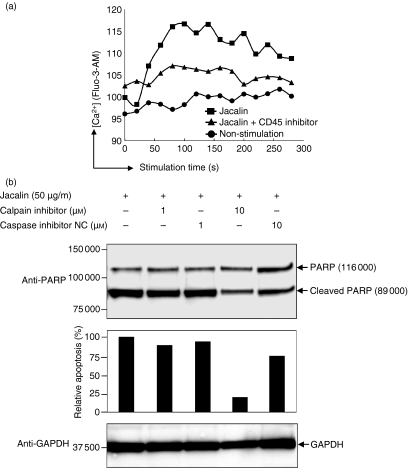
Figure 7.
Calcium–calpain pathway may mediate Jacalin-induced Raji B-cell apoptosis. (a) Jacalin-induced calcium mobilization. Raji B cells were loaded with 10 μm Fluo-3-AM following treatment without or with Jacalin labelled with Jacalin treatment (50 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of 1 μm CD45 inhibitor for the indicated time above, and then intracellular Ca2+ concentrations were recoded on a FACSCalibur. (b) Calpain activation is involved in Jacalin-induced Raji B-cell apoptosis. Raji B cells were incubated with a calpain inhibitor or a caspase inhibitor negative control at 1 μm and 10 μm, respectively, in the presence of 50 μg/ml Jacalin for 72 hr, followed by assessment of apoptosis. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage was analysed by Western blotting for apoptosis detection (upper panel). The arrows indicate 116 000 PARP and the 89 000 apoptosis-related cleavage fragment as indicated above. The relative percentage of the apoptosis was determined by comparing the decreases in the 89 000 apoptosis-related cleavage fragment in the absence and presence of calpain inhibitor or caspase inhibitor negative control (middle panel). The 89 000 apoptosis-related cleavage bands were scanned by laser densitometry. GAPDH is shown as a control for protein loading (lower panel). The results are representative of three independent experiments.