Abstract
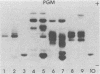
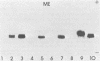
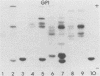
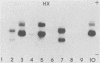
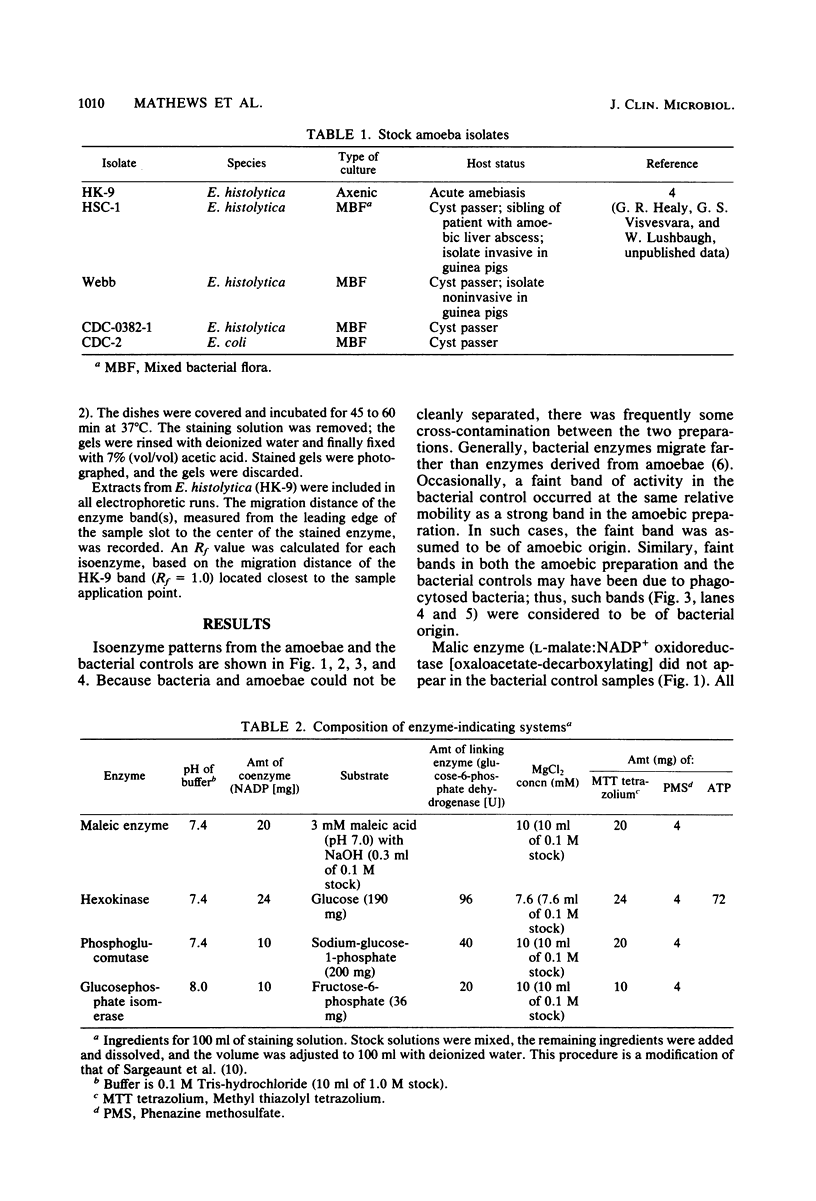
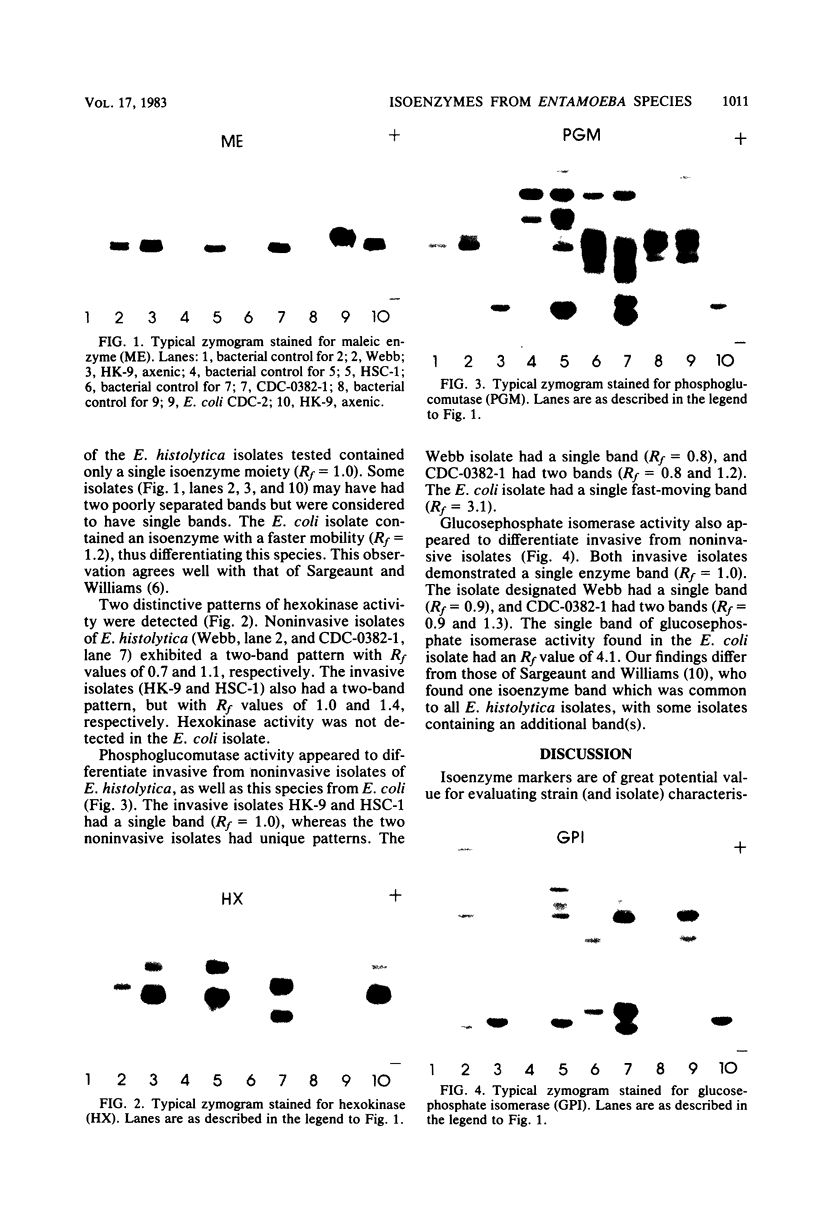
In this preliminary report, we describe a polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis technique for the resolution of isoenzyme patterns of four isolates of Entamoeba histolytica and one isolate of Entamoeba coli. Our findings were similar to previous findings for three enzyme systems: maleic enzyme (malate dehydrogenase [EC 1.1.1.40]), hexokinase (EC 2.7.1.1), and phosphoglucomutase (EC 2.7.5.1). We found preliminary evidence that glucosephosphate isomerase (EC 5.3.1.9) may also differentiate invasive amoebae from noninvasive amoebae, when the isoenzymes are separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, whereas this differentiation is not evident with starch-gel electrophoresis. We used an Rf system to relate isoenzyme band mobility to the migration distance of a standard E. histolytica strain (HK-9). The numerical identification of isoenzyme bands can simplify the grouping of isolates into zymodemes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Diamond L. S. A new liquid medium for xenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other lumen-dwelling protozoa. J Parasitol. 1982 Oct;68(5):958–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. Techniques of axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae. J Parasitol. 1968 Oct;54(5):1047–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito J. J., Obijeski J. F. High resolution polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis. Prep Biochem. 1976;6(6):431–442. doi: 10.1080/00327487608069128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIMAN Q. M., BECKER C. E. In vitro growth and metabolism of Endamoeba histolytica. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1953 Oct 14;56(5):1048–1056. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1953.tb30285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Bhojnani R., Campos J. E., Gomez A. The epidemiology of Entamoeba histolytica in a rural and an urban area of Mexico. A pilot survey II. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(2):208–210. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E. Electrophoretic isoenzyme patterns of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba coli. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(2):164–166. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E. Electrophoretic isoenzyme patterns of the pathogenic and non-pathogenic intestinal amoebae of man. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(2):225–227. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90219-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Grene J. D. The differentiation of invasive and non-invasive Entamoeba histolytica by isoenzyme electrophoresis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(5):519–521. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Neal R. A. A comparative study of Entamoeba histolytica (NIH :200, HK9, etc.), "E. histolytica-like" and other morphologically identical amoebae using isoenzyme electrophoresis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(4):469–474. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]