Abstract
Objective
To determine the psychological consequences for parents of children with Down's syndrome of having received a false negative result on prenatal screening.
Design
Comparison of adjustment of parents who received a false negative result with that of parents not offered a test and those who declined a test.
Setting
Parents were interviewed in their own homes.
Participants
Parents of 179 children with Down's syndrome (mean age 4 (range 2-6) years).
Main outcome measures
Anxiety, depression, parenting stress, attitudes towards the child, and attributions of blame for the birth of the affected child.
Results
Overall, regardless of screening history, parents adjusted well to having a child with Down's syndrome. Compared with mothers who declined a test, mothers in the false negative group had higher parenting stress (mean score 81.2 v 71.8, P=0.016, 95% confidence interval for the difference 1.8 to 17.0) and more negative attitudes towards their children (124.9 v 134.2, P=0.009, −16.2 to −2.4). Fathers in the false negative group had higher parenting stress test scores (77.8 v 70.0, P=0.046, 1.5 to 14.2) than fathers not offered a test. Mothers in the false negative group were more likely to blame others for the outcome than mothers who had not been offered the test (28% v 13%, P=0.032, 3% to 27%). Mothers and fathers in the false negative group were more likely to blame others for this outcome than parents who had declined a test (mothers 28% v 0%, P=0.001, 19% to 37%; fathers 27% v 0%, P=0.004, 17% to 38%). Blaming others was associated with poorer adjustment for mothers and fathers.
Conclusions
A false negative result on prenatal screening seems to have a small adverse effect on parental adjustment evident two to six years after the birth of an affected child.
Introduction
Imperfect sensitivity, a characteristic of all screening tests, will result in a proportion of those screened receiving a false negative test result—that is, a negative result despite the presence of the condition screened for. The current study is, to the best of our knowledge, the first systematic attempt to document the psychological consequences of false negative results.1 The screening test studied was prenatal serum screening for Down's syndrome.
Serum screening for Down's syndrome is offered to about 70% of pregnant women in the United Kingdom.2 In clinical practice, these tests have the ability to detect between 36% and 76% of fetuses affected by Down's syndrome, depending on the combinations of serum markers used.3 Ultrasound measurement of the nuchal fold is increasingly being used but is associated with a similar proportion of false negative results.4 Despite widespread screening parents still give birth to children with Down's syndrome. This is for three main reasons: firstly, screening does not detect all cases (false negative); secondly, some parents are not offered a test; and, thirdly, some parents decline screening, diagnostic tests, or termination of pregnancy if an affected fetus is detected.
There are reports of parents who are very angry at the birth of a child with Down's syndrome, and some have planned to take legal action.5,6 Parents who receive a false negative result from screening may be more angry at the births of their children than parents who did not receive screening, stemming from a mistaken belief that screening tests are highly sensitive.7,8 In a pilot study to develop the methods for the current study we interviewed 51 of the parents of 28 children with Down's syndrome, aged between 1 and 2 years of age.9 Six of the 11 parents who received a negative test result and seven of the 34 not offered testing blamed health professionals or the healthcare system in general for not having prevented the births of their affected children. None of those who declined testing blamed anyone. As has been documented in relation to other events10 blaming others was associated with poorer adjustment in these parents. This pilot study lacked the power to determine whether history of screening was associated with blaming and adjustment. We therefore determined the impact on parents of the receipt of a false negative result on serum screening for Down's syndrome.
Methods
Design
This retrospective study compared the adjustment of parents who received a false negative result on prenatal serum screening with that of parents not offered a test or who declined a test.
Procedure
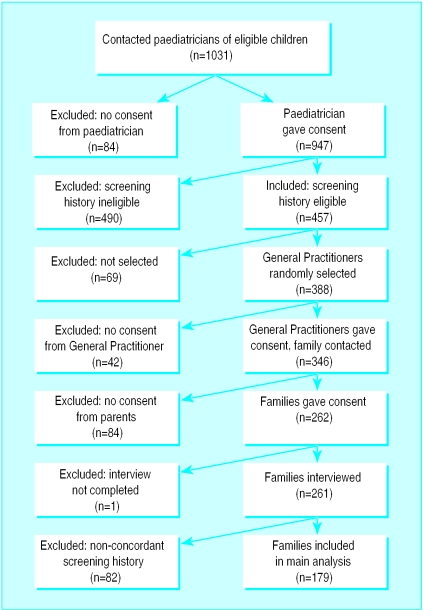
There were five steps to obtaining informed consent from eligible parents (figure).
The register—The National Down's Syndrome Cytogenetics Register11,12 (NDSCR) records all positive results for trisomy 21 in England and Wales. As these data are anonymous, individuals cannot be identified by researchers. The register provided the children's dates of birth, the names of cytogenetics laboratories that carried out the chromosome analyses, sample numbers to identify the children at the laboratories, and the names of the hospitals and paediatricians to whom the results were sent. Data from the register were used to prepare letters to paediatricians. Families were excluded for any of the following reasons: they received a prenatal diagnosis of Down's syndrome; the affected pregnancy was multiple; the child was stillborn or died in the neonatal period; the family had moved overseas or the child had been born overseas; or the parents had participated in the pilot study. There were 1031 eligible children on the register.
Regional cytogenetics laboratories—The 20 of the 34 regional cytogenetics laboratories with the largest number of positive results for trisomy 21 were invited to participate in the study; all agreed. These laboratories contributed 93% of the positive results of trisomy 21 on the register. The laboratories identified the children by using the sample numbers from the register, then entered the children's and mothers' names on our prepared letters and sent them to the paediatricians. Ethical committee approval was obtained to cover 20 laboratories.
Paediatricians—The paediatricians of 947 of the 1031 eligible children gave consent for us to contact general practitioners, gave the children's and mothers' names to the researchers, and provided information on the mothers' screening histories. If paediatricians did not know mothers' screening histories, consent was sought to contact their obstetricians. The response rate from paediatricians was 92% (947/1031).
General practitioners—To have a sample of 250 we contacted the general practitioners of 388 of the 947 children for whom consent was obtained from paediatricians. These 388 were selected randomly across the three screening history groups. We asked general practitioners to forward our letter to the parents of affected children, provided they had no objections. Three hundred and seventy five of the 388 replied. Of these, 346 forwarded our letter to parents. The response rate for was therefore 89% (346/388).
Parents—Parents who were willing to participate were asked to contact the research team by returning the consent form in a prepaid envelope. Seventy six per cent (262/346) of parents replied agreeing to participate. Both fathers and mothers were invited to take part; 259 mothers and 173 fathers were interviewed. The biological parents of children who had been adopted were interviewed. One interview was not completed because the interviewer judged the mother too distressed to continue. Eighty mothers and 51 fathers are not included in the analyses because mothers' reports of screening history were not concordant with those obtained from medical records.
Study population
Parents of children born from 1 January 1992 to 31 December 1993 were sampled from the register. As interviews were conducted over a three year period the ages of affected children ranged from 2.3 to 6.5 years (mean 4.1) when their parents were interviewed. Sample sizes were calculated from the results of the pilot study. It was estimated that 50 parents in each group were required to detect a difference between groups of 10 points on the Speilberger state-trait anxiety inventory13 and 12 points on the Judson scale14 with 95% power at the 5% level of significance. The final study sample comprised 179 mothers (86 with a false negative result, 59 not offered a test, and 34 declined a test) and 122 fathers (55 with a false negative result, 44 not offered a test, and 23 declined a test). The exclusion of parents with discordant screening histories resulted in a substantial reduction of group sizes. As relatively few parents declined tests we were unable to achieve the planned sample size (50). Seven mothers and six fathers did not complete the adjustment measures.
Screening history
A serum screening test for Down's syndrome was defined as any prenatal serum screening test for detecting Down's syndrome in the fetus (α fetoprotein and double, triple, and quadruple tests). Two methods of assessing screening history were used: reports from medical records and mothers' reports. Concordance between reports from mothers and medical records was 76%. The pattern of results obtained by classifying screening history by medical records or mothers' reports was broadly similar. We have assumed that the most valid classification is that made on the basis of agreement between medical records and mothers and therefore report results based on an analysis of the cases where there was such concordance.
Measures
The interview—Parents were interviewed in their own homes. Mothers and fathers were interviewed separately. The interviews were semistructured and covered a range of themes related to adjustment to the birth of their children with Down's syndrome. The interviews were taped and later transcribed. After the interview parents were asked to complete and return the standardised scales.
Anxiety was assessed with the short form of the state scale of the Spielberger state-trait anxiety inventory13 (scale range 20-80; mean for normative sample 35; clinically significant scores are those above 42).
Depression was assessed with the Center for Epidemiologic Studies depression scale15 (scale range 0-60; mean for normative sample 9; clinically significant scores are those above 16).
Parenting stress was measured with the short form of the Abidin parenting stress index16 (scale range 36-180; mean for normative sample 71; clinically significant scores are those above 90).
Attitude towards the disabled child was measured with the Judson scale14 (scale range 22-154; there are no published norms for this scale, lower scores indicate more negative attitudes towards the child; clinically significant scores are those below 11017).
Blaming others was assessed during the interview by the response to the question: “how much do you blame someone else now for you having a baby with Down's syndrome?” (scale 0-6). There were some missing data for this item as it was introduced after the first 28 mothers and fathers had been interviewed. As the distribution for this scale was highly positively skewed we report blaming others as a dichotomised variable (that is, score 0 means no blame, score 1-6 means blame).
Analysis
Independent t tests were used for comparisons of means. χ2 and Fisher's exact tests were used for comparisons of proportions. Confidence intervals for differences in proportions were calculated with confidence interval analysis, a program written for use with the book Statistics with Confidence.18 In view of the strong associations between blaming others and poorer adjustment reported in the literature10 and the increased likelihood of blaming others for parents receiving false negative results reported in the pilot study9 we used one tailed tests for these comparisons.
Results
Demographic characteristics of sample
Table 1 shows demographic details for families according to screening group. There were no significant differences between the false negative groups and the not offered and declined groups in ages of children at interview, whether the child had died or been adopted, family income, or mother's or father's education.
Table 1.
Demographic variables and screening history in families with child with Down's syndrome
| Variable | False negative test result | Comparison with test not offered
|
Comparison with test declined
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No of subjects | Not offered | Difference (95% CI) | P Value | No of subjects | Declined | Difference (95% CI) | P Value | |||
| Mean (range) age (years) of mother at birth of child | 31.0 (19.4-42.7) (n=86) | 59 | 28.8 (20.5-35.8) | 2.1 (0.5 to 3.7) | 0.009 | 34 | 37.4 (24.5-46.3) | −6.4 (−8.6 to −4.2) | 0.001 | |
| Mean (range) age (years) of father at birth of child | 32.2 (19.7-52.4) (n=57) | 45 | 32.5 (22.5-66.6) | −0.3 (−2.9 to 2.4) | 0.838 | 23 | 36.7 (24.5-51.2) | −4.4 (−8.0 to −0.8) | 0.019 | |
| Mean (range) age (years) of child at interview | 3.9 (2.5-6.5) (n=86) | 59 | 4.1 (2.3-6.2) | −0.2 (−0.5 to 8.7) | 0.168 | 34 | 4.1 (2.5-6.2) | −0.2 (−0.5 to 0.2) | 0.336 | |
| Child died | 4/86 (5%) | 1/59 (2%) | 3% (−2% to 8%) | 0.649 | 0/34 (0%) | 5% (0% to 9%) | 0.576 | |||
| Child adopted | 6/86 (7%) | 2/59 (3%) | 4% (−4% to 11%) | 0.473 | 0/34 (0%) | 7% (2% to 12%) | 0.182 | |||
| Higher family income (>£20 000/year) | 37/81 (46%) | 22/59 (37%) | 9% (−8% to 25%) | 0.321 | 15/33 (45%) | 1% (−20% to 20%) | 0.983 | |||
| Mothers with A level or higher | 39/86 (45%) | 24/58 (41%) | 4% (−13% to 20%) | 0.638 | 17/34 (50%) | −5% (−25% to 15%) | 0.645 | |||
| Fathers with A level or higher | 23/55 (42%) | 13/43 (30%) | 12% (−7% to 31%) | 0.238 | 12/23 (52%) | 10% (−35% to 14%) | 0.402 | |||
Missing data: family income n=6; father's education n=2; mother's education n=1.
Mothers who received false negative results were generally older than mothers not offered tests and younger than those who declined tests. Fathers who received false negative results were generally younger than those who declined tests. None of the demographic variables (that is, mother's age, father's age, age of the child, whether the child had died or been adopted, family income, and mother's and father's educational levels) was significantly related to any of the outcome variables. When parents' ages were entered as covariates in the main analyses reported in table 2 the results were unchanged.
Table 2.
Parents' adjustment and screening history (anxiety, depression, parenting stress, and attitudes towards child are expressed as means; figures for blame are frequencies) in families with child with Down's syndrome
| Adjustment | False negative | Comparison with test not offered
|
Comparison with test declined
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not offered | Difference in means (95% CI) | P value | Declined | Difference in means (95% CI) | P value | |||
| Mothers | ||||||||
| No of mothers | 73-84 | 55-57 | 31-32 | |||||
| Anxiety | 35.9 | 35.7 | 0.2 (−4.1 to 4.4) | 0.932 | 31.3 | 4.6 (−0.4 to 9.6) | 0.070 | |
| Depression | 10.7 | 11.8 | −1.1 (−4.6 to 2.4) | 0.539 | 9.5 | 1.3 (−2.9 to 5.4) | 0.548 | |
| Parenting stress | 81.2 | 79.4 | 1.8 (−5.1 to 8.7) | 0.613 | 71.8 | 9.4 (1.8 to 17.0) | 0.016 | |
| Attitudes towards child | 124.9 | 126.3 | −14 (−7.2 to 4.3) | 0.621 | 134.2 | −9.3 (−16.2 to −2.4) | 0.009 | |
| Blames others | 21/75 (28%) | 6/45 (13%) | 15% (3% to 27%) | 0.032* | 0/31 (0%) | 28% (19% to 37%) | 0.001* | |
| Fathers | ||||||||
| No of fathers | 47-53 | 42-43 | 20-22 | |||||
| Anxiety | 34.6 | 34.0 | 0.5 (−3.9 to 5.0) | 0.816 | 32.7 | 1.9 (−4.5 to 8.2) | 0.560 | |
| Depression | 9.3 | 7.8 | 1.5 (−1.5 to 4.5) | 0.319 | 8.2 | 1.1 (−3.2 to 5.3) | 0.621 | |
| Parenting stress | 77.8 | 70.0 | 7.9 (1.0 to 15.4) | 0.042* | 76.8 | 1.0 (−9.4 to 11.4) | 0.849 | |
| Attitudes towards child | 120.8 | 125.0 | −4.2 (−1.4 to 3.0) | 0.248 | 130.3 | −9.5 (−16.9 to −2.0) | 0.035 | |
| Blames others | 13/48 (27%) | 4/28 (14%) | 13% (−2% to 28%) | 0.099* | 0/20 (0%) | 27% (17% to 38%) | 0.004* | |
P value for one-tailed test.
Psychological outcomes and screening history
There were no differences in levels of anxiety, depression, or parenting stress between parents in the false negative group and those in the not offered or declined groups (table 2). Scores for all groups were close to published norms and well below the clinical cut off points for these measures. Population norms and clinical cut off points are reported in the methods section above.
There were, however, significant differences between groups on the parenting measures. Compared with mothers who declined a test, mothers in the false negative group had higher scores on the parenting stress test (means 81.2 v 71.8; 95% confidence interval for difference 1.8 to 17.0; P=0.016) and had more negative attitudes towards their children (means 124.9 and 134.2; −16.2 to −2.4; P=0.009). Compared with fathers who were not offered a test, fathers in the false negative group had higher scores on the parenting stress test (means 77.8 and 70.0; 1.5 to 14.2; P=0.046). There were also significant differences in blame. Mothers in the false negative group were more likely to blame others for this outcome than were mothers who had not been offered the test (28% v 13%; 3% to 27%; P=0.032). Mothers and fathers in the false negative group were more likely to blame others for this outcome than were parents who had declined a test (mothers 28% v 0%; 19% to 37%; P=0.001; fathers 27% v 0%; 17% to 38%; P=0.004). Blame was directed at health professionals or the medical system in general for not detecting the affected child prenatally.
Blaming others and adjustment
Among those receiving a false negative test result, blaming others was associated in mothers and fathers with higher and clinically significant levels of parenting stress and more negative attitudes towards the child (table 3). It was also associated with higher levels of anxiety in mothers but not in fathers.
Table 3.
Blaming others and adjustment for mothers and fathers (means)
| Adjustment | False negative group
|
Not offered group
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No blame | Blame | Difference in means (95% CI) | P Value | No blame | Blame | Difference in means (95% CI) | P Value | ||
| Mothers | |||||||||
| No of mothers | 48-53 | 17-21 | 37-38 | 5-6 | |||||
| Anxiety | 34.6 | 41.0 | −6.4 (−11.5 to −1.2) | 0.022 | 32.6 | 42.8 | −10.2 (−19.4 to −1.0) | 0.036 | |
| Depression | 10.4 | 13.2 | −2.8 (−7.5 to 1.8) | 0.155 | 9.0 | 23.7 | −14.7 (−26.5 to −2.9) | 0.027 | |
| Parenting stress | 77.3 | 92.6 | −15.3 (−24.2 to −6.5) | 0.003 | 74.9 | 89.8 | −14.9 (−30.2 to 0.3) | 0.054 | |
| Attitudes towards child | 127.3 | 113.9 | 13.4 (5.2 to 21.6) | 0.004 | 129.1 | 115.8 | 13.3 (2.1 to 24.4) | 0.026 | |
| Fathers | |||||||||
| No of fathers | 32-34 | 9-13 | 23-24 | 4 | |||||
| Anxiety | 33.4 | 36.9 | −3.5 (−9.5 to 2.5) | 0.167 | 31.8 | 39.2 | −7.4 (−14.6 to −0.1) | 0.048 | |
| Depression | 9.4 | 10.2 | −0.9 (−5.6 to 3.8) | 0.378 | 7.0 | 9.0 | −2.0 (−6.8 to 2.8) | 0.244 | |
| Parenting stress | 75.5 | 91.7 | −16.2 (−29.7 to −2.6) | 0.026 | 66.7 | 77.0 | −10.3 (−22.8 to 2.2) | 0.086 | |
| Attitudes toward child | 123.3 | 110.9 | 12.5 (0.4 to 24.5) | 0.05 | 125.3 | 124.0 | 1.3 (−13.0 to 15.6 | 0.440 | |
P values and confidence intervals are for one-tailed tests.
Among parents not offered screening blaming others was associated with higher and clinically significant levels of depression; anxiety and more negative attitudes towards the child in mothers; and higher anxiety in fathers.
Discussion
Overall, the parents in our sample, regardless of screening history, adjusted well to having a child with Down's syndrome: levels of anxiety, depression, and parenting stress and attitudes towards their disabled child were similar to those in parents of unaffected children.13,15,17 There was, however, some evidence to suggest that having a screening test that did not detect the affected pregnancy undermined this adjustment. For mothers, receiving a false negative result was associated with higher parenting stress and more negative attitudes towards their children with Down's syndrome compared with those who declined a test. For fathers, receiving a false negative result was associated with higher parenting stress compared with those who were not offered a test. Parents who decline screening, however, are a self selected group for whom termination of pregnancy is not an option they would consider, hence their eschewal of screening. A false negative result was also associated with higher levels of blaming others for the birth in both mothers and fathers. Among those receiving a false negative result, blaming others was associated in mothers and fathers with clinically significant levels of parenting stress and more negative attitudes towards the affected child. It was also associated with higher anxiety for mothers.
Caveats to the study
The strength of this study lies in it being, to our knowledge, the first empirical study to describe psychological outcomes after a false negative result on a screening test, though it does have its limitations. Firstly, we do not know how representative study participants are of the total population eligible to participate. Permission to contact parents was denied by 8% of paediatricians and 11% of general practitioners. This might have removed parents who were known to be most distressed, some of whom were known to be pursuing litigation in relation to the perceived failure of the screening test. Secondly, it did not include parents of children in the first two years of life. This was for pragmatic reasons: at the time the study was set up the most recent complete dataset on the register was for children born in 1992-3. While age of child was unrelated to parental adjustment in the current study, the associations between screening history, blame, and adjustment may be different during the early months after the birth of the child when the process of adjustment is beginning and possibly even in late childhood when developmental differences with other children are more evident.
Blame for birth of child with Down's syndrome
Blame was always directed at health professionals or the healthcare system in general. For some of those in the false negative group it arose from the failure of an expectation that the child would be unaffected by Down's syndrome. For example: “...had the people been in front of me [referring to the staff who had provided antenatal care] and told me everything was going to be alright I could quite honestly have killed them because I was so annoyed with them because they hadn't prepared me for it. After all my doubts and my saying they had convinced me that everything was right ...” (mother).
For other parents blame occurred because they were refused invasive tests, having failed to be reassured by a negative test result. The four mothers who reported this had anxiety and depression levels in the clinical ranges (mean (SD) 55 (18) and 25 (15), respectively) with high levels of parenting stress (99 (21)) and more negative attitudes towards their children (105 (30)).
Among those not offered serum screening, blame seemed to be associated with the belief that the affected child should have been detected on routine prenatal ultrasound or that serum screening should have been offered to all women not just those over a certain age. Few parents who were not offered tests blamed others, but blame was associated with clinically significant levels of anxiety and depression and poorer attitudes towards the child for mothers and higher anxiety for fathers. As ultrasound scans are now widely used to screen for Down's syndrome parents' understanding of the limitations of these tests also needs to be examined.
Blaming others is consistently associated with poor adjustment to a wide range of negative events. In 17 of the 22 studies identified in a literature review of the association between blaming others and adjustment to major life events,10 blaming others (spouses, doctors, or strangers) was associated with poorer adjustment. The causal nature of this well documented association and the circumstances under which adverse events lead to blaming is poorly understood. It seems likely that it is characteristics of a situation as well as characteristics of an individual that interact to influence the likelihood that an individual will blame others for an adverse event.10
What could be done to improve outcome
There are several ways in which current practice might be altered to reduce blame and, in turn, perhaps improve adjustment for parents receiving false negative results. These remain speculative as they were not examined empirically in the current study. Firstly, the information given at the time of screening needs to be accurate and communicated effectively to reduce unrealistic expectations about screening.7,19,20 Although we do not know what the parents in our study were told when they underwent screening for the affected pregnancy, another study has shown that many parents do not understand that a negative result means that a residual risk of an affected child remains.8 The way in which health professionals respond to parents' worries about their pregnancies should also be examined. Several parents reported being told, erroneously, that there could be nothing wrong with their baby. Others were denied invasive tests. While offering blanket reassurance may take less time and be more reassuring than an explanation of residual risks, the results of our study suggest that in the small proportion of cases where a residual risk is realised its adverse effects can be long lasting.
In conclusion, our results suggest that overall parents adjust well to having a child with Down's syndrome after screening but for some a false negative result on prenatal screening may have a small, adverse effect on parental adjustment as much as four years after the birth of an affected child. Intervention studies are needed, both to elucidate the causal relation between screening history and emotional outcomes and to evaluate ways of reducing or avoiding poor adjustment to the child.
What is already known on this topic
Serum screening for Down's syndrome is offered to about 70% of pregnant women in the United Kingdom
Screening does not detect all cases; some parents receive a false negative result
Some parents who receive false negative results experience anger, and some have planned to take legal action
What this study adds
This paper documents the psychological consequences of false negative results on any screening test
A false negative result on prenatal screening seems to have a small adverse effect on parental adjustment, evident two to six years after the birth of an affected child
Figure.
Recruitment of parents and flow through study
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor J David Baum (1940-99), Professor Eva Alberman, Mr Humphry Ward, and Dr Jim Sikorski for their help in conducting this study; to Kay Fearon for secretarial support and transcribing the interview tapes; and to the parents, paediatricians, obstetricians, general practitioners, and the staff of the Regional Cytogenetics Laboratories who took part.
Footnotes
Funding: This study was supported by grant number G9433673 from the Medical Research Council. Professor Marteau is supported by the Wellcome Trust.
Competing interests: None declared.
References
- 1.Petticrew M, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D. False negative results in screening programmes: impact and implications. Health Technol Assess (in press). [PubMed]
- 2.Wald NJ, Huttly WJ, Hennessy CF. Down's syndrome screening in the UK in 1998. Lancet. 1999;354:1264. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(99)03819-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wald NJ, Kennard A, Hackshaw A, McGuire A. Antenatal screening for Down's syndrome. J Med Screen. 1997;4:181–246. doi: 10.1177/096914139700400402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Snijders RJM, Noble P, Sebire N, Souka A, Nicolaides KH. UK multicentre project on assessment of risk of trisomy 21 by maternal age and fetal nuchal-translucency thickness at 10-14 weeks' gestation. Lancet. 1998;352:343–346. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(97)11280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.The right to a perfect baby. Independent 1992 August 22:3.
- 6.Parsons L, Richards J, Garlick R. Screening for Down's syndrome. BMJ. 1992;305:1228. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6863.1228-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cockburn J, Redman S, Hill D, Henry E. Public understanding of medical screening. J Med Screen. 1995;2:224–227. doi: 10.1177/096914139500200410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Smith DK, Shaw RW, Marteau T. Informed consent to undergo serum screening for Down's syndrome: the gap between policy and practice. BMJ. 1994;309:776. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6957.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hall S, Bobrow M, Marteau TM. Parents attributions of blame for the birth of a child with Down syndrome: a pilot study. Psychol Health. 1997;12:579–587. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tennen H, Affleck G. Blaming others for threatening events. Psychol Bull. 1990;108:209–232. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mutton DE, Alberman E, Ide R, Bobrow M. Results of first year (1989) of a national register of Down's syndrome in England and Wales. BMJ. 1991;303:1295–1297. doi: 10.1136/bmj.303.6813.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mutton DE, Ide R, Alberman E, Bobrow M. Analysis of national register of Down's syndrome in England and Wales: trends in prenatal diagnosis, 1989-91. BMJ. 1993;306:431–432. doi: 10.1136/bmj.306.6875.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Marteau TM, Bekker H. Development of a short-form of the state scale of the Spielberger state-trait anxiety inventory. Br J Clin Psychol. 1992;31:301–306. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8260.1992.tb00997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Judson SL, Burden RL. Towards a tailored measure of parental attitudes: an approach to the evaluation of one aspect of intervention projects with parents of handicapped children. Child Care Health Dev. 1980;6:47–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2214.1980.tb00796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Radloff L. CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychosoc Measurement. 1977;1:385–340. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Abidin RR. Parenting stress index (short form): test manual. Charlottesville, VA: Pediatric Psychology Press; 1990. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Quine L, Phal J. Stress and coping in mothers caring for a child with severe learning difficulties: a test of Lazarus' transactional model of coping. J Community Appl Soc Psychol. 1991;1:57–90. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gardner SB, Winter PD, Altman DG. Statistics with confidence. London: BMJ Publishing; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Marteau TM, Slack J, Kidd J, Shaw RW. Presenting a routine screening test in antenatal care: practice observed. Public Health. 1992;106:131–141. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(05)80390-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Allanson A, Michie S, Marteau TM. Presentation of screen negative results on serum screening for Down syndrome: variations across Britain. J Med Screen. 1997;4:21–22. doi: 10.1177/096914139700400108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]