Abstract
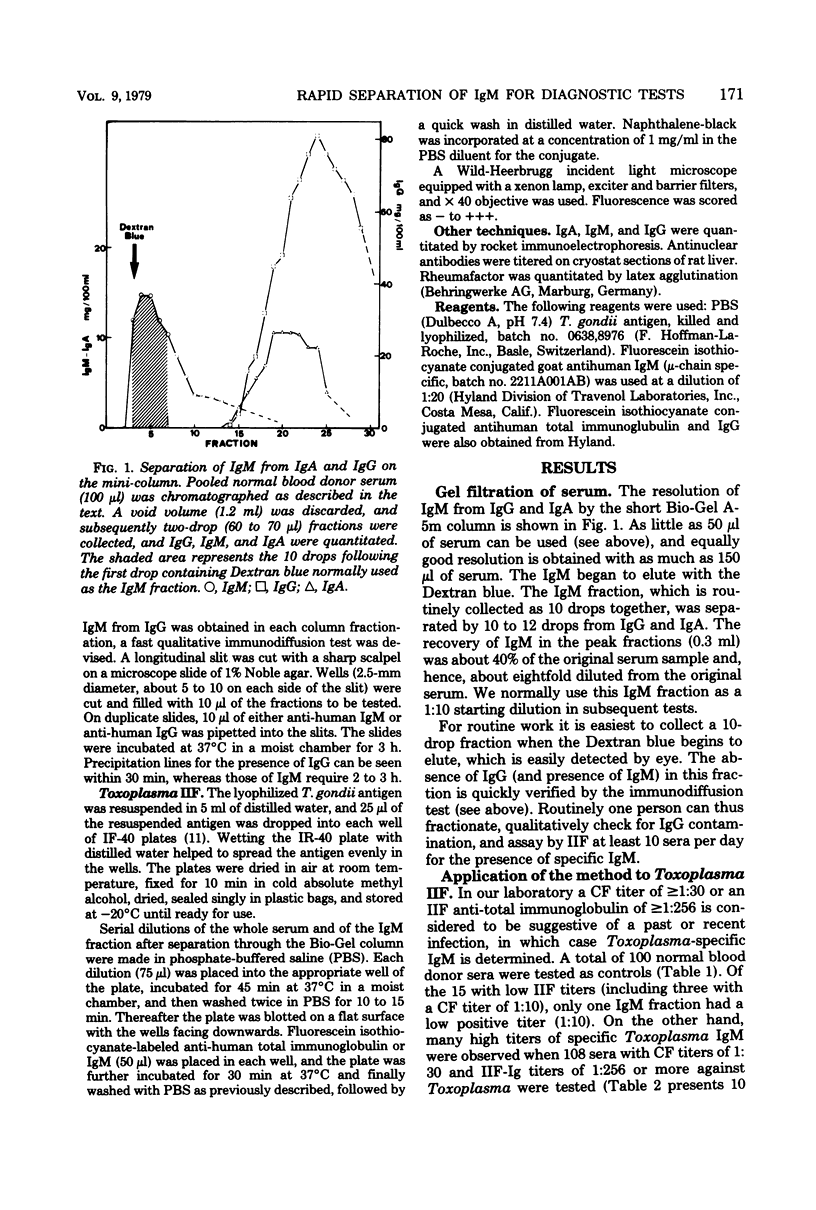
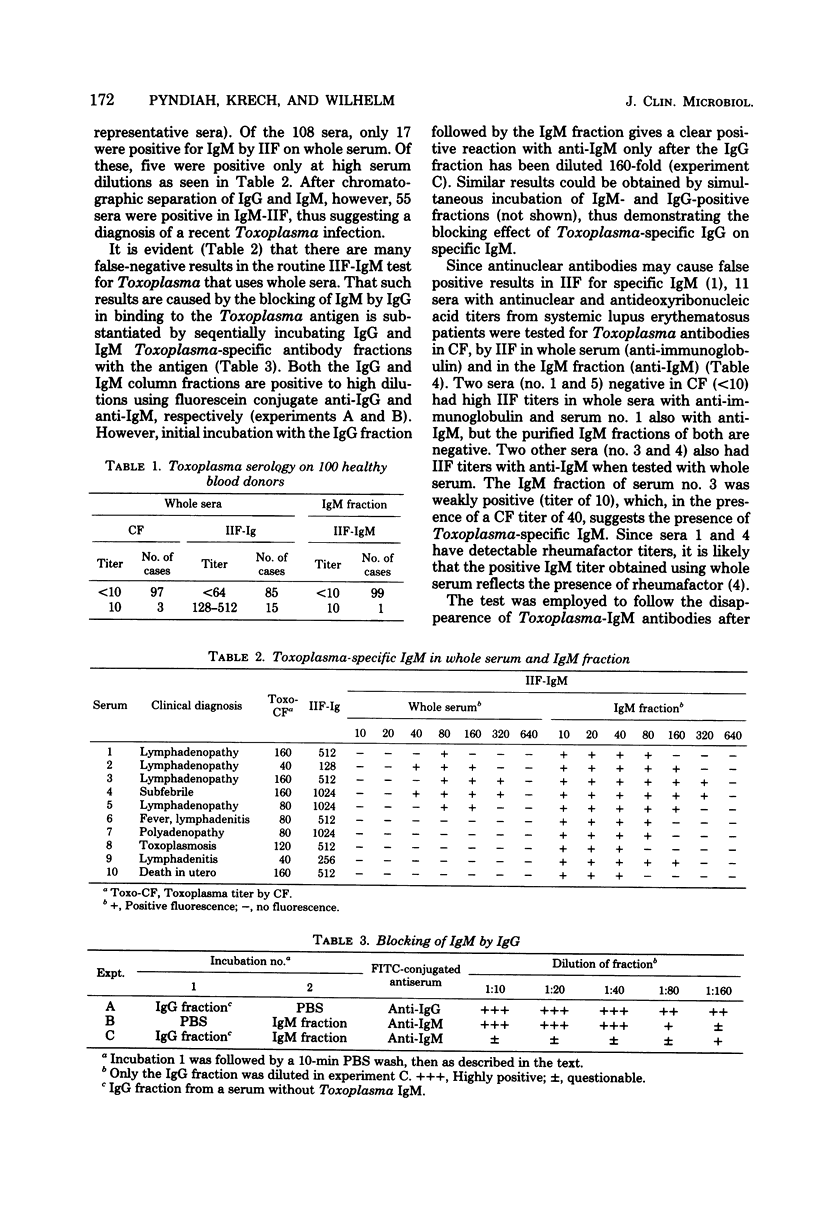
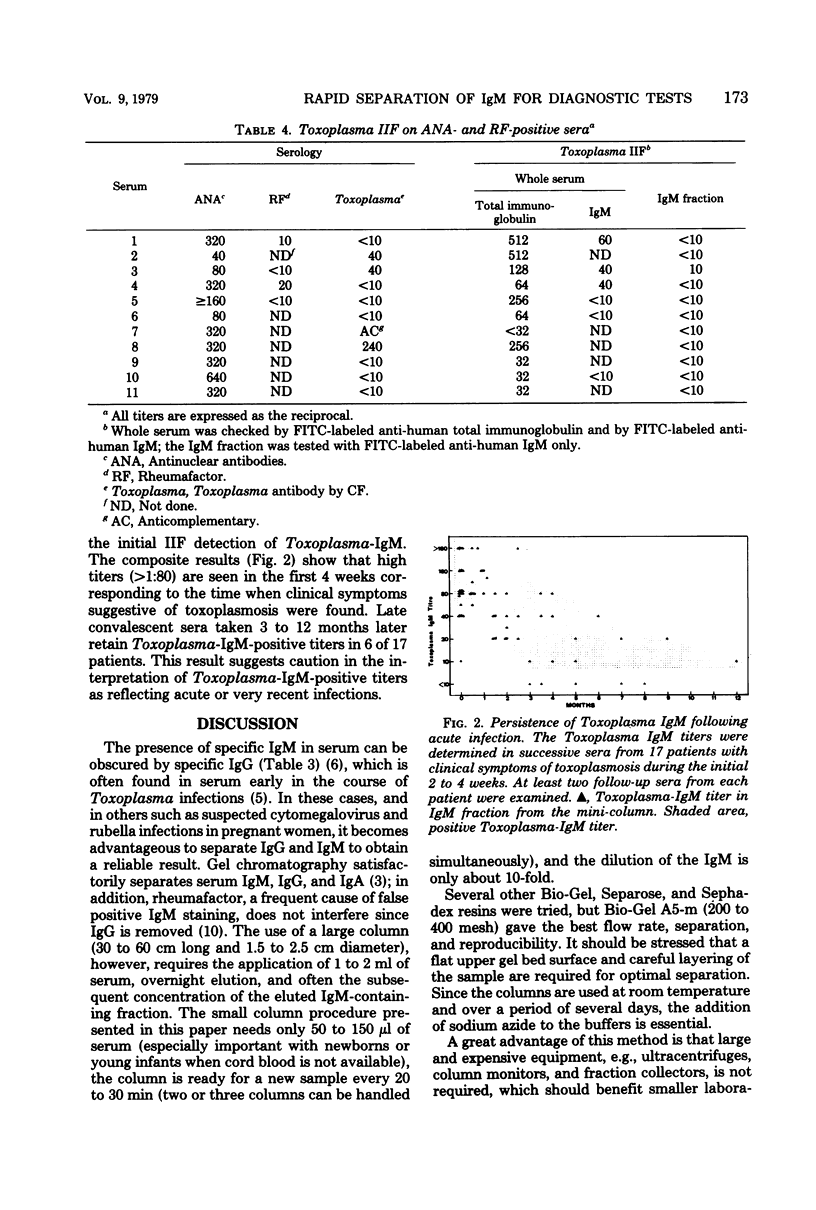
The indirect immunofluorescent (IIF) antibody technique for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii immunoglobulin M (IgM) often gives false negative results, probably due to the competition between IgG and IgM. We therefore adapted a gel filtration procedure for the separation of IgG and IgM to a routine diagnostic test capable handling at least 10 sera per day and requiring only 50 microliters of serum. The results from 108 sera having positive complement fixation titers for Toxoplasma showed that 17 were IgM positive when the whole serum was tested by IIF compared with 55 positive when the IgM fraction was used. Sera with antideoxyribonucleic acid titers do not give false positive results after fractionation, and the removal of IgG eliminates false positive results due to rheumatoid factor. A prospective study showed that Toxoplasma IgM may persist up to 9 months.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo F. G., Barnett E. V., Gentry L. O., Remington J. S. False-positive anti-Toxoplasma fluorescent-antibody tests in patients with antinuclear antibodies. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):270–275. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.270-275.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best J. M., Banatvala J. E., Watson D. Serum IgM and IgG responses in postnatally acquired rubella. Lancet. 1969 Jul 12;2(7611):65–68. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürgin-Wolff A., Hernandez R., Just M. Separation of rubella IgM, IgA, and IgG antibodies by gel filtration on agarose. Lancet. 1971 Dec 11;2(7737):1278–1280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90600-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler S., Devries E., Allen P. R., Hurn B. A. A rapid immunofluorescent procedure for the detection of specific IgG and IgM antibody in sera using Staphylococcus aureus and latex-IgG as absorbents. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):367–380. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Julian A. J. Competition between, and effectiveness of, IgG and IgM antibodies in indirect fluorescent antibody and other tests. J Immunol. 1967 Jan;98(1):143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cradock-Watson J. E., Ridehalgh M. K. Specific immunoglobulins in infants with the congenital rubella syndrome. J Hyg (Lond) 1976 Feb;76(1):109–123. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400055005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmonts G., Couvreur J., Colin J., Peupion J. Vers un diagnostic précoce de la toxoplasmose aiguë. Etude critique du test de Remington. Nouv Presse Med. 1972 Jan 29;1(5):339–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta J. D., Peterson V., Stout M., Murphy A. M. Single-sample diagnosis of recent rubella by fractionation of antibody on Sephadex G-200 column. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Sep;24(6):547–550. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.6.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handsher R., Fogel A. Modified staphylococcal absorption method used for detecting rubella-specific immunoglobin M antibodies during a rubella epidemic. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):588–592. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.588-592.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon R., Haire M., Wisdom G. B., Neill D. W. The use of indirect immunofluorescence to evaluate the gel filtration method of fractionating human immunoglobulins. J Immunol Methods. 1975;8(1-2):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krech U., Jung M., Pyndiah N., Price P. C. IF-40. A new polystyrene microscope tray for immunofluorescent studies. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Jan;234(1):136–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie M. R., Gutman G. A., Warner N. L. The binding of murine IgM to Staphylococcal A protein. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(5):367–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison J. R., Mace J. E. A simple, inexpensive gel filtration technique for use in diagnostic serology. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Apr;26(4):309–311. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.4.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Miller M. J. 19S and 7S anti-toxoplasma antibodies in diagnosis of acute congenital and acquired toxoplasmosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Feb;121(2):357–363. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Vaheri A. Rubella: a method for rapid diagnosis of a recent infection by demonstration of the IgM antibodies. Br Med J. 1968 Jan 27;1(5586):221–223. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5586.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


