Abstract
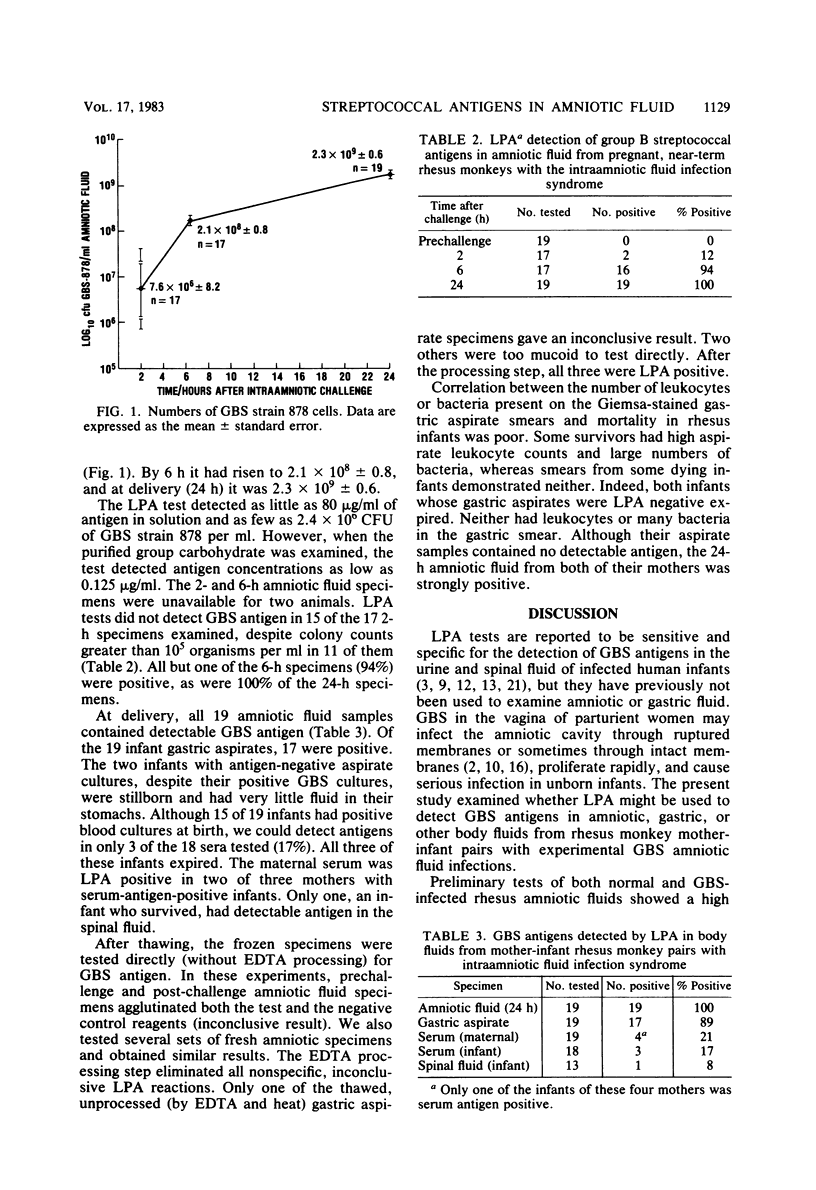
To simulate group B streptococci (GBS) amniotic fluid infections common in humans and to examine bacterial growth and the appearance of GBS antigens in vivo, GBS were injected into the amniotic cavity of 19 near-term rhesus monkeys. Transabdominal aspirates of amniotic fluid were obtained before bacterial challenge, after 2 and 6 h, and during cesarean section delivery (24 h). Each fluid was quantitatively cultured for GBS. Specimens of amniotic fluid and gastric aspirate from each infant were tested for the presence of GBS antigens with a commercial latex particle agglutination test (Wellcogen Strep B; Wellcome Diagnostics, Dartford, England). To eliminate nonspecific latex particle agglutination reactivity, presumably caused by proteins, a processing procedure was required. Despite active proliferation of bacteria, only 12% of the 2-h amniotic specimens were latex particle agglutination positive. In contrast, 94% of th3 6-h and 100% of the 24-h specimens had detectable antigens, as did 89% of the gastric fluid specimens aspirated from the 19 newborns. Latex particle agglutination tests, after proper processing, will readily detect GBS antigens in amniotic or gastric aspirate fluid from experimentally infected rhesus monkeys.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony B. F. Carriage of group B streptococci during pregnancy: a puzzler. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):789–793. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J. Early onset group B streptococcal disease. J Pediatr. 1978 Jul;93(1):124–125. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80623-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberger P. I., Chandler B., Gezon H., Haddow J. E. Rapid detection of neonatal group B streptococcal infections by latex agglutination. J Pediatr. 1980 Jan;96(1):104–106. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey R. B., Eisenstein T. K., Shockman G. D., Greber T. F., Swenson R. M. Soluble group- and type-specific antigens from type III group B Streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):195–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.195-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courcol R. J., Roussel-Delvallez M., Puech F., Delecour M., Martin G. R. Quantitative bacteriological analysis of amniotic fluid. Biol Neonate. 1982;42(3-4):166–173. doi: 10.1159/000241591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon H. C., Jr, Gray E., Pass M. A., Gray B. M. Anorectal and vaginal carriage of group B streptococci during pregnancy. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):794–799. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. I., Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J. Extracellular antigens of serotype III group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):890–893. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.890-893.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doskeland S. O., Berdal B. P. Bacterial antigen detection in body fluids: methods for rapid antigen concentration and reduction of nonspecific reactions. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):380–384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.380-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICKHOFF T. C., KLEIN J. O., DALY A. K., INGALL D., FINLAND M. NEONATAL SEPSIS AND OTHER INFECTIONS DUE TO GROUP B BETA-HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI. N Engl J Med. 1964 Dec 10;271:1221–1228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196412102712401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Kasper D. L., Baker C. J. Rapid diagnosis of type III group B streptococcal meningitis by latex particle agglutination. J Pediatr. 1979 Aug;95(2):202–205. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80651-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemming V. G., McCloskey D. W., Hill H. R. Pneumonia in the neonate associated with group B streptococcal septicemia. Am J Dis Child. 1976 Nov;130(11):1231–1233. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1976.02120120065011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram D. L., Pendergrass E. L., Bromberger P. I., Thullen J. D., Yoder C. D., Collier A. M. Group B streptococcal disease: its diagnosis with the use of antigen detection, Gram's stain, and the presence of apnea, hypotension. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Aug;134(8):754–758. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130200024009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram D. L., Suggs D. M., Pearson A. W. Detection of group B streptococcal antigen in early-onset and late-onset group B streptococcal disease with the Wellcogen Strep B latex agglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):656–658. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.656-658.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. W., Jr, London W. T., Baker C. J., Curfman B. L., Sever J. L. Intraamniotic infection due to group G streptococcus: treatment and antibody response. Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Aug;58(2):222–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. W., Jr, London W. T., Palmer A. E., Tossell J. W., Bronsteen R. A., Daniels M., Curfman B. L., Sever J. L. Experimental group B streptococcal infection in the rhesus monkey. I. Disease production in the neonate. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1978 Nov 15;132(6):686–690. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(78)90865-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. M., Jr, Pupkin M. J., Hill G. B. Bacterial colonization of amniotic fluid from intact fetal membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Mar 15;136(6):796–804. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims L. C., Medawar M. S., Perkins J. R., Grubb W. R. Predicting neonatal infections by evaluation of the gastric aspirate: a study in two hundred and seven patients. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Sep 15;114(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pass M. A., Gray B. M., Khare S., Dillon H. C., Jr Prospective studies of group B streptococcal infections in infants. J Pediatr. 1979 Sep;95(3):437–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80531-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirante J., Ceballos R., Cassady G. Group B beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection in the newborn. I. Early onset infection. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Nov;128(5):659–665. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110300069009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos A., Stern L. Relationship of premature rupture of the membranes to gastric fluid aspirate in the newborn. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1969 Dec 15;105(8):1247–1251. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(69)90298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm W. Rapid detection of streptococcal antigens by latex agglutination test in neonatal body fluids. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1982 Jan;71(1):145–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1982.tb09388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasan U., Lim D. M., Greenstein R. M., Raye J. R. Origin of gastric aspirate polymorphonuclear leukocytes in infants born after prolonged rupture of membranes. J Pediatr. 1977 Jul;91(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh H., Hildebrandt R. J., Prystowsky H. Growth inhibition factors in amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1965 Oct 15;93(4):590–591. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(65)90523-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb B. J., Baker C. J. Commercial latex agglutination test for rapid diagnosis of group B streptococcal infection in infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):442–444. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.442-444.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


