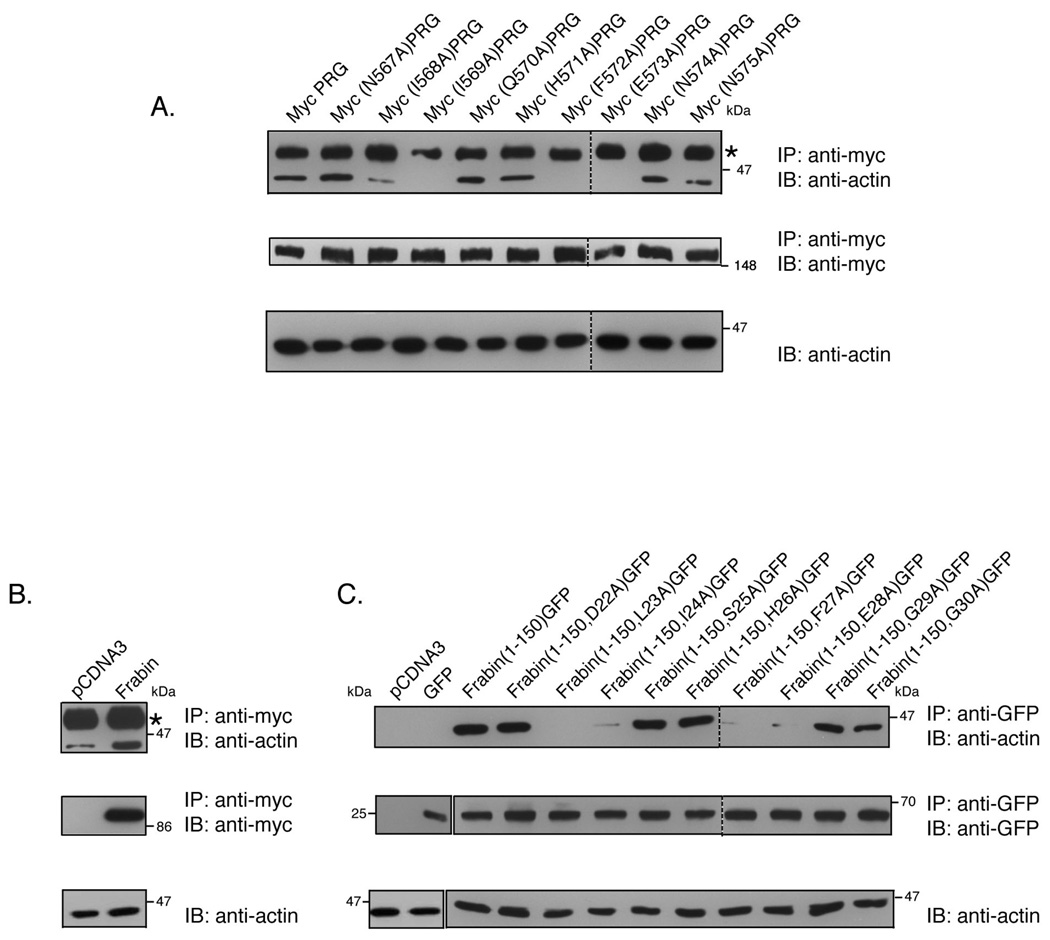
Figure 4. PRG and frabin co-immunoprecipitate with actin.
(A) COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with 7 µg of an expression vector encoding PRG or the indicated mutants. PRG was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with a mouse monoclonal anti-Myc antibody, and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-actin mAb (upper panel). Immunoprecipitation of the Myc-tagged PRG proteins was confirmed by immunoblotting of the immunoprecipitates using anti-Myc antibody (middle panel). Presence of actin in the lysates was detected by immunoblotting using anti-actin mAb (lower panel). (B) COS-7 cells were transfected with 7 µg empty vector or with expression plasmid for Myc-tagged full-length frabin. Cells were lysed and lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation by monoclonal anti-Myc antibody. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblot using anti-actin mAb (upper panel) and anti-Myc Ab (middle panel). Actin in the cell lysates was detected using anti-actin mAb (lower panel). (C) COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with 7 µg of empty vector, GFP alone or with the indicated GFP-tagged frabin mutants. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with polyclonal anti-GFP antibody and immunoprecipitates were probed for actin using anti-actin mAb (upper panel). Immunoprecipitation of GFP-tagged frabin constructs were confirmed by immunoblot of immunoprecipitates using anti-GFP antibody (middle panel), and presence of actin in the cell lysates was confirmed by anti-actin mAb (lower panel). Asterisks (*) indicate the antibody heavy chain that migrates slower than actin.