Abstract
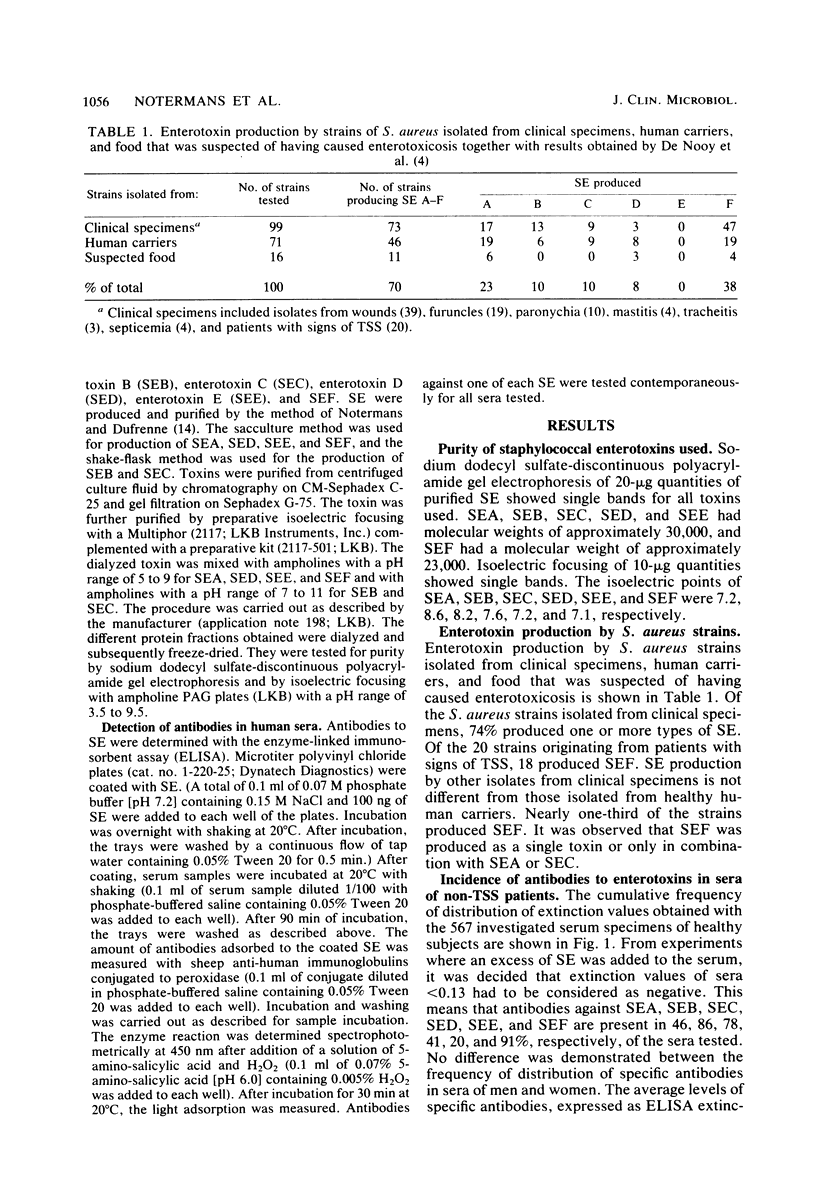
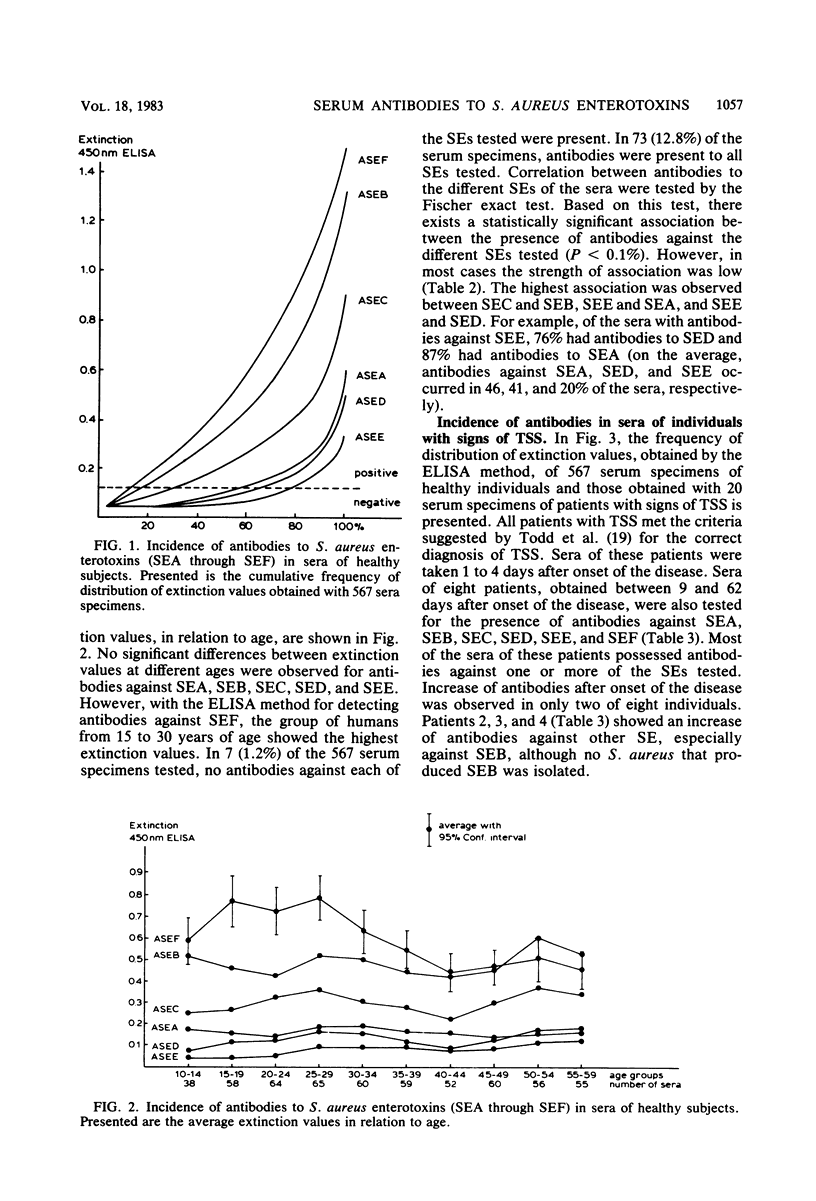
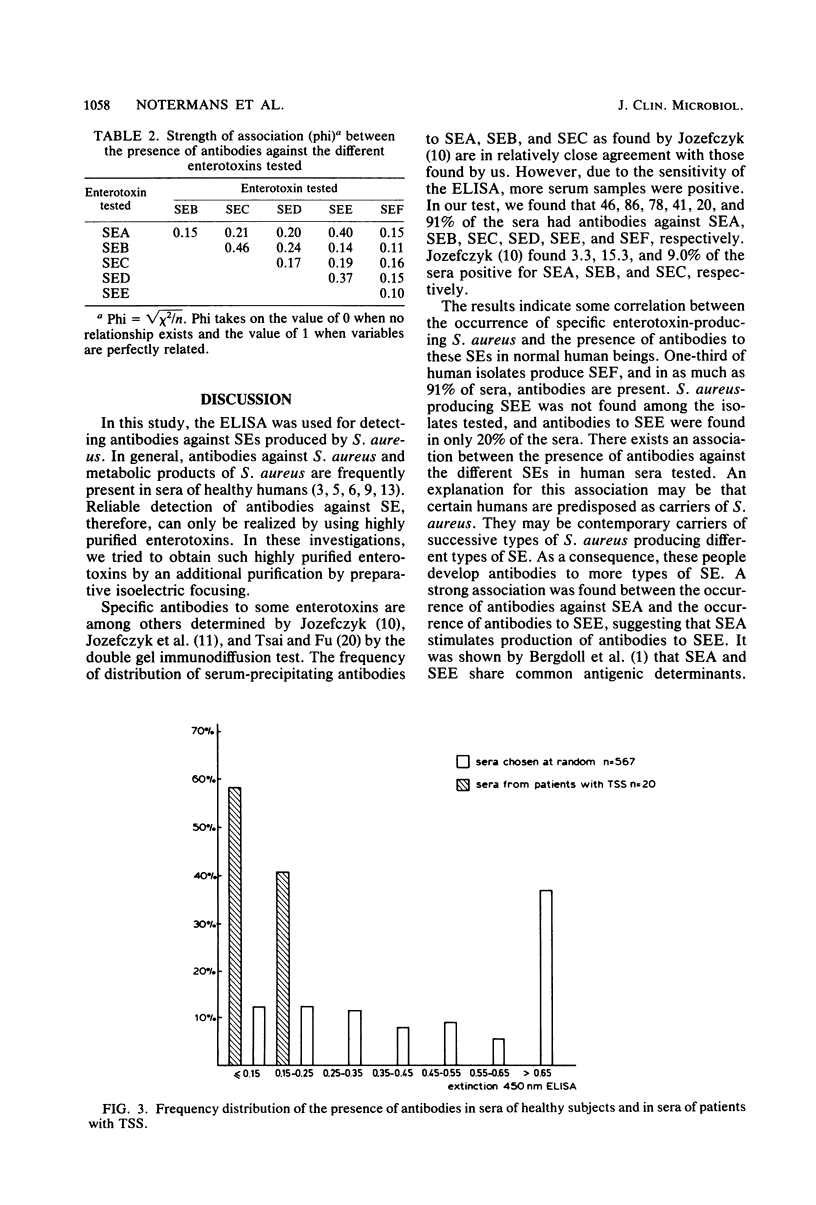
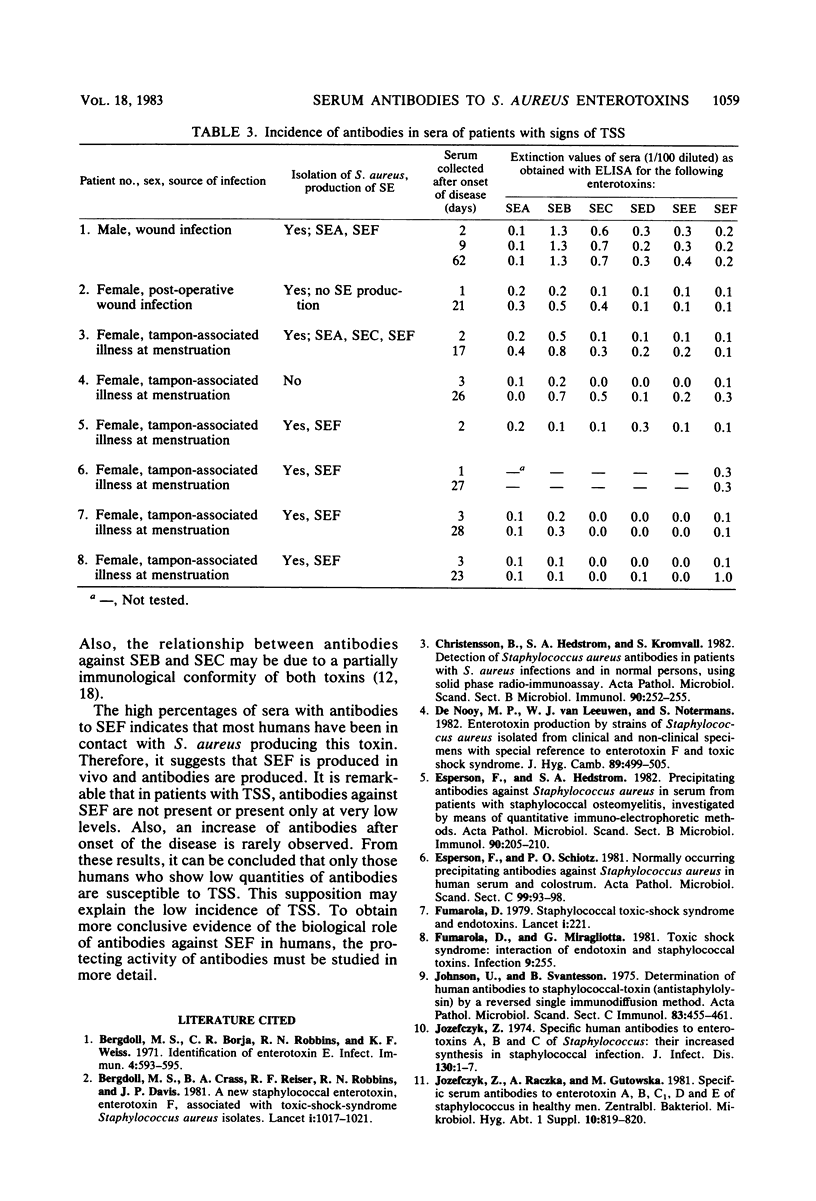
The presence of antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins (enterotoxins A through F) in sera of healthy subjects (n = 567) and in sera of patients with toxic shock syndrome (n = 20) was determined. Furthermore, production of enterotoxins by Staphylococcus aureus isolated from humans was investigated. In 46, 86, 78, 41, 20, and 91% of the sera of healthy subjects, antibodies were found against enterotoxins A, B, C, D, E, and F, respectively. The high percentage of sera with antibodies against enterotoxin F correlated with the relatively high frequency of enterotoxin F-producing S. aureus isolated from humans (one-third of the isolates produced enterotoxin F). In patients with toxic shock syndrome, antibodies against enterotoxin F were not present or were present only at very low levels. An increase of antibodies after onset of the disease was observed in two of eight patients investigated. From the results, it can be concluded that only those humans who show low levels of antibodies are susceptible to toxic shock syndrome.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergdoll M. S., Borja C. R., Robbins R. N., Weiss K. F. Identification of enterotoxin E. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):593–595. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.593-595.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensson B., Hedström S. A., Kronvall G. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus antibodies in patients with S. aureus infections and in normal persons, using solid phase radioimmunoassay. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Jun;90(3):251–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Hedström S. A. Precipitating antibodies against Staphylococcus aureus in serum from patients with staphylococcal osteomyelitis, investigated by means of quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Jun;90(3):205–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Schiøtz P. O. Normally-occurring precipitating antibodies against Staphylococcus aureus in human serum and colostrum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1981 Apr;89(2):93–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb02670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fumarola D., Miragliotta G. Toxic shock syndrome: interaction of endotoxin and staphylococcal toxins. Infection. 1981;9(5):255–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Józefczyk Z. Specific human antibodies to enterotoxins A, B, and C1 of Staphylococcus: their increased synthesis in staphylococcal infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jul;130(1):1–7. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. C., Robbins R. N., Reiser R. F., Bergdoll M. S. Isolation of specific and common antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins B, C1, and C2. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):431–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.431-434.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentino J. R., Rytel M. W. Detection of circulating free and complexed staphylococcal antigens by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1019–1024. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1019-1024.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Dufrenne J. B. A simple purification method for enterotoxin F produced by Staphylococcus aureus and some properties of the toxin. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1982 Dec;48(5):447–455. doi: 10.1007/BF00448416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roels H., Bernard A., Buchet J. P., Goret A., Lauwerys R., Chettle D. R., Harvey T. C., Haddad I. A. Critical concentration of cadmium in renal cortex and urine. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):221–221. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90630-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Osterholm M. T., Kelly J. A., Nishimura R. D. Toxin and enzyme characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with and without toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):937–940. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands K. N., Schmid G. P., Dan B. B., Blum D., Guidotti R. J., Hargrett N. T., Anderson R. L., Hill D. L., Broome C. V., Band J. D. Toxic-shock syndrome in menstruating women: association with tampon use and Staphylococcus aureus and clinical features in 52 cases. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1436–1442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spero L., Morlock B. A., Metzger J. F. On the cross-reactivity of staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, and C. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):86–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J., Fishaut M., Kapral F., Welch T. Toxic-shock syndrome associated with phage-group-I Staphylococci. Lancet. 1978 Nov 25;2(8100):1116–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. C., Fu S. Y. Antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins in Chinese on Taiwan. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1976 Sep;75(9):506–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Nooij M. P., van Leeuwen W. J., Notermans S. Enterotoxin production by strains of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical and non-clinical specimens with special reference to enterotoxin F and toxic shock syndrome. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Dec;89(3):499–505. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400071060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



