Abstract
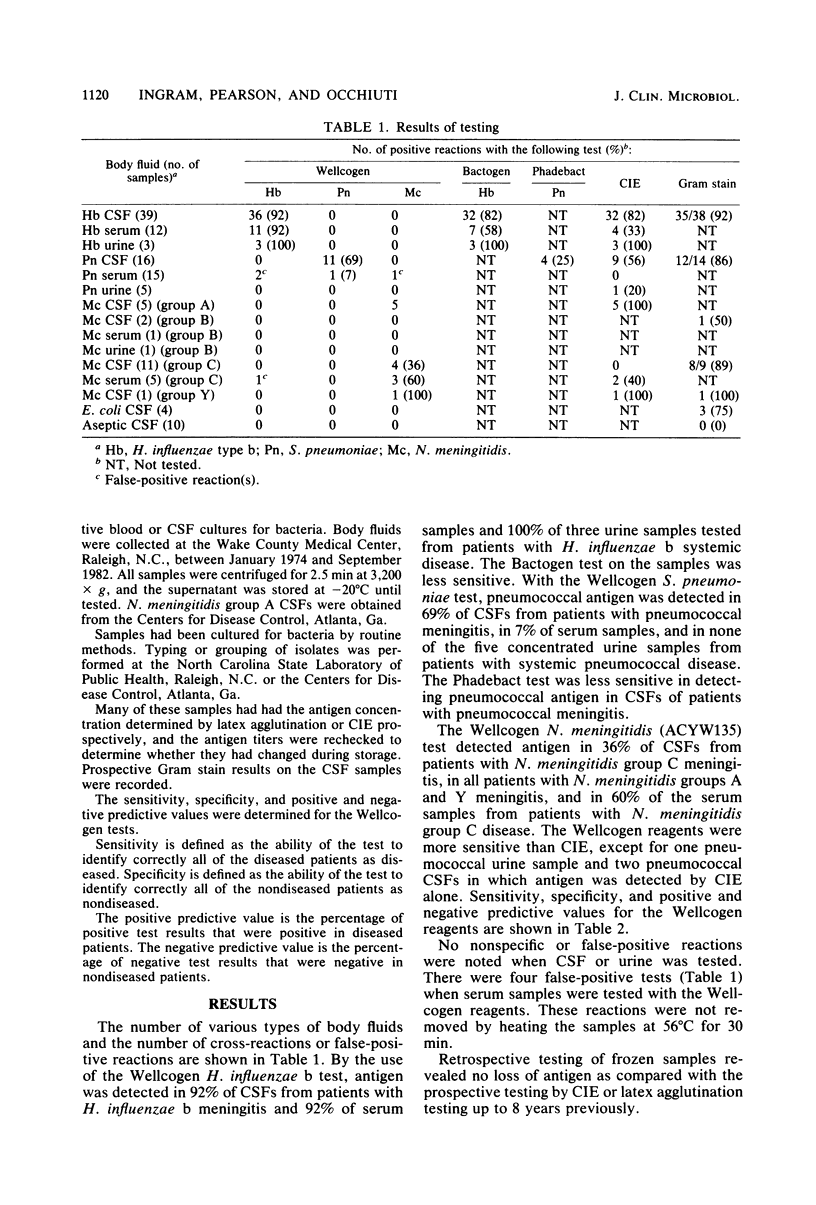
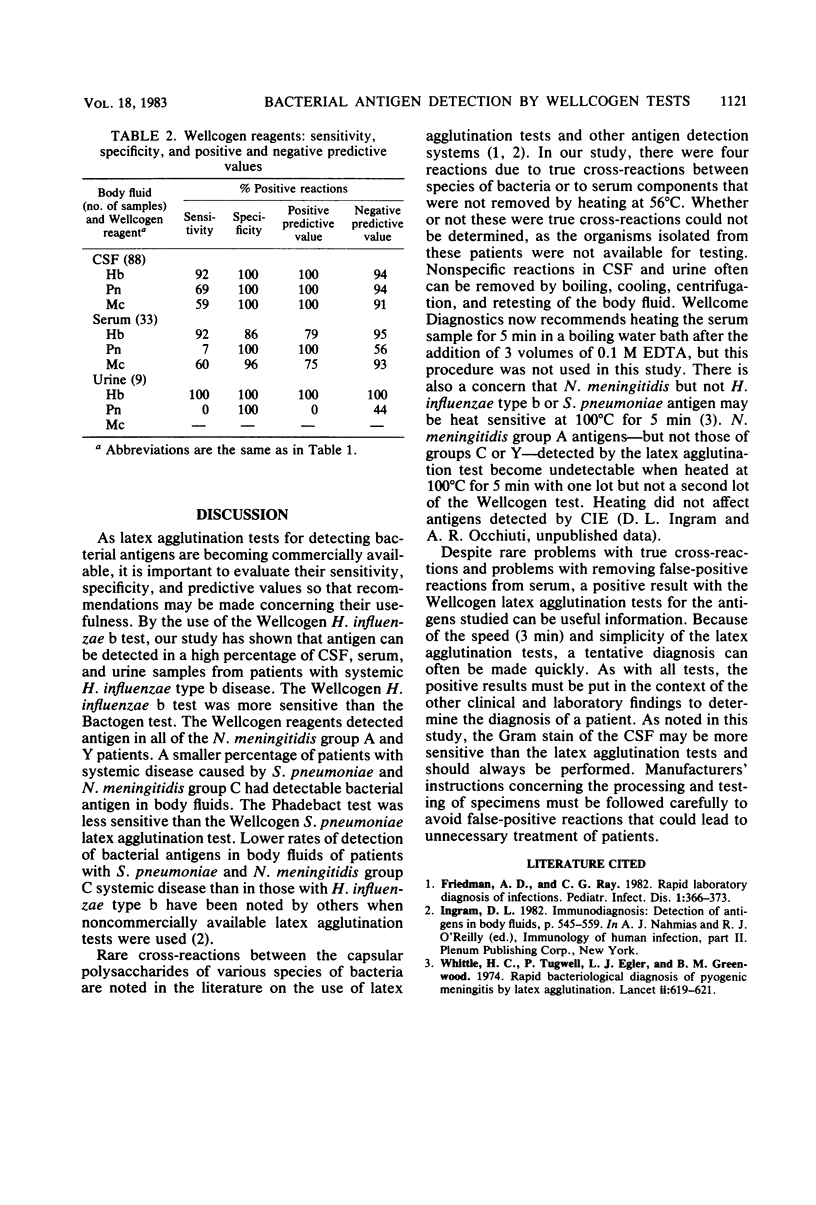
The Wellcogen Haemophilus influenzae b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Neisseria meningitidis (ACYW135) latex agglutination tests (Wellcome Diagnostics, Dartford, England) were evaluated as methods to detect bacterial antigens in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), urine, and serum from patients with meningitis or sepsis. Antigen was detected in 92% of CSFs from H. influenzae b, 100% of CSFs from N. meningitidis groups A and Y, 36% of CSFs from N. meningitidis group C, and 69% of CSFs from pneumococcal meningitidis patients. Serum samples presented a problem, with a few false-positive or possible cross-reactions. The Wellcogen latex agglutination tests were more sensitive than the Bactogen (H. influenzae type b) latex agglutination test and the Phadebact (S. pneumoniae) coagglutination test.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Friedman A. D., Ray C. G. Rapid laboratory diagnosis of infections. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1982 Sep-Oct;1(5):366–373. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198209000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle H. C., Tugwell P., Egler L. J., Greenwood B. M. Rapid bacteriological diagnosis of pyogenic meningitis by latex agglutination. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):619–621. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91943-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



