshard S., Nord E., Revillard J. P. Detection of specific IgA antibodies in serum of kidney transplant patients with recurrent cytomegalovirus infection. Intervirology. 1981;15(4):228–234. doi: 10.1159/000149236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., von Deimling U., Flehmig B. Detection of IgM antibodies to cytomegalovirus (CMV) using an enzyme-labelled antigen (ELA). J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):59–68. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann E., Stagno S. Serologische Untersuchungen über den Nachweis von IgM-Antikörpern bei akuter und chronischer Toxoplasmose. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1972 Feb;219(2):249–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Vaheri A. Rubella: a method for rapid diagnosis of a recent infection by demonstration of the IgM antibodies. Br Med J. 1968 Jan 27;1(5586):221–223. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5586.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. M., Heessen F. W., van der Logt J. T., van der Veen J. Direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay that uses peroxidase-labeled antigen for determination of immunoglobulin M antibody to cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):416–422. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.3.416-422.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. M., van Der Logt J. T., van der Veen J. Diagnosis of herpes encephalitis by elisa. Lancet. 1981 Nov 28;2(8257):1228–1229. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91461-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. M., van der Veen J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitation of toxoplasma antibodies in human sera. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jul;33(7):635–639. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.7.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Nunen M. C., van der Veen J. Examination for toxoplasmosis by the fluorescent antibody technique. Trop Geogr Med. 1965 Sep;17(3):246–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Logt J. T., Heessen F. W., van Loon A. M., van der Veen J. Hemadsorption immunosorbent technique for determination of mumps immunoglobulin M antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):82–86. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.82-86.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Logt J. T., van Loon A. M., van der Veen J. Hemadsorption immunosorbent technique for determination of rubella immunoglobulin M antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):410–415. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.3.410-415.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen J., Polak M. F. Prevalence of toxoplasma antibodies according to age with comments on the risk of prenatal infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Oct;85(2):165–174. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


