Abstract
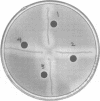
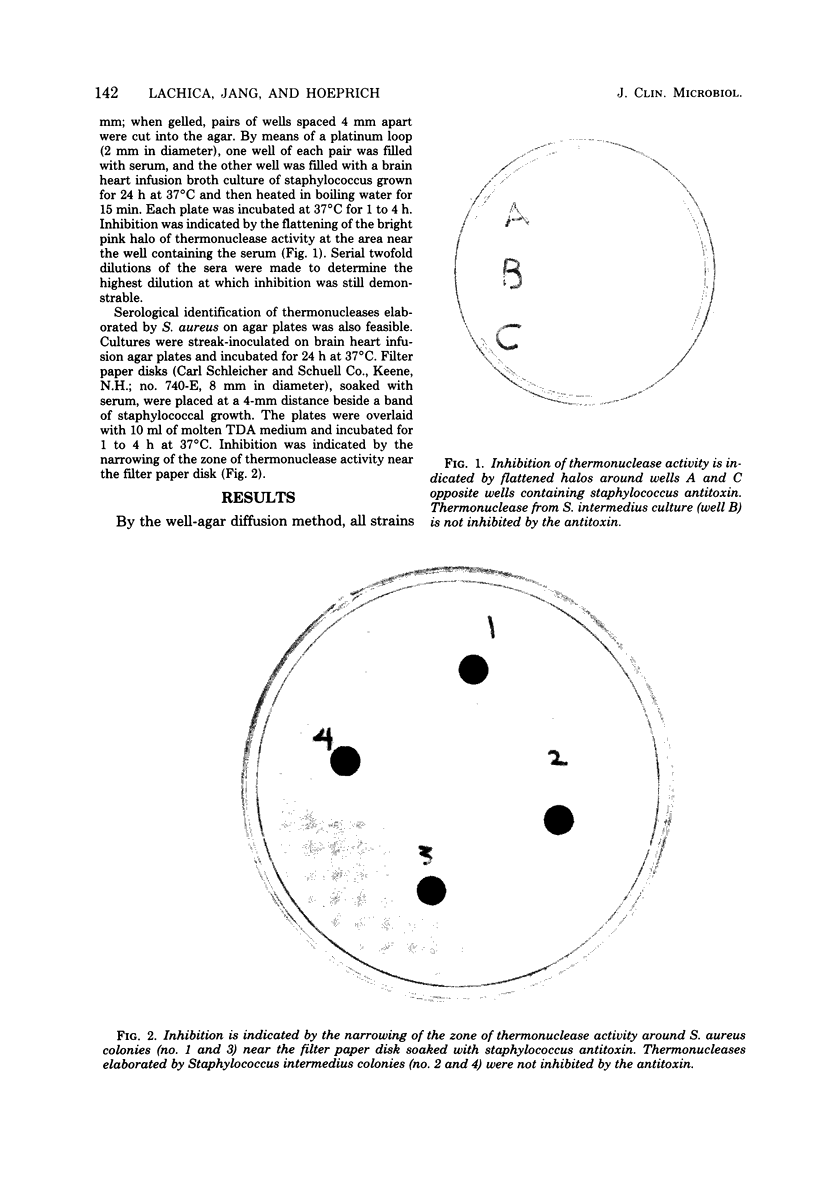
Since coagulase-positive staphylococci from animals are heterogeneous, another test is necessary to distinguish Staphylococcus aureus from them. Staphylococcal thermonucleases appear to be heterogeneous; antisera raised against S. aureus isolated from humans inhibit thermonuclease activity as demonstrated by the metachromatic well-agar diffusion method. The serological specificity of the thermonuclease elaborated by S. aureus of human origin was demonstrated using three antisera and 407 strains of staphylococci from diverse human and animal sources.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Lachica R. V., Atchison F. W. Identification of Staphylococcus aureus by simultaneous use of tube coagulase and thermonuclease tests. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):496–497. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.496-497.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. W., Sandvik O., Scherer R. K., Rose D. L. Differentiation of strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from bovine udders. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 May;47(2):273–287. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Oeding P. Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from different animal species. Res Vet Sci. 1976 Nov;21(3):284–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Oeding P. Coagulase and heat-resistant nuclease producing Staphylococcus epidermidis strains from animals. J Appl Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;39(2):197–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1975.tb00562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch K., Nord C. E., Olsson B., Wadström T. Some properties of coagulase-negative deoxyribonuclease-producing strains of staphylococci from human infections. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1976 Jun 1;162(2):143–152. doi: 10.1007/BF02121324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs S., Cuatrecasas P., Ontjes D. A., Anfinsen C. B. Correlation between the antigenic and catalytic properties of staphylococcal nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):943–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hájek V., Marsálek E. Differenzierueng pathogener Staphylokokken und Vorschlag für ihre taxonomische Klassifikation. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1971 Jun;217(2):176–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Genigeorgis C., Hoeprich P. D. Metachromatic agar-diffusion methods for detecting staphylococcal nuclease activity. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.585-587.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Hoeprich P. D., Franti C. E. Convenient assay for staphylococcal nuclease by the metachromatic well-agar-diffusion technique. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Dec;24(6):920–923. doi: 10.1128/am.24.6.920-923.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Hoeprich P. D., Genigeorgis C. Nuclease production and lysostaphin susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus and other catalase-positive cocci. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):823–826. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.823-826.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotter L. P., Genigeorgis C. A. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition and biochemical properties of certain coagulase-negative enterotoxigenic cocci. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):152–158. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.152-158.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Schumacher-Perdreau F., Götz F., Popp B. Chemical and biochemical studies for the differentiation of coagulase-positive staphylococci. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Nov 2;110(23):263–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00690237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]