Abstract
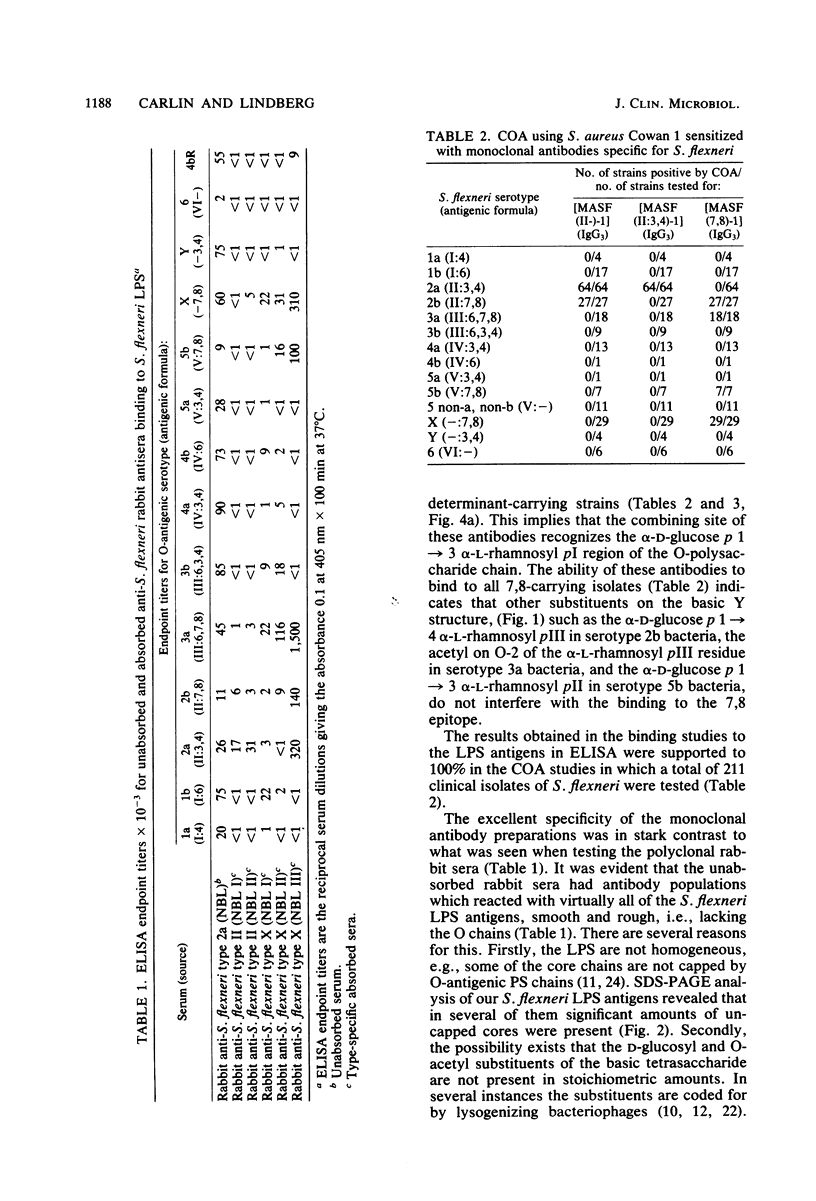
Hybrid cells producing monoclonal antibodies against the O-antigens of Shigella flexneri were obtained by polyethylene glycol-mediated fusion of myeloma cells and lymphocytes from BALB/c mice immunized with whole heat-killed S. flexneri bacteria of serotypes 2a and 2b. Clones were selected for their binding specificity to structurally defined S. flexneri lipopolysaccharides (LPS). The following three groups were identified as recognizing three different epitopes: monoclonal antibodies binding to (i) S. flexneri LPS with the II:3,4 antigens, (ii) S. flexneri LPS with the II:3,4 antigens and the II:7,8 antigens, and (iii) S. flexneri LPS with the 7,8 group antigen only. Of cloned and characterized antibodies, more than 90% had either the mu or gamma 3 heavy chain and 98% had the kappa light chain. The exquisite specificity of each monoclonal antibody preparation was in complete contrast to the polyclonal specificities seen in sera from immunized rabbits. Even absorbed rabbit S. flexneri typing sera contained antibodies reacting with several different LPS, i.e., they were not type antigen specific. Ascites from immunoglobulin G monoclonal antibody preparations representing the three different specificities were used for sensitizing Staphylococcus aureus Cowan 1 bacteria and were used in coagglutination. In testing 211 clinical isolates of all different serotypes of S. flexneri, the reagents were shown to be sensitive and specific in correctly identifying all S. flexneri II and 7,8 antigen-containing strains with no false positives. Two isolated immunoglobulin M antibody clones specific for the II:3,4 and 7,8 antigens were used as successfully for identification by direct slide agglutination. These results suggest that the monoclonal reagents are superior to conventional typing antisera.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlsson H. E., Lindberg A. A., Hammarström S. Titration of antibodies to salmonella O antigens by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):703–708. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.703-708.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. H., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Production of monoclonal antibodies in serum free medium. J Immunol Methods. 1980;39(4):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitriev B. A., Knirel Y. A., Sheremet O. K., Shashkov A. A., Kochetkov N. K., Hofman I. L. Somatic antigens of Shigella. The structure of the specific polysaccharide of Shigella newcastle (Sh. flexneri type 6) lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):309–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Biochemical studies on lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella R mutants. 3. The linkage of the heptose units. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Mar;4(1):126–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Koeltzow D. E., Formal S. B. Phage conversion of Shigella flexneri group antigens. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):685–691. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.685-691.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson P. E., Lindberg A. A., Lindberg B., Wollin R. Structural studies on the hexose region of the core in lipopolysaccharides from Enterobacteriaceae. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):571–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. H., Johnston R. J., Simmons D. A. The immunochemistry of Shigella flexneri O-antigens. The biochemical basis of smooth to rough mutation. Biochem J. 1967 Oct;105(1):79–87. doi: 10.1042/bj1050079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Petersson K. Basic structure of the oligosaccharide repeating-unit of the Shigella flexneri O-antigens. Carbohydr Res. 1977 Jul;56(2):363–370. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)83357-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Petersson K., Katzenellenbogen E., Romanowska E. Structural studies of Shigella flexneri O-antigens. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 2;91(1):279–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Petersson K., Katzenellenbogen E., Romanowska E. Structural studies of the Shigella flexneri variant X, type 5 a and type 5 b O-antigens. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 15;76(2):327–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A rapid slide-agglutination method for typing pneumococci by means of specific antibody adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):187–190. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSUI S. Antigenic changes in Shigella flexneri group by bacteriophage. Jpn J Microbiol. 1958 Apr;2(2):153–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1958.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Draper C., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Microplate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for chagas' disease. Lancet. 1975 Feb 22;1(7904):426–428. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91492-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]