Abstract
A novel set of activity-based probes (ABPs) for functionally profiling metallo-aminopeptidases was synthesized based on the bestatin inhibitor scaffold, the first synthesis of bestatin analogues using solid-phase techniques. These ABPs were shown to label metallo-aminopeptidases, using both a biotin and a fluorophore reporter, in an activity-dependent manner. This probe class was also shown to be amenable to ‘click’ chemistry labeling for possible use in live cells. Finally, we demonstrate that the ABPs are able to label an aminopeptidase in a complex proteome. Thus, these bestatin-based probes should have wide utility to functionally profile aminopeptidases in many biological systems.
Keywords: Aminopeptidase, Activity-based probe, Bestatin, Solid-phase synthesis
Metallo-aminopeptidases (MAPs) are exopeptidases that catalyze the hydrolysis and cleavage of a single N-terminal amino acid from a peptide or protein substrate. The families of MAPs are a large and diverse set of peptidases and comprise the M1, M17, and M18 families, which in humans totals 16 potential enzymes (www.merops.org). MAPs are widely distributed in organisms from bacteria to humans and play essential roles in protein maturation and regulation of the metabolism of bioactive peptides.1–3 In addition, MAPs have been linked to several pathophysiological states including cancer and hypertension.4,5
A major challenge in elucidating the function of peptidases during normal or pathological processes lies in their complex post-translational regulation. Petidase activity is usually tightly controlled post-translationally, with mRNA levels frequently showing little correlation to active protein levels. In addition, peptidases can be localized to any part of a cell and are frequently found in multiple locations with different functions. A targeted proteomics approach whereby only active proteins are enriched by the use of activity-based probes (ABPs) can address these complicating issues and provide complementary data to more traditional genetic and biochemical approaches. These ABPs typically possess three main structural components: (i) a mechanism-based inhibitor scaffold to covalently or non-covalently target catalytic residues or the active site of peptidases, (ii) a linker, and (iii) a reporter tag, such as a fluorophore or biotin, for the visualization and characterization of labeling events, and eventual affinity purification of target proteins. The mechanism-based inhibitor scaffold ensures that the ABP binds to the peptidase in an activity-dependent manner. Therefore, these ABPs can identify peptidases with differential levels of activity during a biological process and potentially identify candidate enzymes that regulate the specific phenotype under study. In addition, ABPs allow for screening of small molecule libraries and identification of specific inhibitors that can be used to validate the role of the target enzyme. To date, ABPs have been developed for more than a dozen enzyme classes including: peptidases,6 kinases,7 phosphatases,8 glycosidases,9 and oxidoreductases.10
Although the MAP superfamily is quite large and divergent, MAPs utilize a common catalytic mechanism by the coordination of one or two Zn atoms in the active site to activate water for nucleophilic attack of a peptide or protein substrate. To exploit this mechanism several classic inhibitor scaffolds have been developed to target the MAP family including, most prominently, phosphinic acids,11 hydroxamic acids12,13 and the bestatin family.14,15 Both phosphinic acids and hydroxamic acids have the capacity to inhibit metallo-endopeptidases and peptide deformylase while the bestatin scaffold appears specific for MAPs.
We have thus chosen to explore the bestatin scaffold to develop ABPs to specifically target the MAP superfamily. Bestatin is a natural product of Actinomycetes that inhibits most MAP families, including the M1, M17, and M18 families. Bestatin was originally found to be a potent aminopeptidase B16 and leucine aminopeptidase inhibitor and has been crystallized with leucine aminopeptidase,17 leukotriene A4 hydrolase,18 and aminopeptidase N.19 Bestatin is thought to modulate many biological pathways, including apoptosis.20,21 and inflammation.22 Therefore, MAP-specific ABPs would be powerful tools to tease apart the functions of multiple MAP pathways. In the present study, we set out to develop the first MAP-specific ABP, exploiting bestatin for use as the inhibitor scaffold.
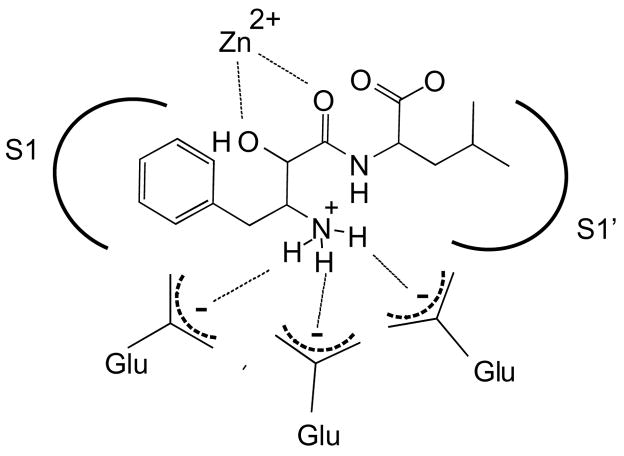
Bestatin resembles a Phe-Leu dipeptide substrate. However, the first residue contains a α-hydroxy group that, along with the neighboring carbonyl, co-ordinates the catalytic zinc atom resulting in a competitive active site-directed inhibitor (Fig. 1). In addition, the free amine of bestatin is co-ordinated by one or more glutamate residues in the MAP active site.19 Bestatin family members are slow- and tight-binding inhibitors15 with well-defined interactions with the S1 and S1′ active site pockets. Thus, bestatin represents an ideal candidate for ABP development for MAPs due to its family specificity, potency in the low nanomolar to micromolar range, synthetic tractability and potential for expansion through variation of the amino acid side chains in its core structure.
Figure 1.
General model of interactions of bestatin in the active site of metallo-aminopeptidases.
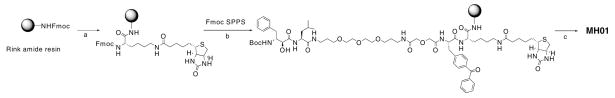
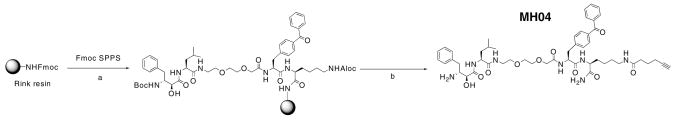
To design an ABP family for MAPs, we chose to derivatize the core bestatin inhibitor scaffold using a solid-phase synthetic strategy (Scheme 1). Bestatin has a free carboxyl group available for functionalization and previous X-ray crystal structures of MAP-bestatin complexes indicated that extension at this carboxylate was unlikely to perturb inhibitor binding.19 Thus, we attached the inhibitor scaffold to solid-phase resin at the carboxyl end of the molecule. Our first attempt to develop a MAP-directed ABP probe involved the addition of a spacer, a UV crosslinker, and a biotin affinity tag to the C-terminus of the core bestatin scaffold (Scheme 1). We included a benzophenone UV crosslinker since this is a non-covalent, reversible inhibitor scaffold. Synthesis was accomplished on solid-phase using Rink amide resin and, to our knowledge, represents the first reported solid-phase synthesis of this class of molecules.23
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of bestatin-based ABPs. Reagents and conditions: (a) i-20% Piperidine/DMF; ii-Fmoc-Lys(Biotin)OH, HBTU, HOBt, DIEA; (b) i-20% Piperidine/DMF; ii-Fmoc-BpaOH, HBTU, HOBt, DIEA; iii-20% Piperidine/DMF; iv—Fmoc-NHPEGOH (20 atoms), HBTU, HOBt, DIEA; v-20% Piperidine/DMF; vi-Fmoc-LeuOH, HBTU, HOBt, DIEA; vii-20% Piperidine/DMF; viii-N-Boc-(2S,3R)-3-amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl butyric acid, HATU, DIEA; (c) 95% TFA:2.5% TIS:2.5% H2O.
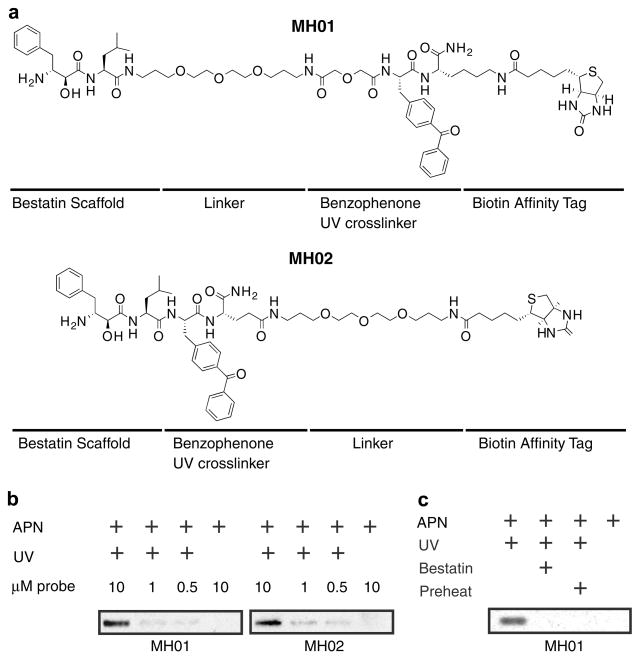
We initially explored the placement of the spacer and UV cross-linker relative to the core bestatin scaffold (MH01 and MH02, Fig. 2a) and found that there was little difference in labeling efficiency of a model enzyme, purified porcine aminopeptidase N (Sigma, Fig. 2b). We then assessed the ability of MH01 to label the model aminopeptidase in an activity-dependent manner (Fig. 2c). Our results show that, indeed, the bestatin-based probe is an activity-dependent probe of MAPs. Firstly, competition with the unbiotinylated parental compound, bestatin, blocked all labeling seen in lane 1, indicating that the probe was competitive and therefore binding at the active site (Fig. 2c, lane 2). Preheating of the sample, a process that denatures all protein targets, abrogated labeling (Fig. 2c, lane 3), indicating that this labeling was dependent on properly folded, active enzyme. Lastly, UV exposure was necessary for labeling owing to the fact that bestatin is a non-covalent, reversible inhibitor (Fig. 2c, lane 4).
Figure 2.
Anatomy of ABPs and labeling of aminopeptidase N. (a) Structure of ABPs MH01 and MH02. (b) Aminopeptidase N (0.13 U) was treated with 10, 1, or 0.5 μM of either MH01 or MH02 for 1 h in 50 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.8, 0.5 μM ZnCl2 (buffer A). Certain reaction mixtures were UV crosslinked for 1 h on ice. Reactions were quenched with SDS–PAGE buffer, and labeled protein was visualized via SDS–PAGE and western blotting for biotin. (c) Aminopeptidase N was treated with 100 μM of the aminopeptidase inhibitor bestatin or DMSO for 1 h in buffer A followed by labeling with MH01 for 1 h. Reactions were UV crosslinked (or not) for 1 h on ice, and labeled protein was visualized as in Figure 2b.
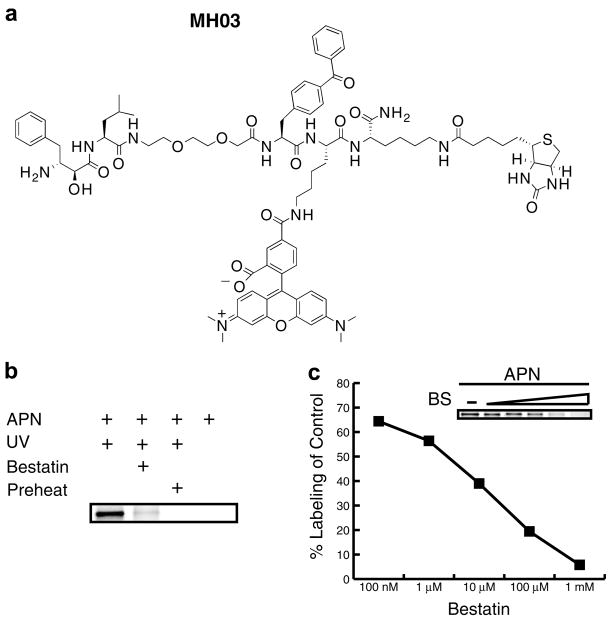
While a biotin tag is ideal for affinity tagging purposes, its use is not optimal for higher throughput activity-based profiling due to the time and labor involved in producing western blots. Additionally, many cells and tissues contain endogenously biotinylated proteins that complicate analysis of biotinylated probe-based western blots. To circumvent these shortcomings we synthesized a fluorophore-tagged version of the bestatin-based probe, which would allow for direct detection of labeled targets in a gel-based read-out. For the fluorescent bestatin-based probe we added a TAMRA group in addition to the biotin, creating a dual function ABP, MH03, making it suitable for both affinity purification and fluorescence applications (Fig. 3a).24 Labeling of purified porcine aminopeptidase N with the dual label probe was performed under the same conditions as with the original biotinylated MH01 (Fig. 3b). Labeled proteins were analyzed by SDS–PAGE coupled with in-gel fluorescent scanning (Typhoon, GE). MH03 showed similar activity-dependent labeling as MH01 (Fig. 3b) demonstrating the robustness of this ABP scaffold. Some residual labeling was observed (Fig. 3b, lane 2), which is normal in ABP labeling experiments, although this may have been enhanced since bestatin is a slow- and tight-binding inhibitor.
Figure 3.
Aminopeptidase N ABP labeling by fluorophore-containing bestatin-based ABP. (a) Structure of MH03 probe. (b) Labeling of aminopeptidase N was performed as described in Figure 2, but using MH03 and visualized using SDS–PAGE and in-gel fluorescent scanning. (c) Aminopeptidase N was pretreated with multiple concentrations of bestatin (BS) for 1 h and then labeled with 10 μM fluorescent MH03. After in-gel fluorescent scanning labeling was quantified using ImageQuant software (GE).
Next, we wanted to demonstrate that utility of the fluorescent MH03 for relative quantification of enzyme labeling. To do this, porcine aminopeptidase N was preincubated with increasing concentrations of bestatin followed by the addition of a single concentration of the fluorescent MH03. The densities of each labeled band, representing active enzyme, were quantified using a Typhoon flatbed fluorescent scanner (GE). In-gel fluorescent scanning of the labeled peptidase band showed a decrease in aminopeptidase N labeling by MH03 relative to increasing concentration of bestatin preincubation (insert in Fig. 3c). Percent competition values were calculated by dividing the density of each of the bestatin preincubated aminopeptidase N bands (lanes 2–5) by density of the untreated band in lane 1 (Fig. 3c). We demonstrate a dose dependent relationship that is amenable to quantification with a dynamic range of several orders of magnitude, which will allow future screening efforts of derivative libraries.
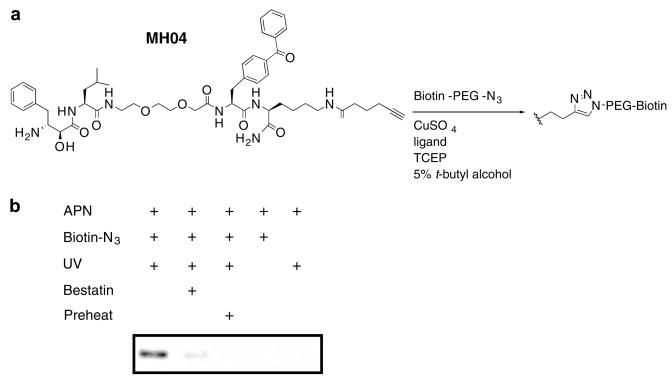
One of the technical challenges facing the development and use of ABPs with biotin or fluorophore tags is limited or biased uptake by live cells. In some cases, ABPs have been used to label enzymes in living cells, but a more universal system for labeling would employ a small, hydrophobic tag. We therefore chose to add a small alkyne tag to our MAP probe in order to utilize the popular ‘click’ bio-orthogonal chemistry, which employs a 1,3-dipolar azide/alkyne cycloaddition.25,26 We thus replaced the biotin of MH01 with a C-terminal alkyne resulting in a click probe, MH04 (Scheme 2 and Fig. 4).27 We observed facile ‘click’ addition of a biotinylated azide following labeling of porcine aminopeptidase N with MH04. Importantly the activity-dependent labeling of the enzyme was not affected by this procedure, as illustrated by bestatin preincubation, UV, and preheat controls.
Scheme 2.
Reagents and conditions: (a) i-20% Piperidine/DMF; ii-Fmoc-Lys(Aloc)OH, HBTU, HOBt, DIEA; iii -20% Piperidine/DMF; iv—Fmoc-BpaOH, HBTU, HOBt, DIEA; v-20% Piperidine/DMF; vi—Fmoc-NHPEGOH (9 atoms), HBTU, HOBt, DIEA; vii-20% Piperidine/DMF; viii—Fmoc-LeuOH, HBTU, HOBt, DIEA; ix-20% Piperidine/DMF; x-N-Boc-(2S,3R)-3-amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl butyric acid, HATU, DIEA; (b) i-Pd(PPh3)4, PhSiH3, DCM; ii-hexynoic acid, HBTU, HOBt, DIEA; iii-95% TFA:2.5% TIS:2.5% H2O.
Figure 4.
‘Click’ chemistry-based ABP labeling of aminopeptidase N. (a) Structure of MH04 probe. (b) Aminopeptidase N labeling was performed as described in Figure 2c using MH04. The ligation of the biotin-azide reporter tag was performed by adding 100 μM of the biotin-azide tag, followed by 1 mM TCEP (tris(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine hydrochloride), 100 μM ligand (tris[(1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl]amine) (17× stock in DMSO/tert-butanol 1:4), and 1 mM CuSO4. Reactions were allowed to proceed for 1 h at room temperature, then quenched with equal volume of SDS–PAGE loading buffer. Labeled protein was visualized as in Figure 2b.
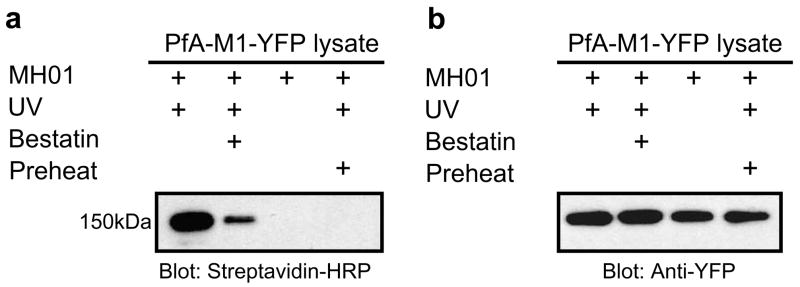
Finally, to validate the utility of the probe as an ABP for MAPs in the context of a complex proteome, we assessed labeling of an aminopeptidase N homolog from the malarial parasite (PFA-M1) from whole cell lysates. To facilitate the identification of PFA-M1 from Plasmodium falciparum we utilized a parasite line that expresses the endogenous PFA-M1 as a YFP C-terminal fusion.28 Homogenized whole cell lysates from P. falciparum were labeled with MH01. The resulting proteome was separated by SDS–PAGE and western blot analysis was performed to first visualize biotinylated proteins. A 150 kDa protein was labeled by MH01, which corresponds to the approximate weight of the PFA-M1-YFP fusion protein (Fig. 5a). Preincubation of the protein lysate with unbiotinylated bestatin (Fig. 5a, lane 2) resulted in loss of labeling of the 150 kDa band illustrating that bestatin was competitive with MH01 for this protein target. Additionally, the target was labeled in an activity-dependent manner, as preheating of the proteome prior to labeling abrogated any labeling (Fig. 5a, lane 3). Finally, to identify this target the blot was stripped and reprobed using an anti-YFP antibody (Fig. 5b). The anti-YFP revealed the presence of the expected 150 kDa fusion protein in all lanes and this band overlaid the exact position where the biotinylated protein appeared. It should be noted that PFA-M1-YFP fusion appeared in all lanes with the anti-YFP antibody, whereas the biotinylated species only appeared when the active peptidase was labeled. This data thus confirmed the specific activity-based labeling of the PFA-M1 aminopeptidase by MH01 within a complex malarial parasite proteome.
Figure 5.
ABP labeling of the malarial M1 metallo-aminopeptidase in cell lysates. (a) P. falciparum cells (in buffer A) were freeze/thawed 3× on dry ice. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation, and the lysate was retained for labeling. MH01 was incubated with parasite lysate for 1 h and then UV crosslinked for 1 h. In one reaction, 100 μM unbiotinylated bestatin was preincubated with the lysate prior to probe addition. Labeled protein was visualized via a western blot for biotin. (b) The same blot was then stripped and reprobed using anti-YFP.
In conclusion, we have developed a novel activity-based probe class, with specificity for MAPs, based on the bestatin inhibitor scaffold. The use of a biotin, fluorophore, or alkyne moiety did not alter the activity-dependent labeling profile for the scaffold and, thus, the suite of ABPs presented in this manuscript should allow for a variety of labeling methodologies. We therefore believe that this ABP may prove to be a valuable tool for future characterization of MAP activity in a wide variety of biological systems. We are now currently pursuing the expansion and application of these probes for use against the malarial parasite.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the University of Pennsylvania Genome Frontiers Institute and the Ritter Foundation. We are grateful to Dr. Michael Klemba (Virginia Tech) for the PFA-M1-YFP parasite line.
References and notes
- 1.Luan Y, Xu W. Curr Med Chem. 2007;14:639. doi: 10.2174/092986707780059571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sato Y. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004;27:772. doi: 10.1248/bpb.27.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Foulon T, Cadel S, Cohen P. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;31:747. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(99)00021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sato Y. Endothelium. 2003;10:287. doi: 10.1080/10623320390272334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Danziger RS. Heart Fail Rev. 2008;13:293. doi: 10.1007/s10741-007-9061-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Greenbaum D, Medzihradszky KF, Burlingame A, Bogyo M. Chem Biol. 2000;7:569. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(00)00014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Liu Y, Jiang N, Wu J, Dai W, Rosenblum JS. J Biol Chem. 2006;282:2505. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609603200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kumar S, Zhou B, Liang F, Wang WQ, Huang Z, Zhang ZY. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:7943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402323101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vocadlo DJ, Bertozzi CR. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2004;43:5338. doi: 10.1002/anie.200454235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Adam GC, Cravatt BF, Sorensen EJ. Chem Biol. 2001;8:81. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(00)90060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Giannousis PP, Bartlett PA. J Med Chem. 1987;30:1603. doi: 10.1021/jm00392a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chan WW, Dennis P, Demmer W, Brand K. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:7955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Saghatelian A, Jessani N, Joseph A, Humphrey M, Cravatt BF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:10000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402784101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wilkes SH, Prescott JM. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:13154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rich DH, Moon BJ, Harbeson S. J Med Chem. 1984;27:417. doi: 10.1021/jm00370a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Suda H, Aoyagi T, Takeuchi T, Umezawa H. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976;177:196. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90429-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Burley SK, David PR, Lipscomb WN. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:6916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tsuge H, Ago H, Aoki M, Furuno M, Noma M, Miyano M, Minami M, Izumi T, Shimizu T. J Mol Biol. 1994;238:854. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Addlagatta A, Gay L, Matthews BW. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:13339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606167103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sekine K, Fujii H, Abe F. Leukemia. 1999;13:729. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ezawa K, Minato K, Dobashi K. Biomed Pharmacother. 1996;50:283. doi: 10.1016/0753-3322(96)84827-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Penning TD. Curr Pharm Design. 2001;7:163. doi: 10.2174/1381612013398248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.General method for solid-phase peptide synthesis of ABPs: Standard solid-phase peptide synthesis was performed on Rink amide resin using HBTU/HOBt/DIEA in an equimolar ratio in DMF for 30 min at RT. Coupling of the α-hydroxy-β-amino acid required HATU for 1 h. Each amino acid was double coupled. Fmoc protecting groups were removed with 20% piperidine/DMF for 30 min. To cleave products from resin, a solution of 95% TFA:2.5% TIS:2.5% H2O was added to the resin. After standing for 2 h, the cleavage mixture was collected, and the resin was washed with fresh cleavage solution. The combined fractions were evaporated to dryness and the product was purified by reverse phase-HPLC. Fractions containing product were pooled and lyophilized. Reverse phase HPLC was conducted on a C18 column using an Agilent 1200 HPLC. Purifications were performed at room temperature and compounds were eluted with a concentration gradient 0–70% of acetonitrile (0.1% Formic acid). LC/MS data were acquired using LC/MSD SL system (Agilent). Solid-phase peptide chemistry was conducted in polypropylene cartridges, with 2-way Nylon stopcocks (Biotage, VA). The cartridges were connected to a 20 port vacuum manifold (Biotage, VA) that was used to drain excess solvent and reagents from the cartridge. MH01: C62H90N10O14S, predicted mass 1230.64, observed [M+H] 1231.4. MH02: C57H81N9O12S, predicted mass 1115.57, observed [M+H] 1116.3.
- 24.The synthesis of the dual function ABP MH03 was accomplished using standard solid-phase peptide synthesis as detailed above, However, the TAMRA was added after product cleavage from resin due to the instability of TAMRA to TFA. This was accomplished using a Boc protected lysine and addition of TAMRA using HBTU/HOBt/DIEA in DMF after resin cleavage for 3 h. MH03: C85H107N13O16S, predicted mass 1597.77, observed [M+2H] 799.8.
- 25.Huisgen R, Mloston G, Polborn K. J Org Chem. 1996;61:6570. doi: 10.1021/jo9607424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kaval N, Ermolat’ev D, Appukkuttan P, Dehaen W, Kappe CO, Van der Eycken E. J Comb Chem. 2005;7:490. doi: 10.1021/cc0498377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Synthesis of MH04 was accomplished as depicted in Scheme 2. The deprotection of the Aloc group was conducted under a positive flow of argon. The resin was solvated with dichloromethane for 5 min. The solvent was drained, and PhSiH3 (24 equiv) in CH2Cl2 was added to the resin followed by Pd(PPh3)4 (0.25 equiv) in CH2Cl2. After agitating the resin for 1 h by bubbling with argon, the solution was drained, and the resin was washed with CH2Cl2 (3×). Synthesis of the Biotin-azide was accomplished using standard solid-phase synthesis using a bromo-acetic acid as the final group. The replacement of the bromo group by the azide was achieved by heating with NaN3 at 60 °C. MH04: C50H67N7O10, predicted mass 925.49, observed [M+H] 926.5.
- 28.Dalal S, Klemba M. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:35978. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703643200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]