Abstract
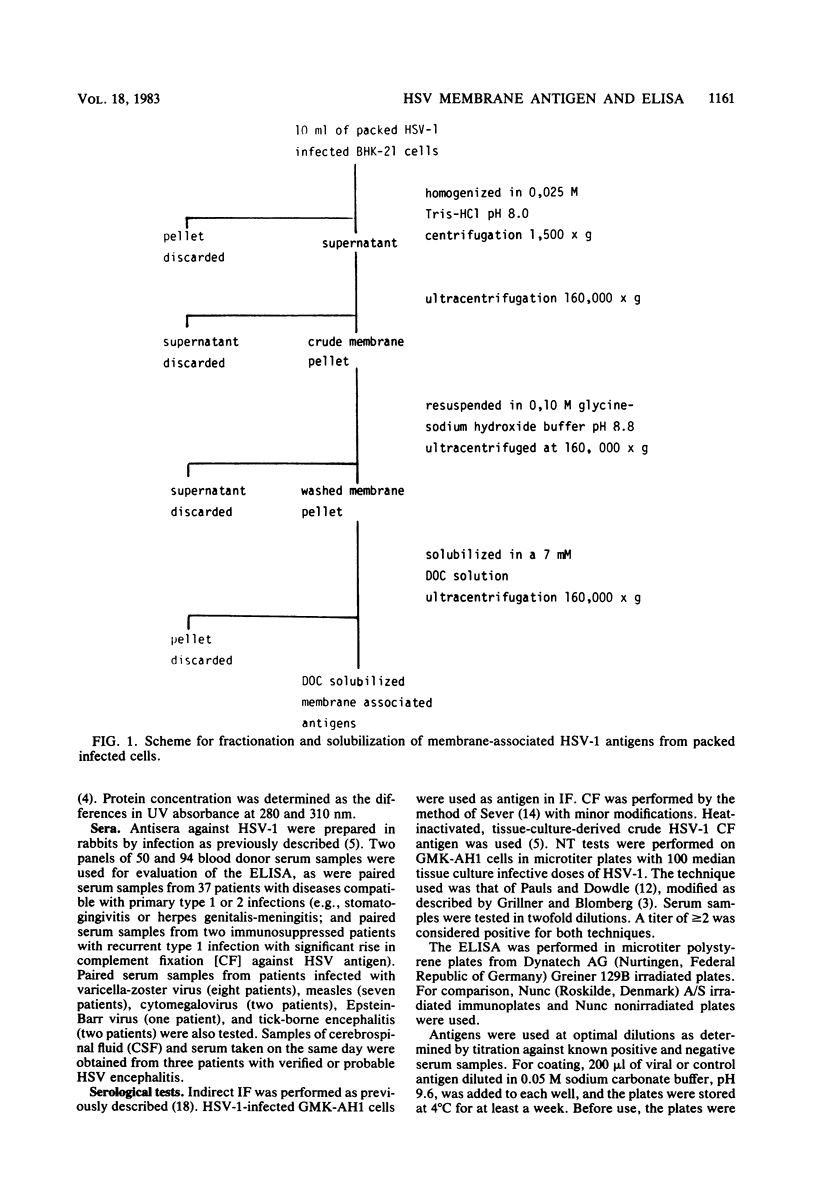
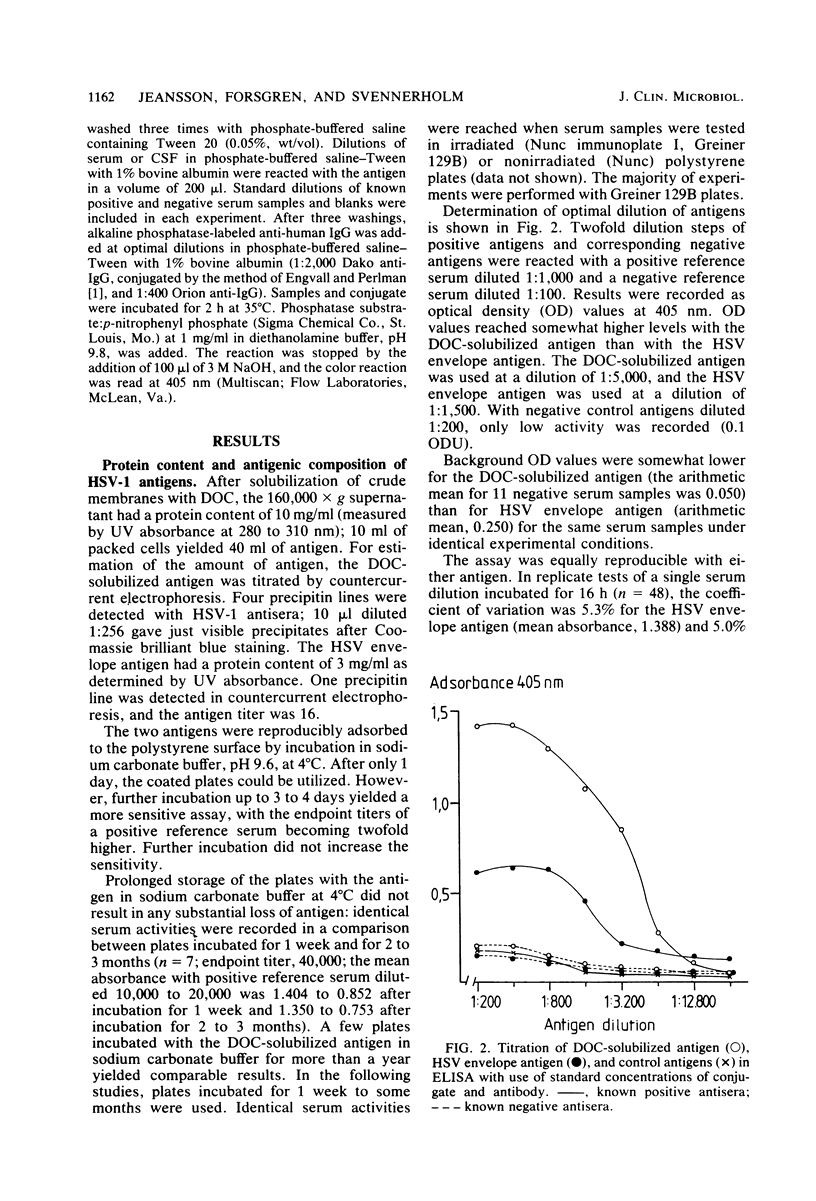
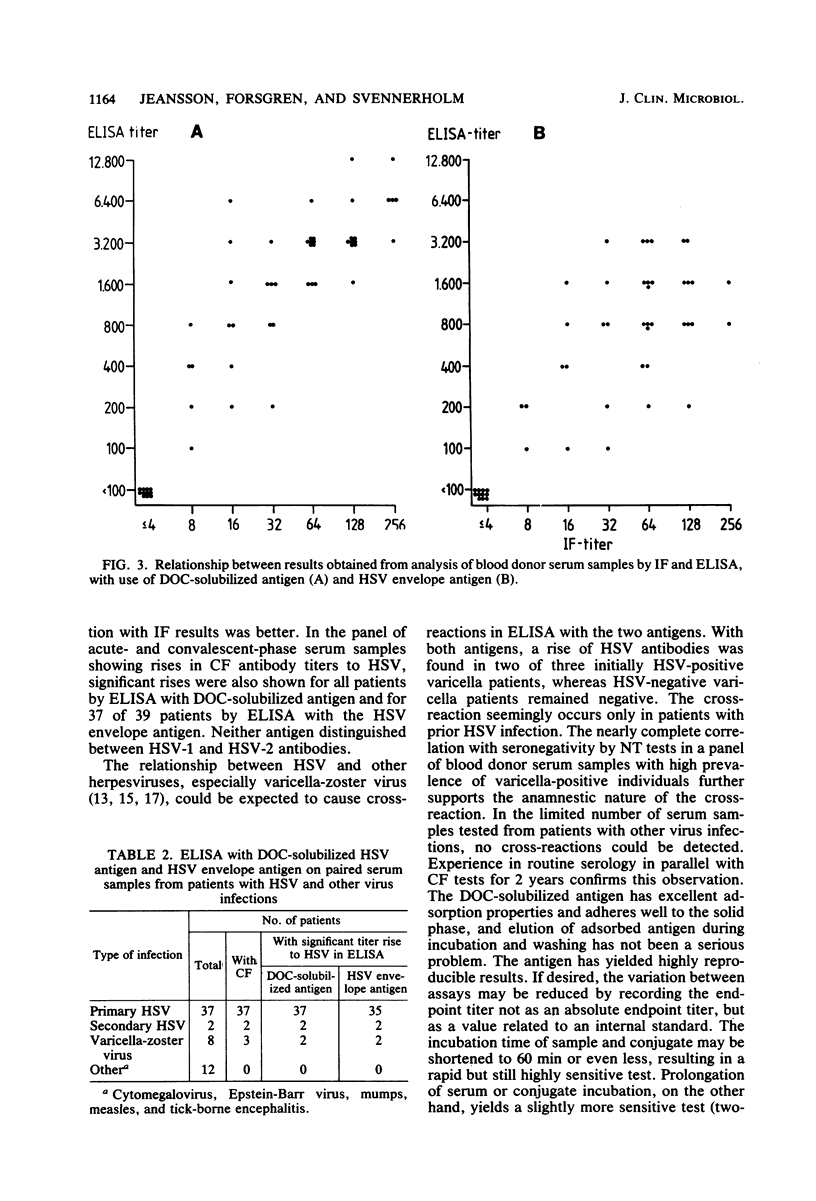
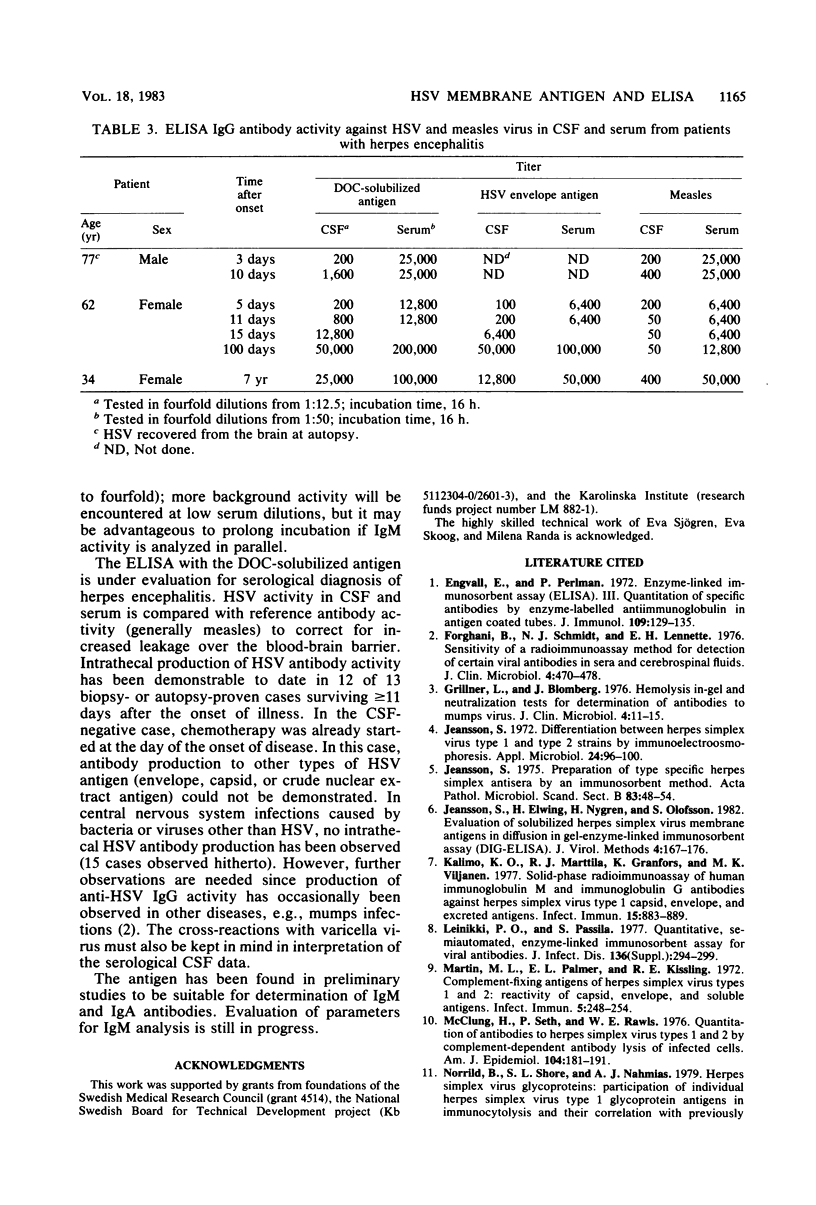
An antigen prepared by solubilization of membranes from herpes simplex virus (HSV)-infected cells with deoxycholate was evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The deoxycholate-solubilized antigen, previously shown to contain all major HSV glycoproteins, was noninfectious and adsorbed easily and reproducibly to a polystyrene surface at pH 9.6. The deoxycholate-solubilized antigen provided an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of high sensitivity and reproducibility with complete correlation with complement fixation for the diagnosis of acute HSV infection. The correlation with neutralization and immunofluorescence for the presence or absence of anti-HSV activity was very good. Comparison with an HSV envelope preparation yielded results slightly in favor of the deoxycholate-solubilized antigen. The assay seems to be useful for demonstration of intrathecal production of antibody activity in HSV encephalitis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Sensitivity of a radioimmunoassay method for detection of certain viral antibodies in sera and cerebrospinal fluids. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Dec;4(6):470–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.6.470-478.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner L., Blomberg J. Hemolysis-in-gel and neutralization tests for determination of antibodies to mumps virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):11–15. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.11-15.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeansson S. Differentiation between herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 strains by immunoelectroosmophoresis. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jul;24(1):96–100. doi: 10.1128/am.24.1.96-100.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeansson S., Elwing H., Nygren H., Olofsson S. Evaluation of solubilized herpes simplex virus membrane antigens in diffusion in gel-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (DIG-ELISA). J Virol Methods. 1982 Apr;4(3):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeansson S. Preparation of type specific herpes simplex antisera by an immunosorbent method;. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Feb;83(1):48–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimo K. O., Marttila R. J., Granfors K., Viljanen M. K. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of human immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G antibodies against herpes simplex virus type 1 capsid, envelope, and excreted antigens. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):883–889. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.883-889.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. L., Palmer E. L., Kissling R. E. Complement-fixing antigens of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2: reactivity of capsid, envelope, and soluble antigens. Infect Immun. 1972 Feb;5(2):248–254. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.2.248-254.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClung H., Seth P., Rawls W. E. Quantitation of antibodies to Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 by complement-dependent antibody lysis of infected cells. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Aug;104(2):181–191. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls F. P., Dowdle W. R. A serologic study of herpesvirus hominis strains by microneutralization tests. J Immunol. 1967 May;98(5):941–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H., Magoffin R. L. Immunological relationship between herpes simplex and varicella-zoster viruses demonstrated by complement-fixation, neutralization and fluorescent antibody tests. J Gen Virol. 1969 Apr;4(3):321–328. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-3-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraki K., Okuno T., Yamanishi K., Takahashi M. Polypeptides of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and immunological relationship of VZV and herpes simplex virus (HSV). J Gen Virol. 1982 Aug;61(Pt 2):255–269. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-2-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Nahmias A. J., Starr S. E., Wood P. A., McFarlin D. E. Detection of cell-dependent cytotoxic antibody to cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):350–352. doi: 10.1038/251350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr A. Varicella virus in HeLa cells. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;17(3):495–503. doi: 10.1007/BF01241206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahlne A., Lycke E. Herpes simplex virus infection of mouse neuroblastoma cells (39880). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Oct;156(1):82–87. doi: 10.3181/00379727-156-39880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard B. F., Norrild B. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis and viral neutralizing activity of five monospecific antisera against five different herpes simplex virus glycoproteins. IARC Sci Publ. 1978;(24 Pt 1):225–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


