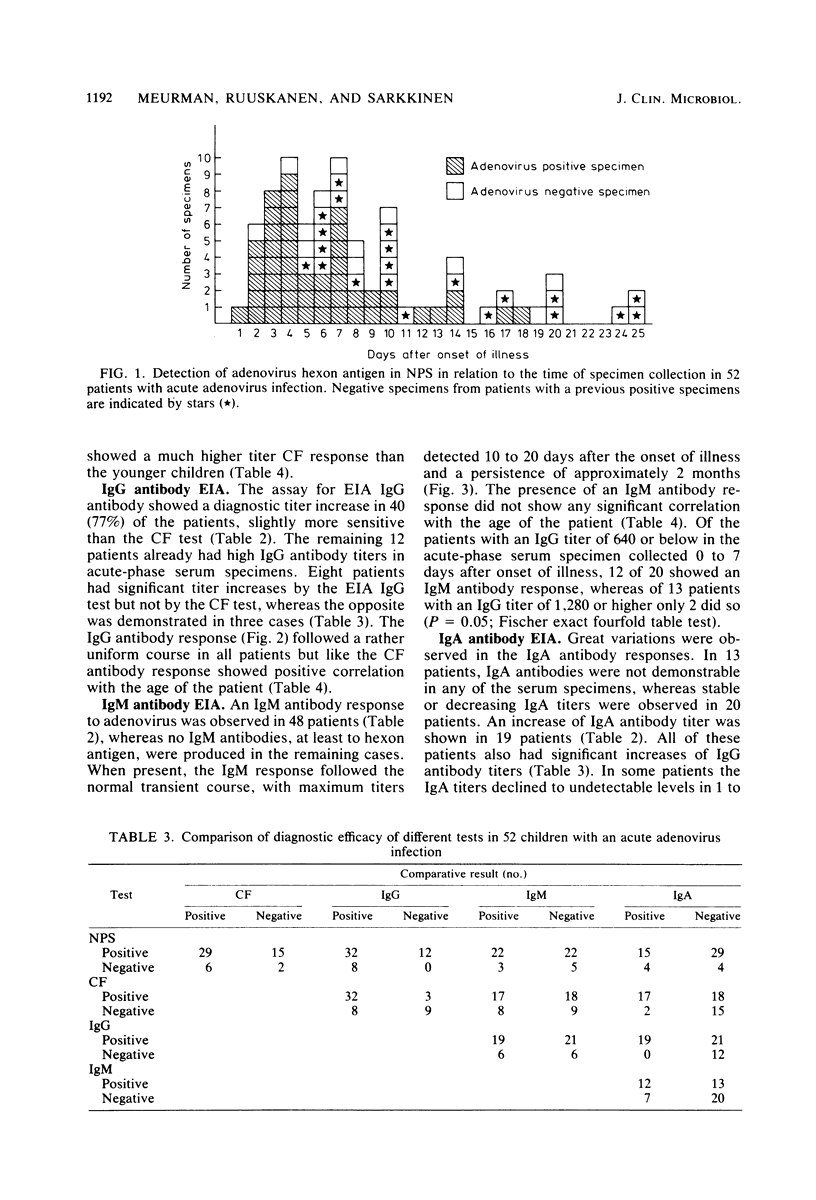
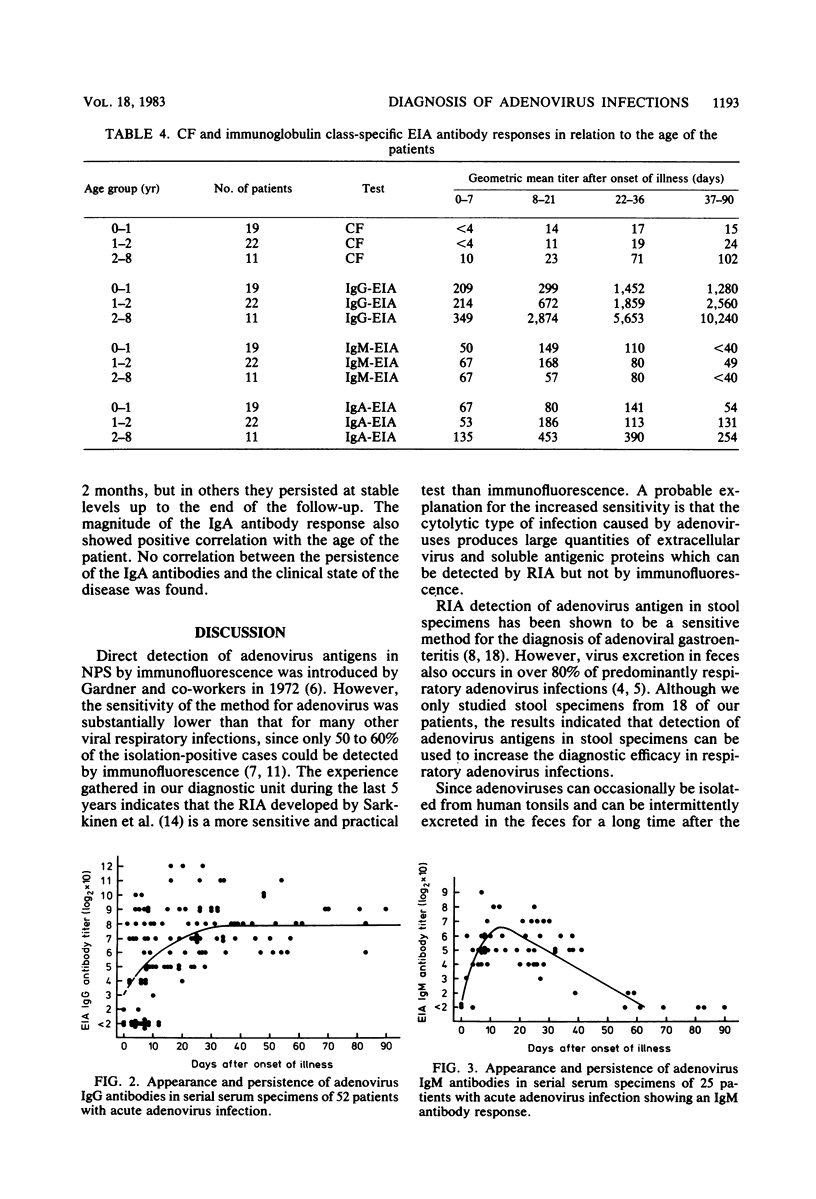
Abstract
Direct detection of viral antigen in nasopharyngeal secretions and stool specimens by radioimmunoassay and the determination of serum antibody responses by complement fixation and immunoglobulin class-specific enzyme immunoassay against the hexon antigen were compared for diagnostic efficacy in 52 children with acute adenovirus infections. The highest diagnosis rate (85% of the cases) was obtained by antigen detection in nasopharyngeal secretions. Adenovirus antigen was also detected in stools of 72% of the 18 patients tested. The immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody enzyme immunoassay detected 77% of the cases, being more sensitive than the complement fixation test with a 67% detection rate. The IgM antibody response was variable with no clear correlation with the age of the patient or severity of the clinical symptoms. IgM antibody response was detected in 48% of the patients and had the normal transient course, with a persistence of the IgM antibodies of approximately 2 months. Determination of IgA antibodies gave a diagnostic increase in titer in 37% of the cases and was found less suitable for serological diagnosis. Because of the clinical importance of rapid laboratory diagnosis, the direct detection of viral antigen in nasopharyngeal secretions or stool or both should be used as the primary diagnostic test in adenovirus infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellanti J. A., Artenstein M. S., Brandt B. L., Klutinis B. S., Buescher E. L. Immunoglobulin responses in serum and nasal secretions after natural adenovirus infections. J Immunol. 1969 Nov;103(5):891–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broniţki A., Isaia G., Popescu G., Teodosiu O., Sternberg I. Investigations on the circulation of viruses occurring in the respiratory tract of apparently healthy schoolchildren aged 7 to 14 years. Virologie. 1981 Jul-Sep;32(3):193–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdle W. R., Lambriex M., Hierholzer J. C. Production and evaluation of a purified adenovirus group-specific (hexon) antigen for use in the diagnostic complement fixation test. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):718–722. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.718-722.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. P., Brandt C. D., Wassermann F. E., Hall C. E., Spigland I., Kogon A., Elveback L. R. The virus watch program: a continuing surveillance of viral infections in metropolitan New York families. VI. Observations of adenovirus infections: virus excretion patterns, antibody response, efficiency of surveillance, patterns of infections, and relation to illness. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Jan;89(1):25–50. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. P., Hall C. E., Cooney M. K. The Seattle Virus Watch. VII. Observations of adenovirus infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Apr;105(4):362–386. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. S., McGuckin R., McQuillin J. Adenovirus demonstrated by immunofluorescence. Br Med J. 1972 Jul 15;3(5819):175–175. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5819.175-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P., Sarkkinen H., Arstila P., Hjertsson E., Torfason E. Four-layer radioimmunoassay for detection of adenovirus in stool. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):614–617. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.614-617.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrich J. R., Kasel J. A., Rossen R. D. Immunoglobulin classes of neutralizing antibody formed after human inoculation with soluble adenoviral antigens. J Immunol. 1966 Nov;97(5):654–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnich L., Ray C. G. Comparison of direct immunofluorescent staining of clinical specimens for respiratory virus antigens with conventional isolation techniques. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):391–394. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.391-394.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Philipson L., Höglund S. Structural proteins of adenoviruses. I. Purification and characterization of the adenovirus type 2 hexon antigen. Virology. 1967 Dec;33(4):575–590. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggendorf M., Wigand R., Deinhardt F., Frösner G. G. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for acute adenovirus infection. J Virol Methods. 1982 Feb;4(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkkinen H. K., Halonen P. E., Arstila P. P., Salmi A. A. Detection of respiratory syncytial, parainfluenza type 2, and adenovirus antigens by radioimmunoassay and enzyme immunoassay on nasopharyngeal specimens from children with acute respiratory disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):258–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.258-265.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. A comparison of the diagnostic value of adenoviral complement-fixing antigens prepared from various immunotypes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Jan;55(1):34–39. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H., King C. J. Neutralizing, hemagglutination-inhibiting and group complement-fixing antibody responses in human adenovirus infections. J Immunol. 1966 Jul;97(1):64–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Mäki M., Sarkkinen H. K., Arstila P. P., Halonen P. E. Rotavirus, adenovirus, and non-viral enteropathogens in diarrhoea. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Apr;56(4):264–270. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.4.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen M., Palva A., Laaksonen M., Halonen P., Söderlund H., Ranki M. Novel test for rapid viral diagnosis: detection of adenovirus in nasopharyngeal mucus aspirates by means of nucleic-acid sandwich hybridisation. Lancet. 1983 Feb 19;1(8321):381–383. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91500-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


